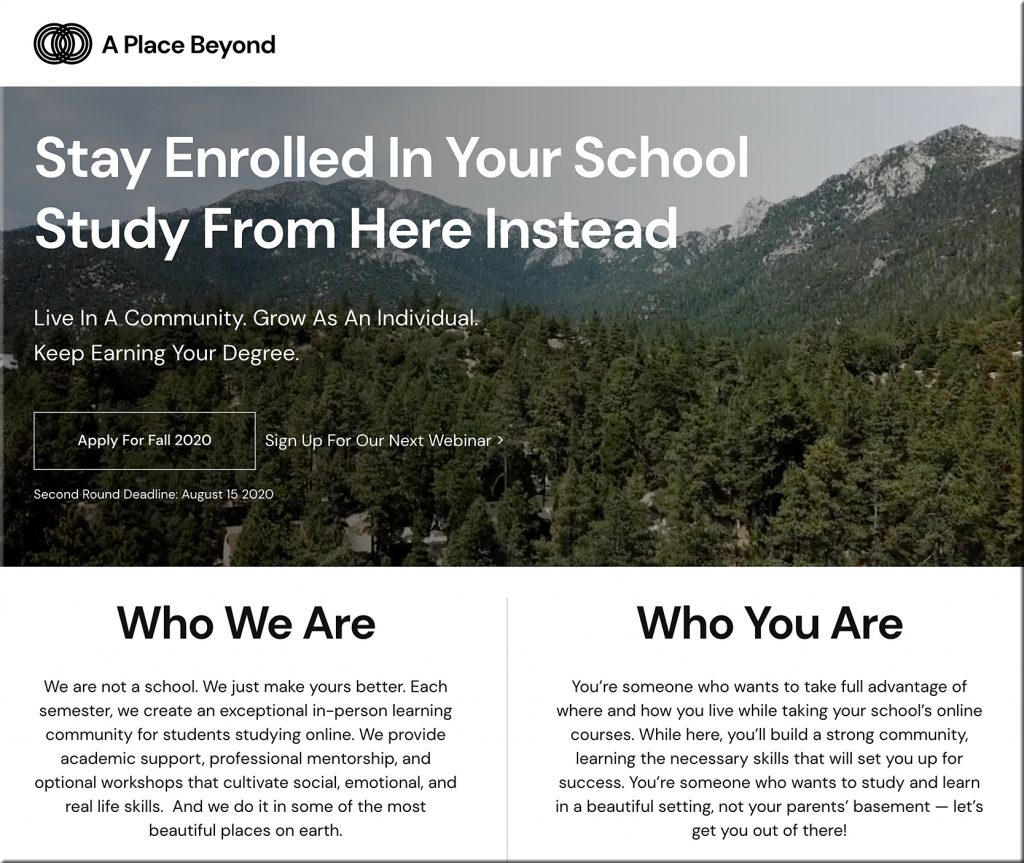
From DSC:
Some of the following questions came to my mind recently:
- In this age of the Coronavirus, how can we think differently about learning experience design (#LXD)?
- How can *teams* of people come together to reimagine what learning could look like in the future? Who might be some new players at the table? More students? Artists? Actors? More animators? More technicians and people from A/V? Specialists in XR? Corporate trainers coming together with Instructional Designers from higher ed and from K-12? #learningecosystems #future
- How can we better tighten up the alignment between K-12, higher ed / vocational programs, and the corporate world?
- How can we make self-directed learning more prevalent (which would release an enormous amount of energy & creativity)? #heutagogy
Maybe those aren’t even the right questions…
If not, what do you think? What questions should we be asking about learning these days?
#LXD #learningecosystems #future #lifelonglearning #onlinelearning #highereducation #K12 #corporatelearning #heutagogy
The main thing we need to remember is that this space no longer serves as an accessory to face-to-face teaching. It is now our main contact point with learners, so it needs to play different roles: communication channel, learning path, interaction platform and community space. Teachers therefore need a certain degree of freedom to design this space in the best way that suits their teaching style and philosophy as well as their course content and learning objectives.
…
What became obvious in the past months is that when it comes to teaching and learning fully online, the learning experience design aspect, including look, feel and logic of the platform from the users’ perspective- be it teachers or students-, are at least as important as the content.(source)