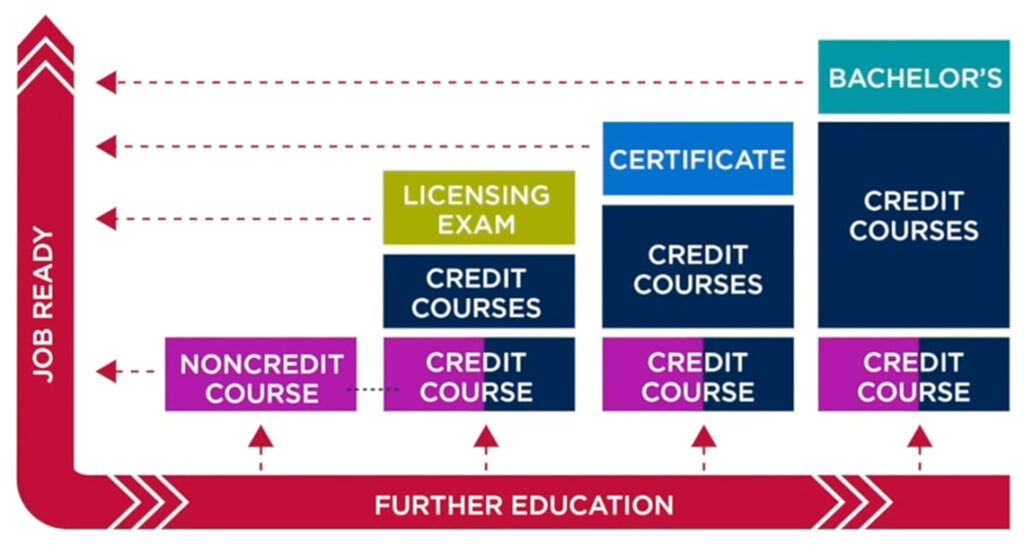
‘Stackable credentials’ could be future of higher education in Colorado — from thedenverchannel.com by Nicole Brady; with thanks to Ray Schroeder for this resource out on LinkedIn
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
DENVER — Metropolitan State University of Denver is one of Colorado’s largest four-year institutions, but some students are spending just months there — not years — before joining the workforce.
They’re doing it by “stacking” credentials.
“Stackable credentials are really a convergence of individuals wanting to learn in smaller chunks and industries being willing to accept those chunks,” said Terry Bower, associate vice president of Innovative and Lifelong Learning at MSU Denver.
The career launchpad lays out exactly what steps are needed to work in those industries and how much money a person can earn with different credentials.
For students who decide they want to add more credentials or work toward a degree, they can return to MSU with no credits lost.
From DSC:
That part that says “The career launchpad lays out exactly what steps are needed to work in those industries and how much money a person can earn with different credentials” will likely be a part of a next-generation learning platform. Here are the skills in demand. Here are the folks offering you the ability to learn/develop those skills and here’s what you can expect to earn at different levels of this type of job. The platform will be able to offer this type of information and these types of opportunities throughout your lifetime.
Cloud-based learner profiles will be part of this new setup — along with recommendation engine-based results based upon one’s learning preferences (not learning styles — which don’t exist — but upon one’s learning preferences).