5 Must-Have Microlearning Assets That’ll Make Your Online Training More Effective — from blog.commlabindia.com by Nikhil Bhogaraju
We often hear about the advantages of microlearning, but what about its applications in corporate training? This blog explores how we can deliver effective training to a learning workforce through microlearning assets. Do you have them in your eLibrary?
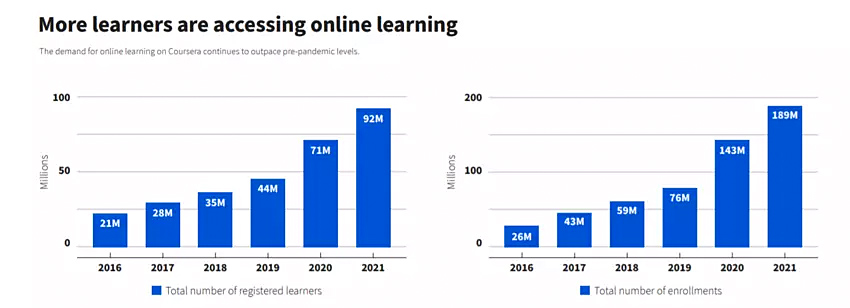
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning — from weforum.org by Johnny Wood; with thanks to Ray Schroeder out on LinkedIn
Example chart:
Also relevant/see:
- 2U plans for international expansion as it integrates operations with edX — from highereddive.com by Natalie Schwartz
- Coursera bets on degrees — a small but growing part of the business — from highereddive.com by Natalie Schwartz
The company has launched 13 new degrees with colleges since 2021, bringing the total number of bachelor’s, master’s and postgraduate degrees up to 38, according to Maggioncalda.
…
2U saw $152.4 million from its degree segment in 2021’s fourth quarter, about 11 times the revenue Coursera brought in from its degree business over the same period.
Beyond traditional learning programs — from chieflearningofficer.com by Gorana Sandric
To prepare for Industry 4.0 and a diverse, shrinking workforce, we need to open the door of meaningful learning to everyone.
Excerpt:
Hybrid learning creates an ecosystem of various stakeholders and methods that produce a desired outcome. This type of ecosystem is vivid, playful and allure, and therefore capable of transforming attention into intention to learn, grow and reach the maximum potential. Starting with the end in mind (SPP), building blocks of engagement with stakeholders into multifaceted L&D programs delivers a learning experience that is diverse, engaging and inclusive.
Rethinking the Faculty Role in Students’ Career Readiness — from insidehighered.com by Rachel Toor; with thanks to Ryan Craig for this solid, well-written resource
It’s time for all of us on campuses, not just the people in career services, to step up and help offer the competencies employers say they’re looking for, Rachel Toor writes.
Excerpts:
Career centers on campuses can offer students coaching, resources and connections. But, as Angle points out, they tend to be a just-in-time service. They are also, he says, “scary places for a lot of students.” Many young people don’t want to face the reality of life after graduation. Often, it’s a case of too little, too late.
Instead, they come to people they know—professors like me—for help with cover letters and résumés. And while I can comment on language, until recently I had no idea about how most résumés are read first by a version of R2-D2 and his little robot friends who make up automated tracking systems. If an applicant doesn’t include the right keywords in a résumé or cover letter, into the trash bin they go.
The truth is, I have not applied for a job in 15 years; for many of my colleagues it’s been even longer, and some of them have never worked outside academe. It’s not surprising that employers are seeing recent college grads—smart students, hard workers—who don’t know how to present themselves as potential employees.
From DSC:
I can relate to that part about R2-D2 reading the resumes first (i.e., trying to get by the Applicant Tracking Systems before one’s resume ever makes it in front of the eyes of a fellow human being). Many faculty/staff members and members of administrations haven’t been out interviewing in a long while. So it can be a rude awakening when they/we need to do that.
Also, I wanted to say that it’s not fair to assess the learners coming out of higher education using a different set of learning objectives:
- That is, faculty members within higher ed have one set of learning objectives and their students work hard to learn and meet those learning objectives. Unfortunately, those students did what was asked of them, and then they…
- …come to find out that the corporate/business/legal/etc. worlds have different ideas about what they should know and be able to do. That is, these other organizations and communities of practice are assessing them on different sets of learning objectives that these same students didn’t cover. Some (many?) of these graduates leave their interviews discouraged and think, “Well, it must be me.” Or they can leave frustrated and angry at their former institutions who didn’t prepare them for this new assessment.
As I’ve said on this blog before, this disconnect is not fair to the students/graduates. We need more mechanisms by which faculty and staff members within higher ed can work more collaboratively with those within the corporate world to better align the learning objectives and the curriculum being covered. If this doesn’t occur more frequently, the constant appearance and growth of new alternatives will likely continue to build further momentum (as they should, given the incredibly steep price of obtaining a degree these days!).
P.S. This disconnect of learning objectives can also be found in what happens with legal education — including having to pass today’s Bar Exams — and then these graduates get out into the real world to find employers who are frustrated that these graduates don’t have the “right”/necessary skills.
“The incentive structure is for law schools to teach students how to pass the bar exam, not necessarily to do the things that employers expect,” Gallini said.
A quote from this article, which I also
want to thank Ryan Craig for.
Skill assessments: The future of personalization in learning — from edyoucated.org by Julian Rasch
The future of personalization in professional online learning lies in detailed, but fast and effective skill assessments. Here’s how we do it at edyoucated.