Artificial Intelligence Ethics, Jobs & Trust – UK Government Sets Out AI future — from cbronline.com by Ellie Burns
Excerpt:
UK government is driving the artificial intelligence agenda, pinpointing it as a future technology driving the fourth revolution and billing its importance on par with the steam engine.
The report on Artificial Intelligence by the Government Office for Science follows the recent House of Commons Committee report on Robotics and AI, setting out the opportunities and implications for the future of decision making. In a report which spans government deployment, ethics and the labour market, Digital Minister Matt Hancock provided a foreword which pushed AI as a technology which would benefit the economy and UK citizens.

MIT’s “Moral Machine” Lets You Decide Who Lives & Dies in Self-Driving Car Crashes — from futurism.com
In brief:
- MIT’S 13-point exercise lets users weigh the life-and-death decisions that self-driving cars could face in the future.
- Projects like the “Moral Machine” give engineers insight into how they should code complex decision-making capabilities into AI.
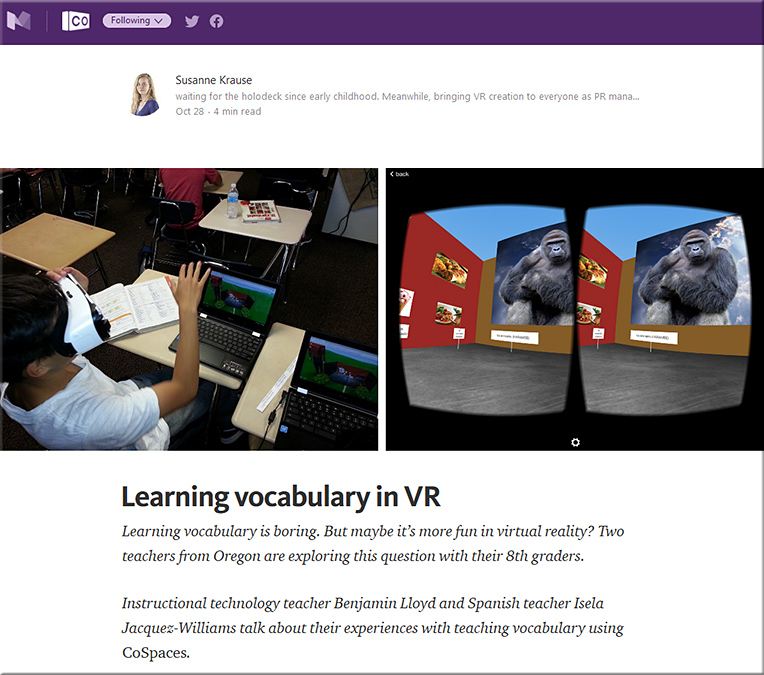
Wearable Tech Weaves Its Way Into Learning — from edsurge.com by Marguerite McNeal
Excerpt:
“Ethics often falls behind the technology,” says Voithofer of Ohio State. Personal data becomes more abstract when it’s combined with other datasets or reused for multiple purposes, he adds. Say a device collects and anonymizes data about a student’s emotional patterns. Later on that information might be combined with information about her test scores and could be reassociated with her. Some students might object to colleges making judgments about their academic performance from indirect measurements of their emotional states.
New era of ‘cut and paste’ humans close as man injected with genetically-edited blood – from telegraph.co.uk by Sarah Knapton
Excerpt:
A world where DNA can be rewritten to fix deadly diseases has moved a step closer after scientists announced they had genetically-edited the cells of a human for the first time using a groundbreaking technique.
A man in China was injected with modified immune cells which had been engineered to fight his lung cancer. Larger trials are scheduled to take place next year in the US and Beijing, which scientists say could open up a new era of genetic medicine.
The technique used is called Crispr, which works like tiny molecular scissors snipping away genetic code and replacing it with new instructions to build better cells.

Troubling Study Says Artificial Intelligence Can Predict Who Will Be Criminals Based on Facial Features — from theintercept.com by Sam Biddle
Artificial intelligence is quickly becoming as biased as we are — from thenextweb.com by Bryan Clark
A bug in the matrix: virtual reality will change our lives. But will it also harm us? — from theguardian.stfi.re
Prejudice, harassment and hate speech have crept from the real world into the digital realm. For virtual reality to succeed, it will have to tackle this from the start
Excerpt:
Can you be sexually assaulted in virtual reality? And can anything be done to prevent it? Those are a few of the most pressing ethical questions technologists, investors and we the public will face as VR grows.
Light Bulbs Flash “SOS” in Scary Internet of Things Attack — from fortune.com by Jeff John Roberts
How Big Data Transformed Applying to College — from slate.com by Cathy O’Neil
It’s made it tougher, crueler, and ever more expensive.
Not OK, Google — from techcrunch.com by Natasha Lomas
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
The scope of Alphabet’s ambition for the Google brand is clear: It wants Google’s information organizing brain to be embedded right at the domestic center — i.e. where it’s all but impossible for consumers not to feed it with a steady stream of highly personal data. (Sure, there’s a mute button on the Google Home, but the fact you have to push a button to shut off the ear speaks volumes… )
In other words, your daily business is Google’s business.
“We’re moving from a mobile-first world to an AI-first world,” said CEO Sundar Pichai…
But what’s really not OK, Google is the seismic privacy trade-offs involved here. And the way in which Alphabet works to skate over the surface of these concerns.
What he does not say is far more interesting, i.e. that in order to offer its promise of “custom convenience” — with predictions about restaurants you might like to eat at, say, or suggestions for how bad the traffic might be on your commute to work — it is continuously harvesting and data-mining your personal information, preferences, predilections, peccadilloes, prejudices… and so on and on and on. AI never stops needing data. Not where fickle humans are concerned.
Welcome to a world without work — from by Automation and globalisation are combining to generate a world with a surfeit of labour and too little work
Excerpt:
A new age is dawning. Whether it is a wonderful one or a terrible one remains to be seen. Look around and the signs of dizzying technological progress are difficult to miss. Driverless cars and drones, not long ago the stuff of science fiction, are now oddities that can occasionally be spotted in the wild and which will soon be a commonplace in cities around the world.
From DSC:
I don’t see a world without work being good for us in the least. I think we humans need to feel that we are contributing to something. We need a purpose for living out our days here on Earth (even though they are but a vapor). We need vision…goals to works towards as we seek to use the gifts, abilities, passions, and interests that the LORD gave to us. The author of the above article would also add that work:
- Is a source of personal identity
- It helps give structure to our days and our lives
- It offers the possibility of personal fulfillment that comes from being of use to others
- Is a critical part of the glue that holds society together and smooths its operation
Over the last generation, work has become ever less effective at performing these roles. That, in turn, has placed pressure on government services and budgets, contributing to a more poisonous and less generous politics. Meanwhile, the march of technological progress continues, adding to the strain.
10 breakthrough technologies for 2016 — from technologyreview.com
Excerpts:
Immune Engineering
Genetically engineered immune cells are saving the lives of cancer patients. That may be just the start.
Precise Gene Editing in Plants
CRISPR offers an easy, exact way to alter genes to create traits such as disease resistance and drought tolerance.
Conversational Interfaces
Powerful speech technology from China’s leading Internet company makes it much easier to use a smartphone.
Reusable Rockets
Rockets typically are destroyed on their maiden voyage. But now they can make an upright landing and be refueled for another trip, setting the stage for a new era in spaceflight.
Robots That Teach Each Other
What if robots could figure out more things on their own and share that knowledge among themselves?
DNA App Store
An online store for information about your genes will make it cheap and easy to learn more about your health risks and predispositions.
SolarCity’s Gigafactory
A $750 million solar facility in Buffalo will produce a gigawatt of high-efficiency solar panels per year and make the technology far more attractive to homeowners.
Slack
A service built for the era of mobile phones and short text messages is changing the workplace.
Tesla Autopilot
The electric-vehicle maker sent its cars a software update that suddenly made autonomous driving a reality.
Power from the Air
Internet devices powered by Wi-Fi and other telecommunications signals will make small computers and sensors more pervasive
The 4 big ethical questions of the Fourth Industrial Revolution — from 3tags.org by the World Economic Forum
Excerpts:
We live in an age of transformative scientific powers, capable of changing the very nature of the human species and radically remaking the planet itself.
Advances in information technologies and artificial intelligence are combining with advances in the biological sciences; including genetics, reproductive technologies, neuroscience, synthetic biology; as well as advances in the physical sciences to create breathtaking synergies — now recognized as the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
…
Since these technologies will ultimately decide so much of our future, it is deeply irresponsible not to consider together whether and how to deploy them. Thankfully there is growing global recognition of the need for governance.
Scientists create live animals from artificial eggs in ‘remarkable’ breakthrough — from telegraph.co.uk by Sarah Knapton
Robot babies from Japan raise questions about how parents bond with AI — from singularityhub.com by Mark Robert Anderson
Excerpt:
This then leads to the ethical implications of using robots. Embracing a number of areas of research, robot ethics considers whether the use of a device within a particular field is acceptable and also whether the device itself is behaving ethically. When it comes to robot babies there are already a number of issues that are apparent. Should “parents” be allowed to choose the features of their robot, for example? How might parents be counseled when returning their robot baby? And will that baby be used again in the same form?
Amazon’s Vision of the Future Involves Cops Commanding Tiny Drone ‘Assistants’ — from gizmodo.com by Hudson Hongo
DARPA’s Autonomous Ship Is Patrolling the Seas with a Parasailing Radar — from technologyreview.com by Jamie Condliffe
Forget self-driving cars—this is the robotic technology that the military wants to use.
China’s policing robot: Cattle prod meets supercomputer — from computerworld.com by Patrick Thibodeau
China’s fastest supercomputers have some clear goals, namely development of its artificial intelligence, robotics industries and military capability, says the U.S.
Report examines China’s expansion into unmanned industrial, service, and military robotics systems
Augmented Reality Glasses Are Coming To The Battlefield — from popsci.com by Andrew Rosenblum
Marines will control a head-up display with a gun-mounted mouse
———-
Addendum on 12/2/16:
Regulation of the Internet of Things — from schneier.com by Bruce Schneier
Excerpt:
Late last month, popular websites like Twitter, Pinterest, Reddit and PayPal went down for most of a day. The distributed denial-of-service attack that caused the outages, and the vulnerabilities that made the attack possible, was as much a failure of market and policy as it was of technology. If we want to secure our increasingly computerized and connected world, we need more government involvement in the security of the “Internet of Things” and increased regulation of what are now critical and life-threatening technologies. It’s no longer a question of if, it’s a question of when.
…
An additional market failure illustrated by the Dyn attack is that neither the seller nor the buyer of those devices cares about fixing the vulnerability. The owners of those devices don’t care. They wanted a webcam — or thermostat, or refrigerator — with nice features at a good price. Even after they were recruited into this botnet, they still work fine — you can’t even tell they were used in the attack. The sellers of those devices don’t care: They’ve already moved on to selling newer and better models. There is no market solution because the insecurity primarily affects other people. It’s a form of invisible pollution.















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)