How to create an AV standards document — from campustechnology.com by Mike Tomei
Defining standards will help prevent audiovisual support headaches and keep your institution on the path to its strategic goals.
Excerpt:
Audiovisual technology is becoming increasingly complex and important in today’s classrooms. And with higher education IT departments being tasked with the design, installation and support of instructional AV systems — areas in which IT staff may or may not have expertise — it’s extremely important to develop, define and enforce AV system design/technical standards on campus.
The easiest way to do so is to create a comprehensive audiovisual design and technical standards document that can be referenced by all the parties involved with classroom AV installations. The goal of this document is to standardize AV installations across the institution, as well as streamline the design and construction process for these systems. A standards document will also help your IT department make progress toward the institution’s audiovisual strategic goals.
…
Many readers from state schools will recognize this scenario: A different audiovisual design consultant and systems integration firm are chosen for each project, based on the lowest bid. You end up with a revolving door of AV professionals installing equipment on your campus. They have very limited knowledge of your existing classroom systems, and what direction you’re trying to go in with new installations. This is a great reason to have an AV standards document written and ready to hand to these individuals at the beginning of a project.
…it’s all the more important to develop an audiovisual design/technical standards document that all parties can rely on.
Why campus infrastructure standards are so important — from blog.infocommblog.org by Greg Brown
Excerpt:
And here’s a excerpt from part one, to help set the scene: “Most colleges and universities have some assemblage of ‘classroom standards.’ Many of them are poorly thought out, incomplete, and not as effective as they could be….For the sake of discussion, I’m going to break standards down into four areas to make their respective advantages and disadvantages easier to illustrate. In actuality, what you have on campus will (ideally) be a mix of all four areas — a combination of four types — compiled as one under the bailiwick of ‘campus standards.’”
The next group of standards I want to talk about I’m calling campus infrastructure standards. What I am referring to here are your building infrastructure items. Where do you need power, conduit, or data? What type of lighting zones or switching do you expect in rooms? Is there a particular lighting system you use or a particular interface your control system requires? What do you need from the building systems in order to build the teaching space? Where do you need it?
Classroom standards: The good, bad, and ugly — from blog.infocommblog.org by Greg Brown
Excerpt (additional emphasis DSC):
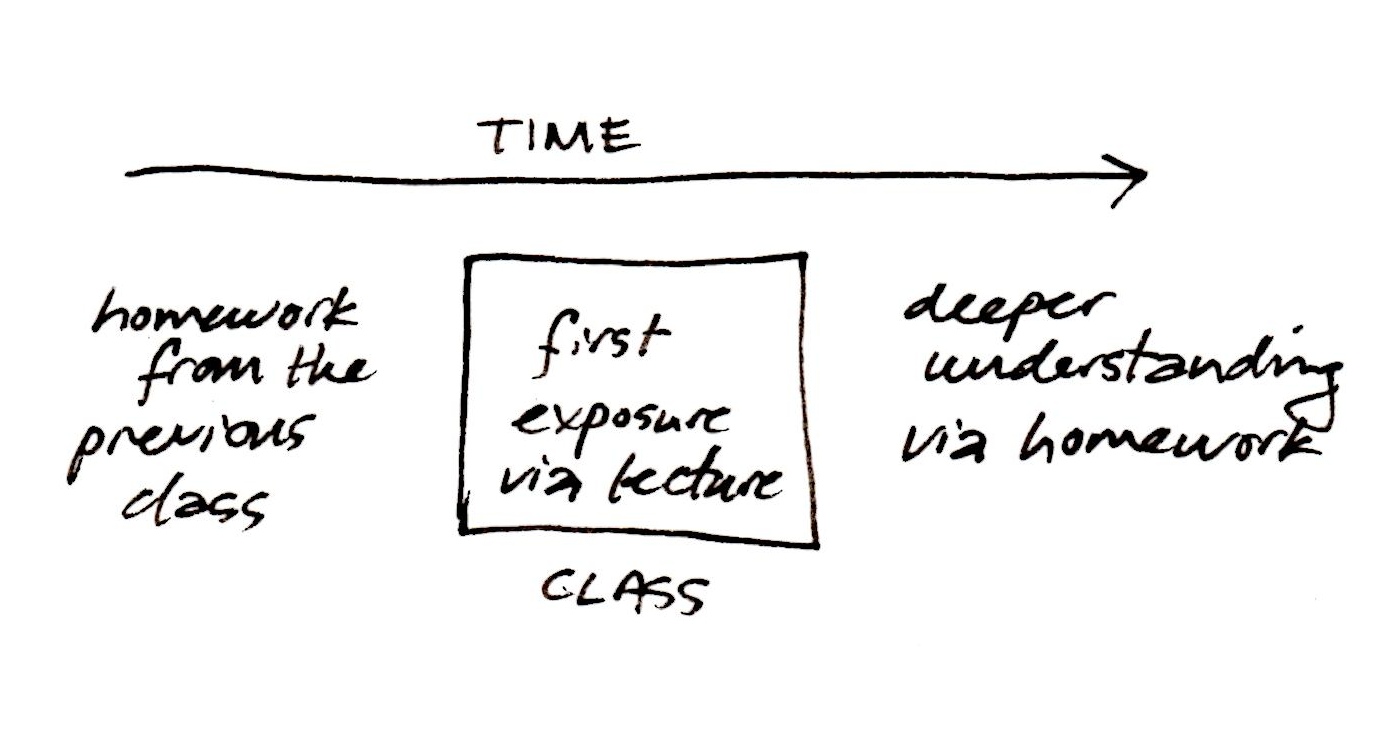
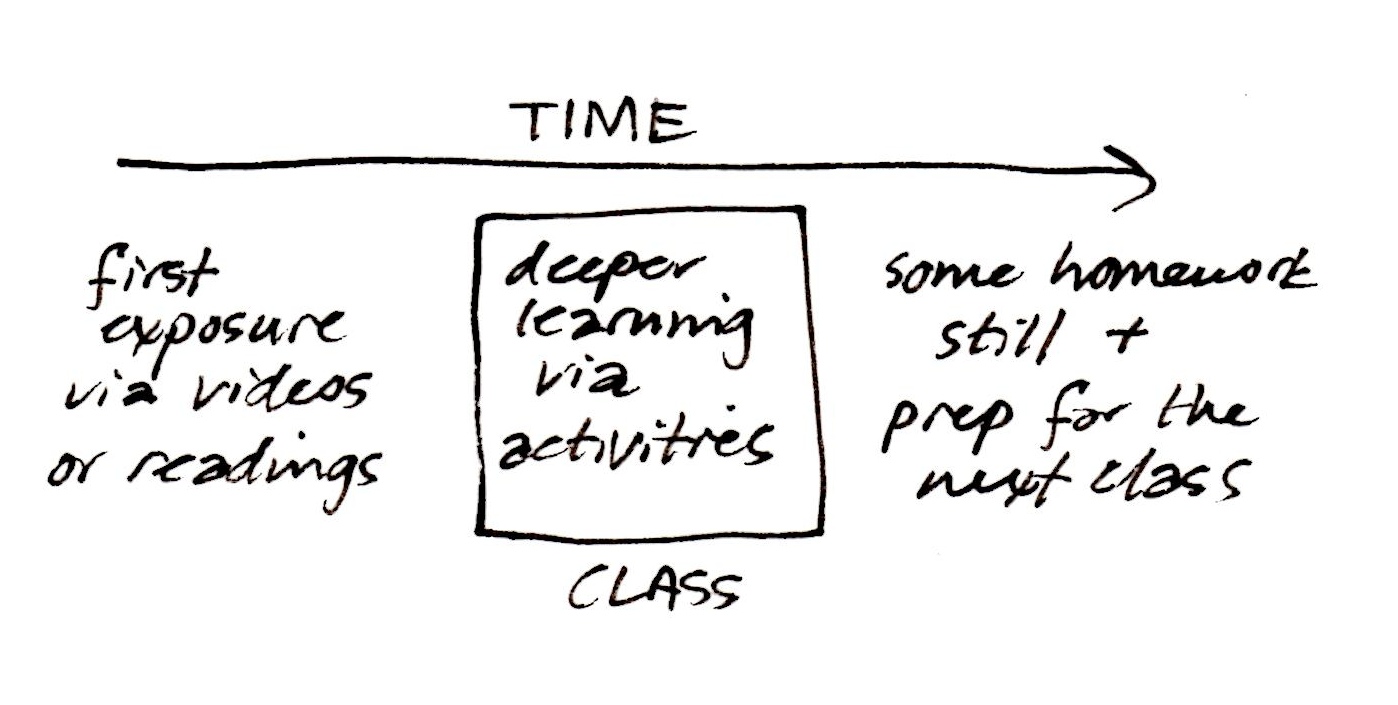
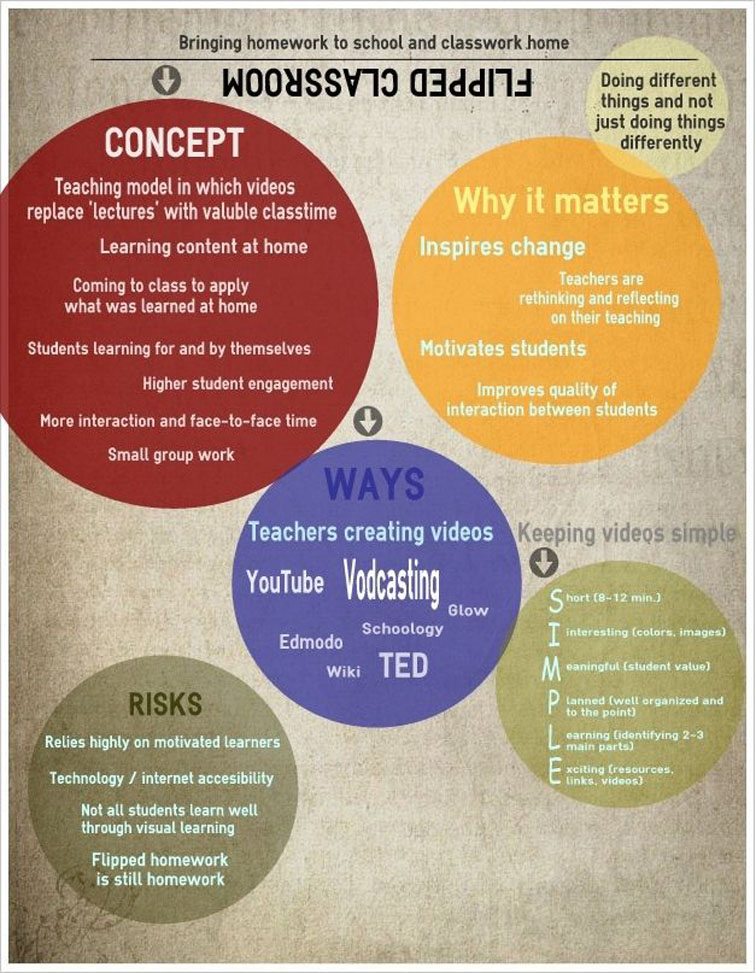
In addition, consider some current hot topics like active learning and flipped classrooms — where those terms undoubtedly mean completely different things to everyone at the table — and it’s clear why the responsible campus will want to steal a march and spell out some teaching-space-design ground rules in advance.
…
The four areas I will divide standards into — again, just for the sake of illustration — I call: industry standards, campus infrastructure standards, classroom design standards, and classroom equipment preferences.
Classroom design standards: Spelling out ‘look and feel’ — from blog.infocommblog.org by Greg Brown
Excerpt:
For part three, let’s talk about what I am calling classroom design standards. These are the parts of classroom standards that speak most specifically to the “look and feel” of the teaching space. These are the guidelines that address types of equipment (in general terms), where those items should be located, and how they operate. Here we lay out the look and function of the room from the perspective of an end user. What does an instructor expect in the room and how are they are going to use it?
This information would typically include: How many projectors are there? Do you use monitors instead? What sort of writing surfaces, and how many? Is there a formal instructor’s lectern or console? Where is it? What sort of equipment will it be equipped with? What about podcasting or webcasting?
Also, see:
Revealing statistics highlight campus video boom — from ecampusnews.com by
Survey reveals video plays an increasingly large role in instruction.
Excerpt:
Using video for remote teaching/learning is now commonplace in higher education (66 percent), while flipped classrooms are becoming a widely used form of pedagogy (46 percent).
Seventy percent of institutions use webcasting for various purposes including teaching (47 percent), training (42 percent) and broadcasting live events (42 percent).















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)