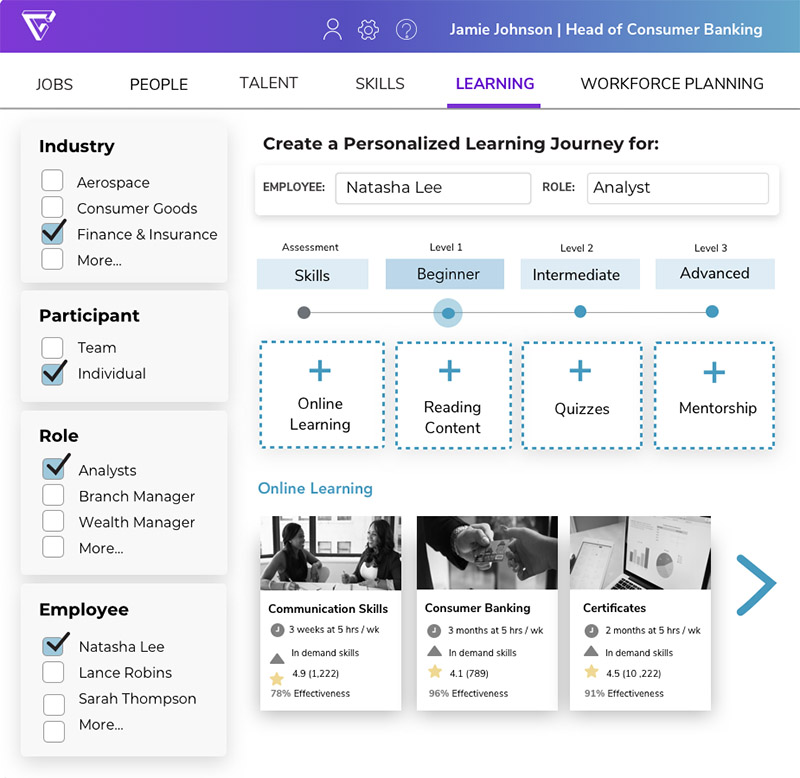
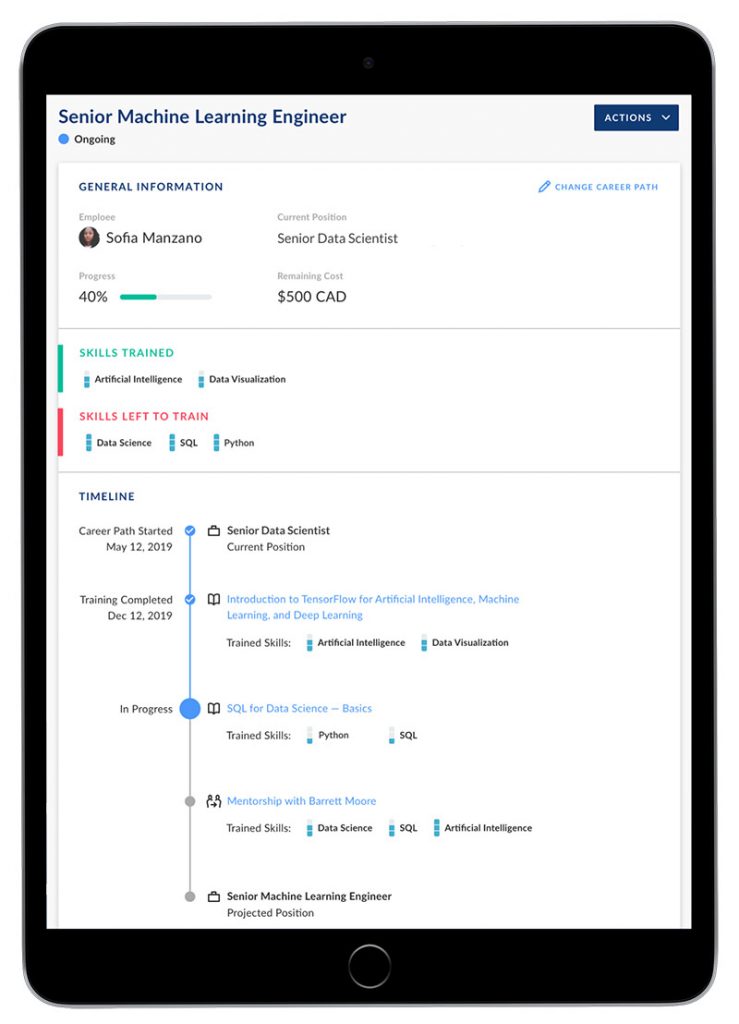
President Speaks: 5 higher education trends the pandemic is accelerating — from highereddive.com by Adam Weinberg
Technology, student choice and career prep will factor more heavily into colleges’ decision-making going forward, one president explains.
Excerpt:
Over the last several weeks, it has become clearer what the post-COVID-19 higher education landscape will look like. The trends that will shape the sector’s future are not new. But the pandemic has accelerated them.
Trends are like water. As they run faster, they cut deeper and in unexpected ways. Here are five that COVID-19 has given momentum to.