Planning for a blended future: A research-driven guide for educators — from everylearnereverywhere.org by Every Learner Everywhere in partnership with Online Learning Consortium (OLC) & National Research Center for Distance Education and Technological Advancements (DETA)
Excerpt:
The purpose of this guide
This resource is a collaboration among the National Research Center for Distance Education and Technological Advances (DETA), the Online Learning Consortium (OLC), and the Every Learner Everywhere Network. It is designed to serve as a resource for educators — faculty, instructors, instructional staff, instructional improvement staff, instructional designers, learning experience designers and developers, technological support staff, and other stakeholders — to guide strategic planning for blended learning courses and programs.
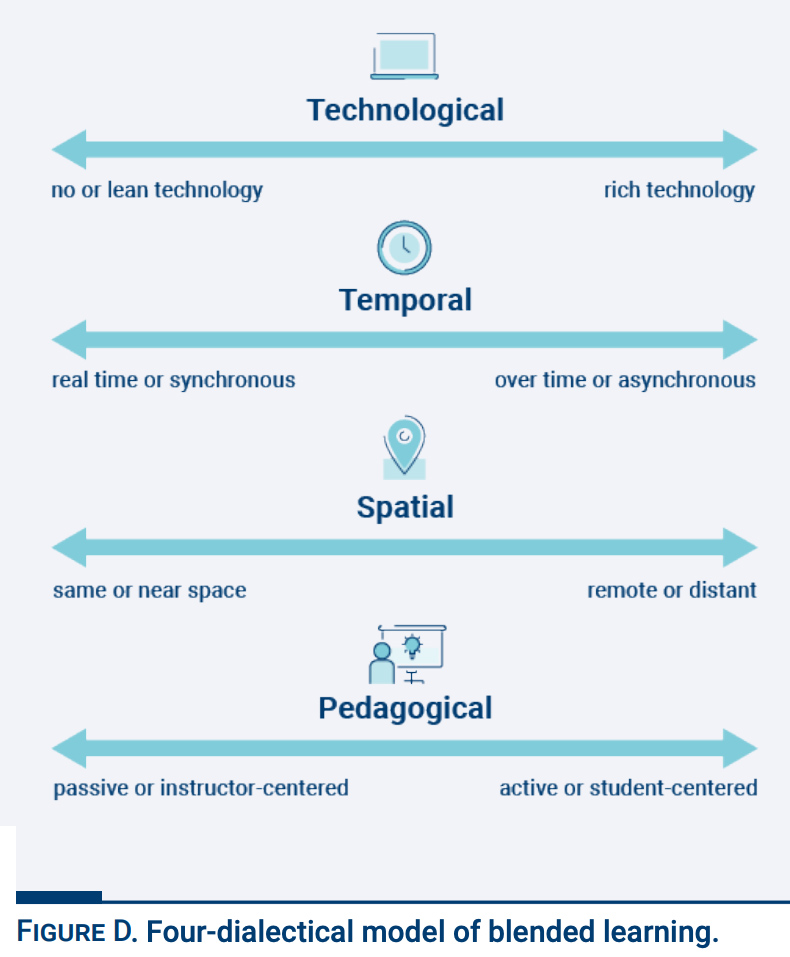
Therefore, blended learning is instruction that blends technological, temporal, spatial, and pedagogical dimensions to create actualized learning. Students feel they are successful when they actually learn and that does not always equate to grade and course completion.
KEY IDEAS
- Designing courses to meaningfully integrate the different environments and temporal cadence (online and onsite, live and overtime) while incorporating an active learning approach can improve student outcomes in blended and hybrid courses.
- Faculty must become guides for students and their engagement by intentionally and strategically using a variety of modalities to scaffold learning.
- By designing and scaffolding blended courses effectively, faculty can avoid the common pitfall of course and-a-half-syndrome, which occurs when the online portion of a course is tacked on, creating busywork for students.