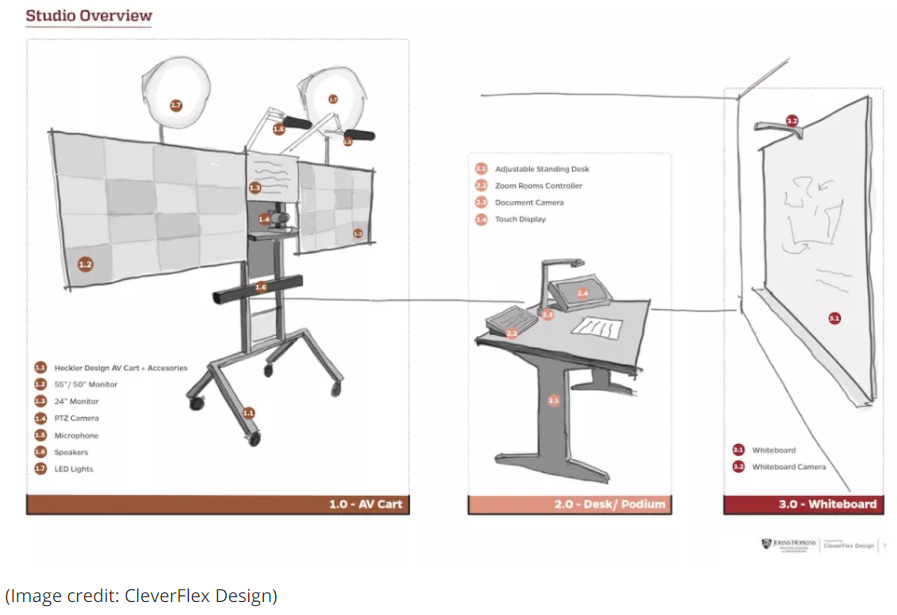
Reimagining Online Culture: Project-Based Learning, Inclusion, and Reach in Online Education — from er.educause.edu by Christian Schneider
The pandemic created a unique opportunity for educators to rethink their approach to online learning and explore how this educational environment can expand access while increasing and building on diversity.
Excerpt:
The move to online education during the pandemic has been one of the greatest experiments ever conducted. It was initially met with reluctance and fatigue, but once we moved beyond the attempts to replicate what we do in real life, it brought to light important innovations.
We cut out constraints, categorizations, and biases while concentrating on our faces, voices, and work, and we extended the reach of geographical, cultural, and social access.
During the pandemic, however, when most students were in their home countries, they seemed to be more comfortable as their authentic selves, working on projects that related to their local environments.
…
Teaching online can not only make education available to more people around the globe but also open a space where students can share “a piece of themselves,” where different perspectives can interact, where we can learn from each other and our local environments and opportunities. This creates an enormous opportunity for equity and inclusion.