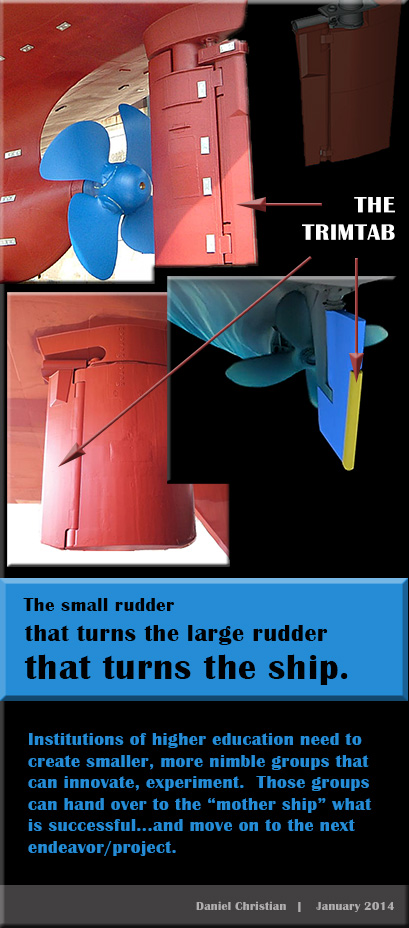
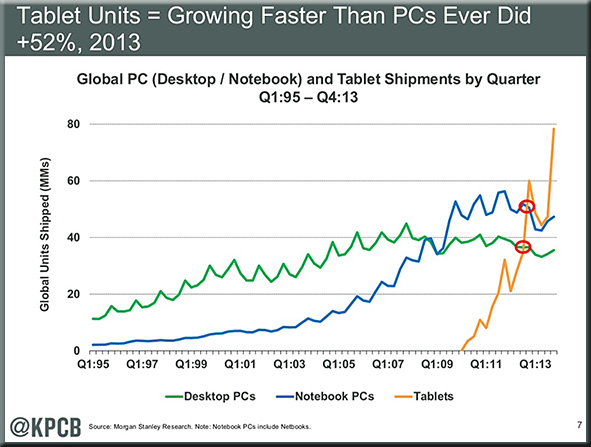
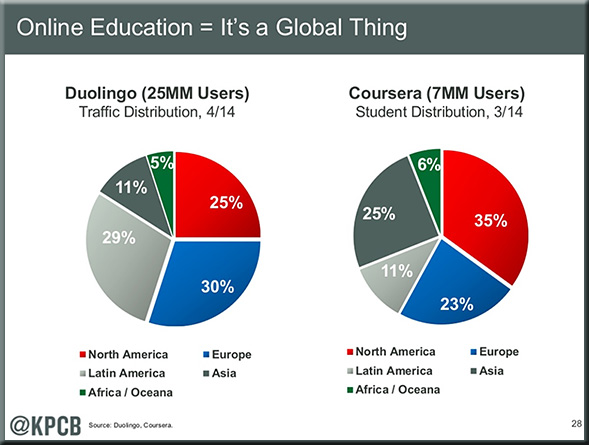
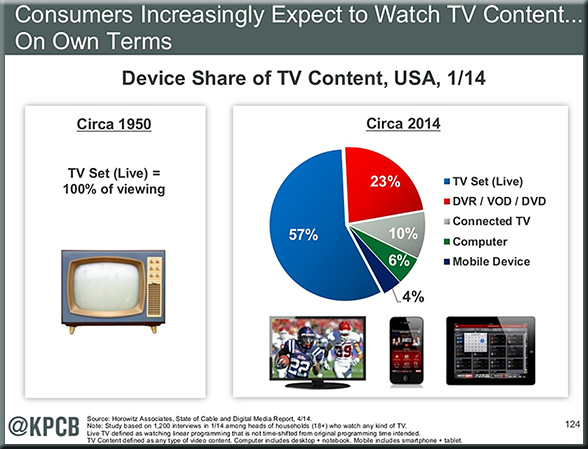
Isaiah 53:5-6 NIV
But he was pierced for our transgressions, he was crushed for our iniquities; the punishment that brought us peace was on him, and by his wounds we are healed. We all, like sheep, have gone astray, each of us has turned to our own way; and the Lord has laid on him the iniquity of us all.
2 Corinthians 5:21 (NIV)
God made him who had no sin to be sin for us, so that in him we might become the righteousness of God.
Romans 5:6-8 NIV
You see, at just the right time, when we were still powerless, Christ died for the ungodly. Very rarely will anyone die for a righteous person, though for a good person someone might possibly dare to die. But God demonstrates his own love for us in this: While we were still sinners, Christ died for us.
1 Corinthians 15:1, 3-4 NIV
[ The Resurrection of Christ ] Now, brothers and sisters, I want to remind you of the gospel I preached to you, which you received and on which you have taken your stand.
…
For what I received I passed on to you as of first importance: that Christ died for our sins according to the Scriptures, that he was buried, that he was raised on the third day according to the Scriptures,
1 Corinthians 15:20-22 (NIV)
But Christ has indeed been raised from the dead, the firstfruits of those who have fallen asleep. For since death came through a man, the resurrection of the dead comes also through a man. For as in Adam all die, so in Christ all will be made alive.
Matthew 28:1-10 (NIV)
Jesus Has Risen
28 After the Sabbath, at dawn on the first day of the week, Mary Magdalene and the other Mary went to look at the tomb.
2 There was a violent earthquake, for an angel of the Lord came down from heaven and, going to the tomb, rolled back the stone and sat on it. 3 His appearance was like lightning, and his clothes were white as snow. 4 The guards were so afraid of him that they shook and became like dead men.
5 The angel said to the women, “Do not be afraid, for I know that you are looking for Jesus, who was crucified. 6 He is not here; he has risen, just as he said. Come and see the place where he lay. 7 Then go quickly and tell his disciples: ‘He has risen from the dead and is going ahead of you into Galilee. There you will see him.’ Now I have told you.”
8 So the women hurried away from the tomb, afraid yet filled with joy, and ran to tell his disciples. 9 Suddenly Jesus met them. “Greetings,” he said. They came to him, clasped his feet and worshiped him. 10 Then Jesus said to them, “Do not be afraid. Go and tell my brothers to go to Galilee; there they will see me.”
Luke 24:1-8 (NIV)
On the first day of the week, very early in the morning, the women took the spices they had prepared and went to the tomb. They found the stone rolled away from the tomb, but when they entered, they did not find the body of the Lord Jesus. While they were wondering about this, suddenly two men in clothes that gleamed like lightning stood beside them. In their fright the women bowed down with their faces to the ground, but the men said to them, “Why do you look for the living among the dead? He is not here; he has risen! Remember how he told you, while he was still with you in Galilee: ‘The Son of Man must be delivered over to the hands of sinners, be crucified and on the third day be raised again.’ ” Then they remembered his words.