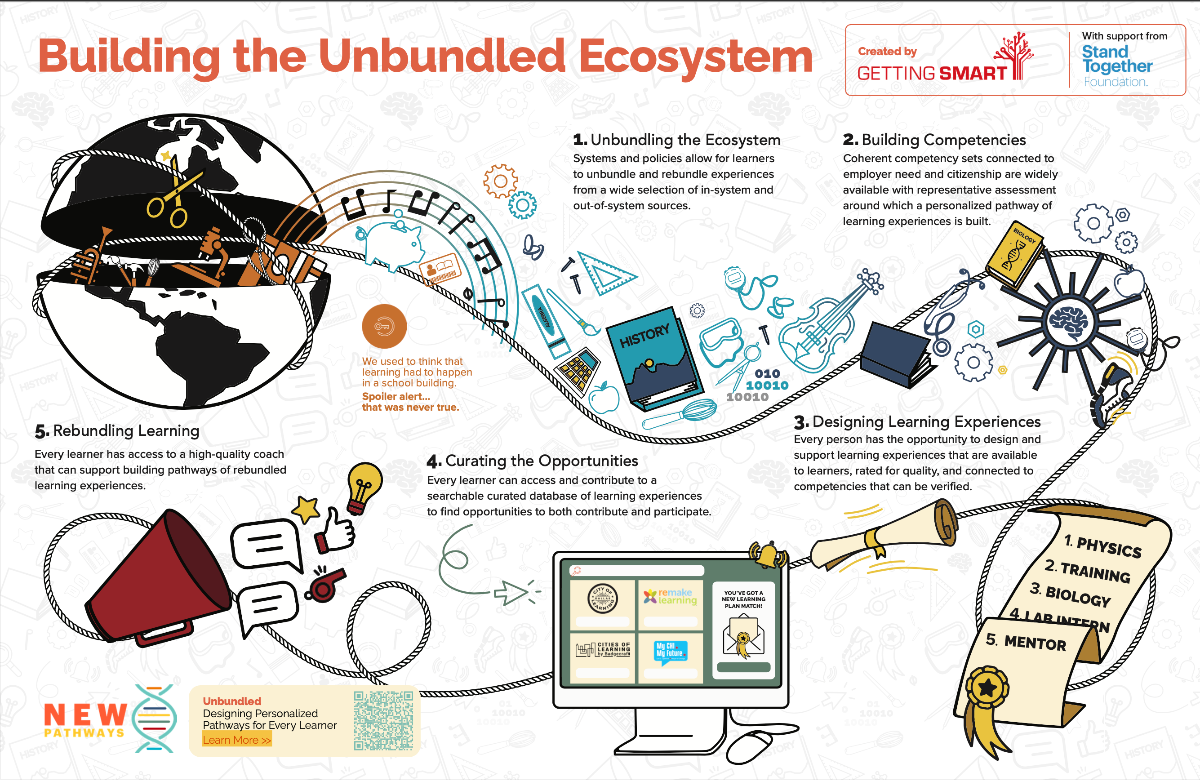
From DSC:
A few items re: ChatGPT — with some items pro-chat and other items against the use of ChatGPT (or at least to limit its use).
How About We Put Learning at the Center? — from insidehighered.com by John Warner
The ongoing freak-out about ChatGPT sent me back to considering the fundamentals.
Excerpt:
So, when people express concern that students will use ChatGPT to complete their assignments, I understand the concern, but what I don’t understand is why this concern is so often channeled into discussions about how to police student behavior, rather than using this as an opportunity to exam the kind of work we actually ask students (and faculty) to do around learning.
If ChatGPT can do the things we ask students to do in order to demonstrate learning, it seems possible to me that those things should’ve been questioned a long time ago. It’s why I continue to believe this technology is an opportunity for reinvention, precisely because it is a threat to the status quo.
Top AI conference bans use of ChatGPT and AI language tools to write academic papers — from theverge.com by James Vincent; with thanks to Anna Mills for this resource
AI tools can be used to ‘edit’ and ‘polish’ authors’ work, say the conference organizers, but text ‘produced entirely’ by AI is not allowed. This raises the question: where do you draw the line between editing and writing?
Excerpt:
The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) announced the policy earlier this week, stating, “Papers that include text generated from a large-scale language model (LLM) such as ChatGPT are prohibited unless the produced text is presented as a part of the paper’s experimental analysis.” The news sparked widespread discussion on social media, with AI academics and researchers both defending and criticizing the policy. The conference’s organizers responded by publishing a longer statement explaining their thinking. (The ICML responded to requests from The Verge for comment by directing us to this same statement.)
How to… use AI to teach some of the hardest skills — from oneusefulthing.substack.com by Ethan Mollick
When errors, inaccuracies, and inconsistencies are actually very useful
Excerpt:
Instead, I want to discuss the opportunity provided by AI, because it can help us teach in new ways. The very things that make AI scary for educators — its tedency to make up facts, its lack of nuance, and its ability to make excellent student essays — can be used to make education better.
This isn’t for some future theoretical version of AI. You can create assignments, right now, using ChatGPT, that we will help stretch students in knew ways. We wrote a paper with the instructions. You can read it here, but I also want to summarize our suggestions. These are obviously not the only ways to use AI to educate, but they solve some of the hardest problems in education, and you can start experimenting with them right now.
NYC education department blocks ChatGPT on school devices, networks — from ny.chalkbeat.org by Michael Elsen-Rooney
Excerpt:
New York City students and teachers can no longer access ChatGPT — the new artificial intelligence-powered chatbot that generates stunningly cogent and lifelike writing — on education department devices or internet networks, agency officials confirmed Tuesday.
Teachers v ChatGPT: Schools face new challenge in fight against plagiarism — from straitstimes.com by Osmond Chia; with thanks to Stephen Downes for this resource
Excerpt:
SINGAPORE – Teachers in Singapore say they will likely have to move from assignments requiring regurgitation to those that require greater critical thinking, to stay ahead in the fight against plagiarism.
This comes on the back of the rise of ChatGPT, an intelligent chatbot that is able to spin essays and solve mathematical equations in seconds.
ChatGPT Is Not Ready to Teach Geometry (Yet) — from educationnext.org by Paul T. von Hippel
The viral chatbot is often wrong, but never in doubt. Educators need to tread carefully.
Excerpt:
Can ChatGPT provide feedback and answer questions about math in a more tailored and natural way? The answer, for the time being, is no. Although ChatGPT can talk about math superficially, it doesn’t “understand” math with real depth. It cannot correct mathematical misconceptions, it often introduces misconceptions of its own; and it sometimes makes inexplicable mathematical errors that a basic spreadsheet or hand calculator wouldn’t make.
Here, I’ll show you.
Addendum on 1/9/23:
9 ways ChatGPT saves me hours of work every day, and why you’ll never outcompete those who use AI effectively. — from .linkedin.com by Santiago Valdarrama
A list for those who write code:
- 1. Explaining code…
- Improve existing code…
- Rewriting code using the correct style…
- Rewriting code using idiomatic constructs…
- Simplifying code…
- Writing test cases…
- Exploring alternatives…
- Writing documentation…
- Tracking down bugs…