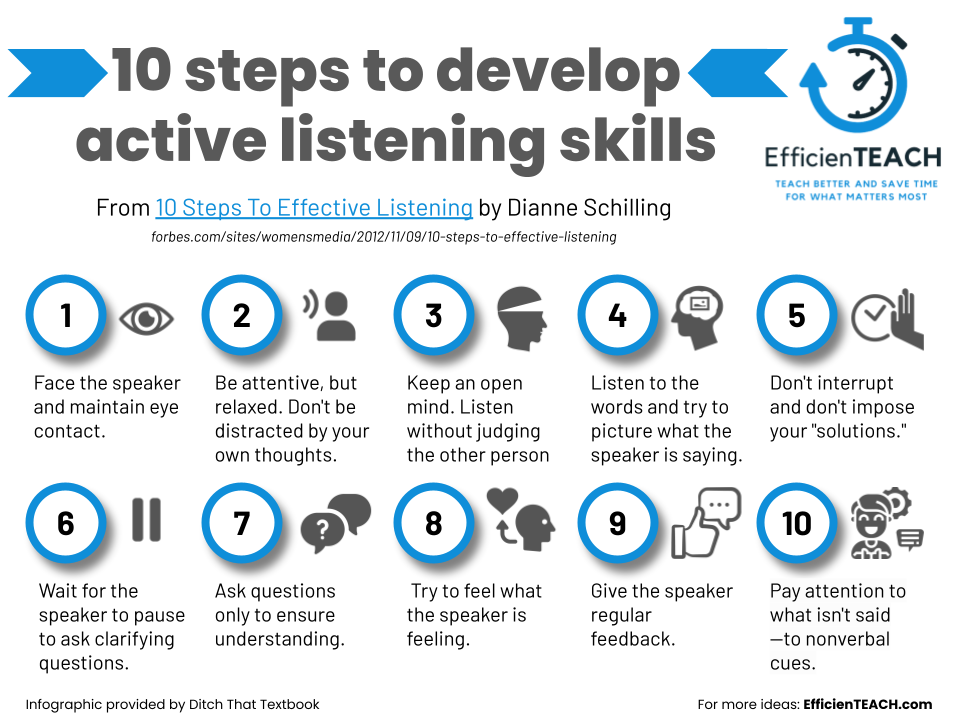
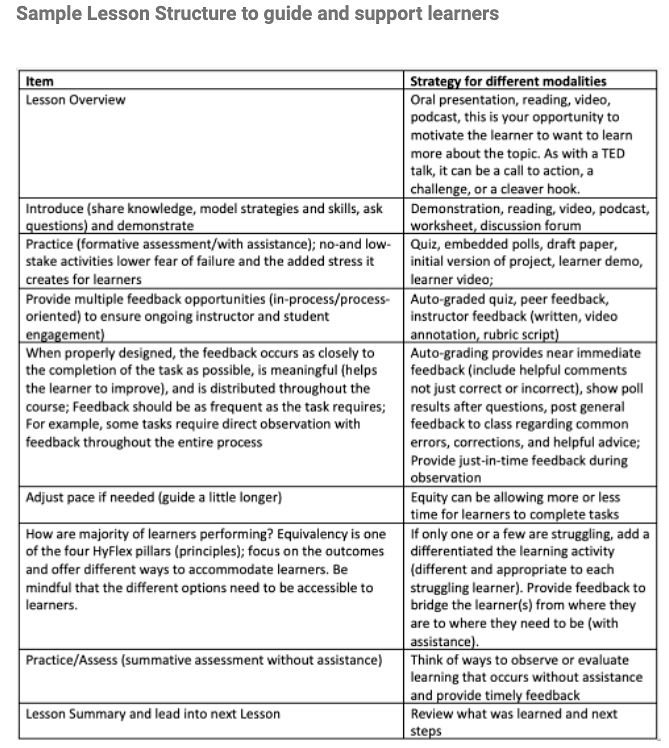
Why Improving Student Learning is So Hard — from opencontent.org by David Wiley
Excerpt:
2. Student behavior will normally change only in response to changes in faculty behavior – specifically, the assignments faculty give and the support faculty provide.
For many students, the things-they-do-to-learn are all located within the relatively small universe of things their faculty assign them to do – read chapters, complete homework assignments, etc. For a variety of reasons, and many of them perfectly good reasons, “students don’t do optional” – they only do what they’re going to be graded on.
Therefore, students will likely engage in more effective learning behaviors ONLY IF their faculty assign them more effective learning activities. Faculty can further increase the likelihood of students engaging in more effective learning activities if they support them appropriately throughout the process.
From DSC:
I can put an “Amen” to the above excerpt. For years I managed a Teaching & Learning Digital Studio. Most of the students didn’t come into the Studio for help, because most of the faculty members assigned the normal kinds of things (papers, quizzes, and such). Had there been more digitally-created means of showing what students knew, there would have been more usage of the T&L Digital Studio.
Also, if we want to foster more creativity and innovation — as well as give our learners more choice and more control over their learning — we should occasionally get away from the traditional papers.
Another comment here is that it’s hard to change what faculty members do, when Instructional Designers can’t even get in the car to help faculty members navigate. We need more team-based efforts in designing our learning experiences.