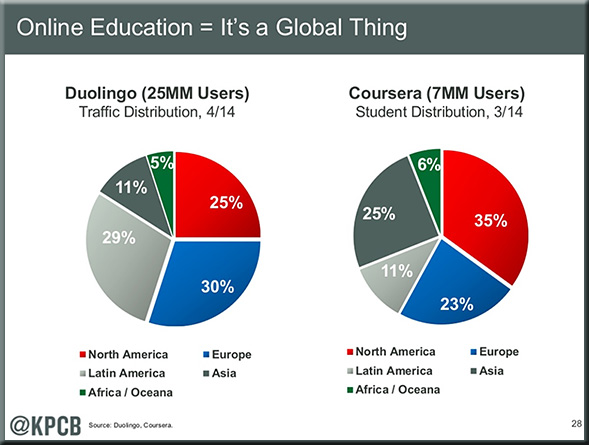
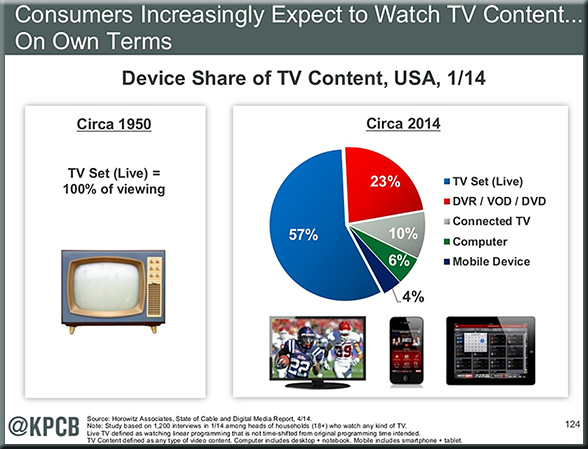
From DSC:
Many times we don’t want to hear news that could be troubling in terms of our futures. But we need to deal with these trends now or face the destabilization that Harold Jarche mentions in his posting below.
The topics found in the following items should be discussed in courses involving economics, business, political science, psychology, futurism, engineering, religion*, robotics, marketing, the law/legal affairs and others throughout the world. These trends are massive and have enormous ramifications for our societies in the not-too-distant future.
* When I mention religion classes here, I’m thinking of questions such as :
- What does God have in mind for the place of work in our lives?
Is it good for us? If so, why or why not?
- How might these trends impact one’s vocation/calling?
- …and I’m sure that professors who teach faith/
religion-related courses can think of other questions to pursue
turmoil and transition — from jarche.com by Harold Jarche
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
One of the greatest issues that will face Canada, and many developed countries in the next decade will be wealth distribution. While it does not currently appear to be a major problem, the disparity between rich and poor will increase. The main reason will be the emergence of a post-job economy. The ‘job’ was the way we redistributed wealth, making capitalists pay for the means of production and in return creating a middle class that could pay for mass produced goods. That period is almost over. From self-driving vehicles to algorithms replacing knowledge workers, employment is not keeping up with production. Value in the network era is accruing to the owners of the platforms, with companies such as Instagram reaching $1 billion valuations with only 13 employees.
…
The emerging economy of platform capitalism includes companies like Amazon, Facebook, Google, and Apple. These giants combined do not employ as many people as General Motors did. But the money accrued by them is enormous and remains in a few hands. The rest of the labour market has to find ways to cobble together a living income. Hence we see many people willing to drive for a company like Uber in order to increase cash-flow. But drivers for Uber have no career track. The platform owners get richer, but the drivers are limited by finite time. They can only drive so many hours per day, and without benefits. At the same time, those self-driving cars are poised to replace all Uber drivers in the near future. Standardized work, like driving a vehicle, has little future in a world of nano-bio-cogno-techno progress.
Value in the network era is accruing to the owners of the platforms, with companies such as Instagram reaching $1 billion valuations with only 13 employees.
For the past century, the job was the way we redistributed wealth and protected workers from the negative aspects of early capitalism. As the knowledge economy disappears, we need to re-think our concepts of work, income, employment, and most importantly education. If we do not find ways to help citizens lead productive lives, our society will face increasing destabilization.
Also see:
Will artificial intelligence and robots take your marketing job? — from by markedu.com by
Technology will overtake jobs to an extent and at a rate we have not seen before. Artificial intelligence is threatening jobs even in service and knowledge intensive sectors. This begs the question: are robots threatening to take your marketing job?
Excerpt:
What exactly is a human job?
The benefits of artificial intelligence are obvious. Massive productivity gains while a new layer of personalized services from your computer – whether that is a burger robot or Dr. Watson. But artificial intelligence has a bias. Many jobs will be lost.
A few years ago a study from the University of Oxford got quite a bit of attention. The study said that 47 percent of the US labor market could be replaced by intelligent computers within the next 20 years.
The losers are a wide range of job categories within the administration, service, sales, transportation and manufacturing.
…
Before long we should – or must – redefine what exactly a human job is and the usefulness of it. How we as humans can best complement the extraordinary capabilities of artificial intelligence.
This development is expected to grow fast. There are different predictions about the timing, but by 2030 there will be very few tasks that only a human can solve.