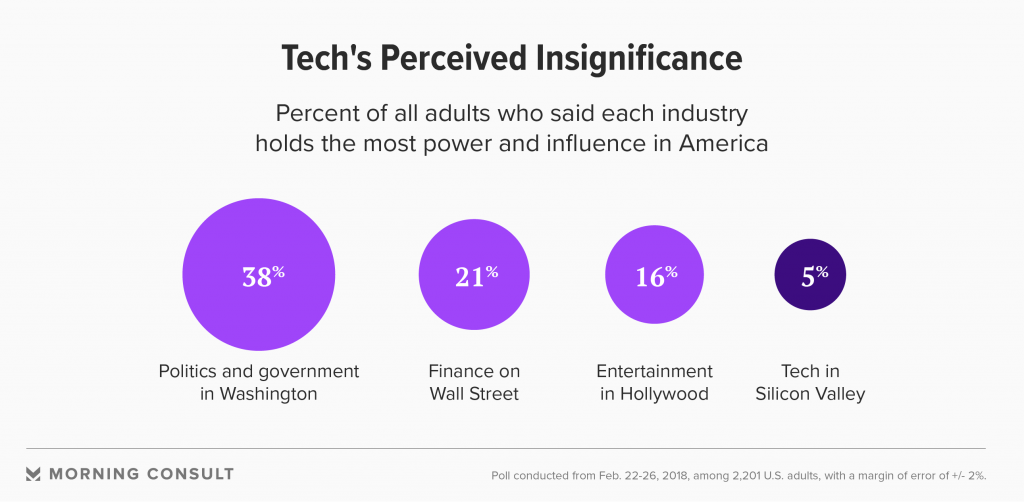
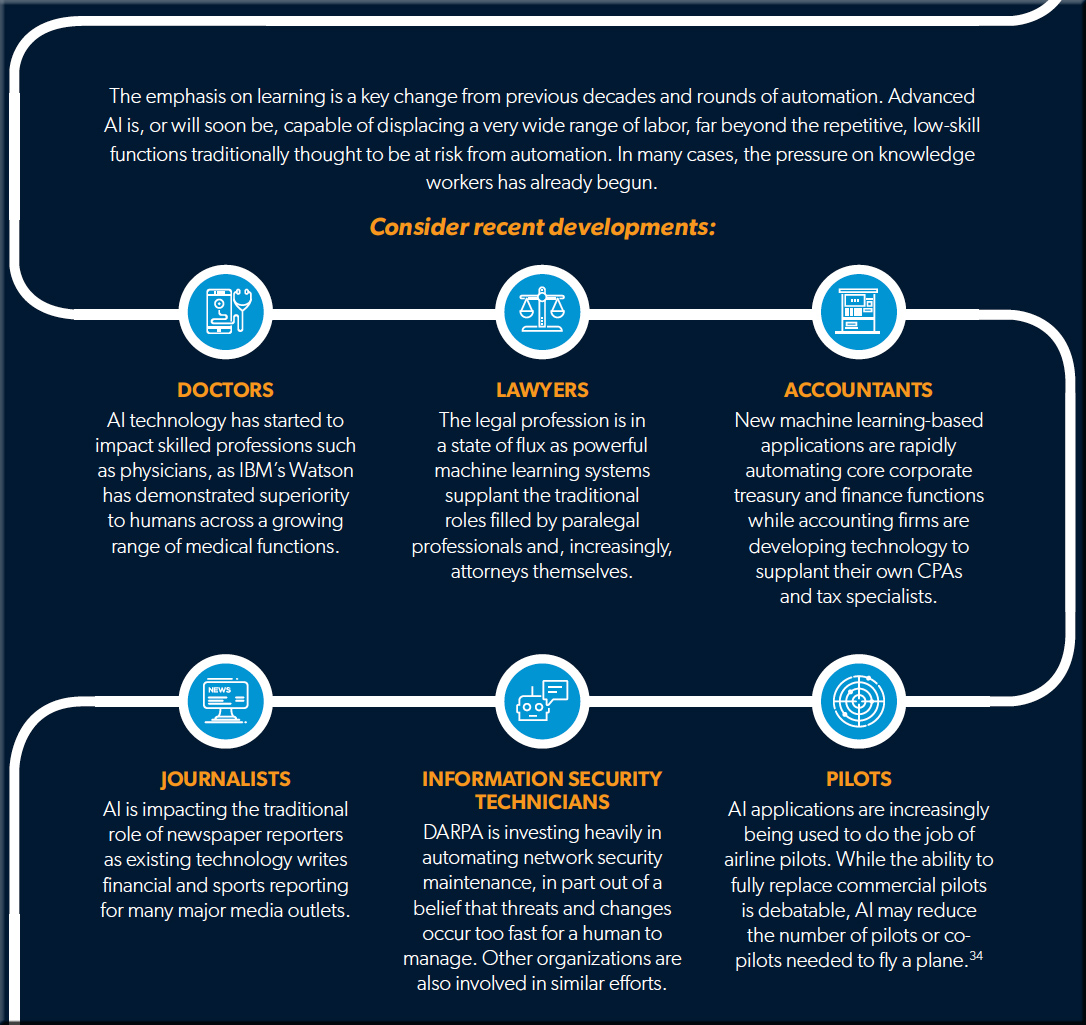
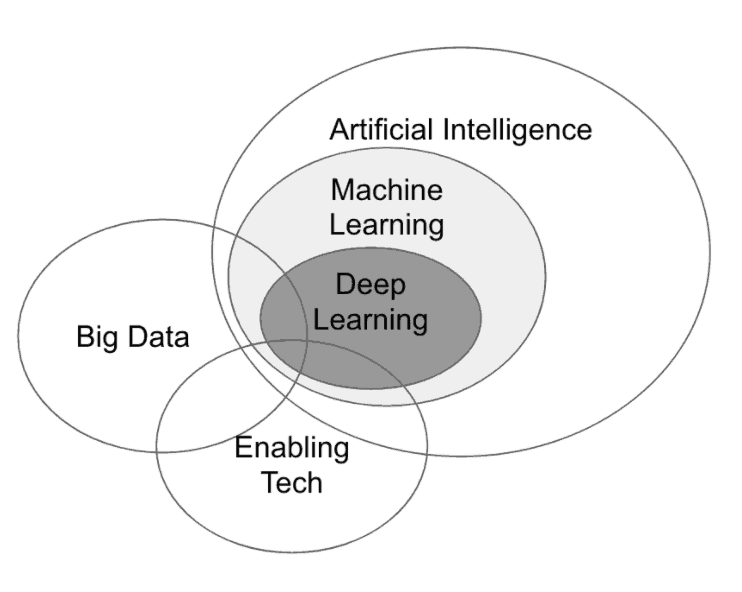
Tech companies should stop pretending AI won’t destroy jobs — from technologyreview.com / MIT Technology Review by Kai-Fu Lee
No matter what anyone tells you, we’re not ready for the massive societal upheavals on the way.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
The rise of China as an AI superpower isn’t a big deal just for China. The competition between the US and China has sparked intense advances in AI that will be impossible to stop anywhere. The change will be massive, and not all of it good. Inequality will widen. As my Uber driver in Cambridge has already intuited, AI will displace a large number of jobs, which will cause social discontent. Consider the progress of Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo software, which beat the best human players of the board game Go in early 2016. It was subsequently bested by AlphaGo Zero, introduced in 2017, which learned by playing games against itself and within 40 days was superior to all the earlier versions. Now imagine those improvements transferring to areas like customer service, telemarketing, assembly lines, reception desks, truck driving, and other routine blue-collar and white-collar work. It will soon be obvious that half of our job tasks can be done better at almost no cost by AI and robots. This will be the fastest transition humankind has experienced, and we’re not ready for it.
…
And finally, there are those who deny that AI has any downside at all—which is the position taken by many of the largest AI companies. It’s unfortunate that AI experts aren’t trying to solve the problem. What’s worse, and unbelievably selfish, is that they actually refuse to acknowledge the problem exists in the first place.
These changes are coming, and we need to tell the truth and the whole truth. We need to find the jobs that AI can’t do and train people to do them. We need to reinvent education. These will be the best of times and the worst of times. If we act rationally and quickly, we can bask in what’s best rather than wallow in what’s worst.
From DSC:
If a business has a choice between hiring a human being or having the job done by a piece of software and/or by a robot, which do you think they’ll go with? My guess? It’s all about the money — whichever/whomever will be less expensive will get the job.
However, that way of thinking may cause enormous social unrest if the software and robots leave human beings in the (job search) dust. Do we, as a society, win with this way of thinking? To me, it’s capitalism gone astray. We aren’t caring enough for our fellow members of the human race, people who have to put bread and butter on their tables. People who have to support their families. People who want to make solid contributions to society and/or to pursue their vocation/callings — to have/find purpose in their lives.
Others think we’ll be saved by a universal basic income. “Take the extra money made by AI and distribute it to the people who lost their jobs,” they say. “This additional income will help people find their new path, and replace other types of social welfare.” But UBI doesn’t address people’s loss of dignity or meet their need to feel useful. It’s just a convenient way for a beneficiary of the AI revolution to sit back and do nothing.
To Fight Fatal Infections, Hospitals May Turn to Algorithms — from scientificamerican.com by John McQuaid
Machine learning could speed up diagnoses and improve accuracy
Excerpt:
The CDI algorithm—based on a form of artificial intelligence called machine learning—is at the leading edge of a technological wave starting to hit the U.S. health care industry. After years of experimentation, machine learning’s predictive powers are well-established, and it is poised to move from labs to broad real-world applications, said Zeeshan Syed, who directs Stanford University’s Clinical Inference and Algorithms Program.
“The implications of machine learning are profound,” Syed said. “Yet it also promises to be an unpredictable, disruptive force—likely to alter the way medical decisions are made and put some people out of work.
Lawyer-Bots Are Shaking Up Jobs — from technologyreview.com by Erin Winick
Excerpt:
Meticulous research, deep study of case law, and intricate argument-building—lawyers have used similar methods to ply their trade for hundreds of years. But they’d better watch out, because artificial intelligence is moving in on the field.
As of 2016, there were over 1,300,000 licensed lawyers and 200,000 paralegals in the U.S. Consultancy group McKinsey estimates that 22 percent of a lawyer’s job and 35 percent of a law clerk’s job can be automated, which means that while humanity won’t be completely overtaken, major businesses and career adjustments aren’t far off (see “Is Technology About to Decimate White-Collar Work?”). In some cases, they’re already here.
“If I was the parent of a law student, I would be concerned a bit,” says Todd Solomon, a partner at the law firm McDermott Will & Emery, based in Chicago. “There are fewer opportunities for young lawyers to get trained, and that’s the case outside of AI already. But if you add AI onto that, there are ways that is advancement, and there are ways it is hurting us as well.”
So far, AI-powered document discovery tools have had the biggest impact on the field. By training on millions of existing documents, case files, and legal briefs, a machine-learning algorithm can learn to flag the appropriate sources a lawyer needs to craft a case, often more successfully than humans. For example, JPMorgan announced earlier this year that it is using software called Contract Intelligence, or COIN, which can in seconds perform document review tasks that took legal aides 360,000 hours.
…
People fresh out of law school won’t be spared the impact of automation either. Document-based grunt work is typically a key training ground for first-year associate lawyers, and AI-based products are already stepping in. CaseMine, a legal technology company based in India, builds on document discovery software with what it calls its “virtual associate,” CaseIQ. The system takes an uploaded brief and suggests changes to make it more authoritative, while providing additional documents that can strengthen a lawyer’s arguments.
Lessons From Artificial Intelligence Pioneers — from gartner.com by Christy Pettey
CIOs are struggling to accelerate deployment of artificial intelligence (AI). A recent Gartner survey of global CIOs found that only 4% of respondents had deployed AI. However, the survey also found that one-fifth of the CIOs are already piloting or planning to pilot AI in the short term.
Such ambition puts these leaders in a challenging position. AI efforts are already stressing staff, skills, and the readiness of in-house and third-party AI products and services. Without effective strategic plans for AI, organizations risk wasting money, falling short in performance and falling behind their business rivals.
“Pursue small-scale plans likely to deliver small-scale payoffs that will offer lessons for larger implementations”
“AI is just starting to become useful to organizations but many will find that AI faces the usual obstacles to progress of any unproven and unfamiliar technology,” says Whit Andrews, vice president and distinguished analyst at Gartner. “However, early AI projects offer valuable lessons and perspectives for enterprise architecture and technology innovation leaders embarking on pilots and more formal AI efforts.”
So what lessons can we learn from these early AI pioneers?
Why Artificial Intelligence Researchers Should Be More Paranoid — from wired.com by Tom Simonite
Excerpt:
What to do about that? The report’s main recommendation is that people and companies developing AI technology discuss safety and security more actively and openly—including with policymakers. It also asks AI researchers to adopt a more paranoid mindset and consider how enemies or attackers might repurpose their technologies before releasing them.
How to Prepare College Graduates for an AI World — from wsj.com by
Northeastern University President Joseph Aoun says schools need to change their focus, quickly
Excerpt:
WSJ: What about adults who are already in the workforce?
DR. AOUN: Society has to provide ways, and higher education has to provide ways, for people to re-educate themselves, reskill themselves or upskill themselves.
That is the part that I see that higher education has not embraced. That’s where there is an enormous opportunity. We look at lifelong learning in higher education as an ancillary operation, as a second-class operation in many cases. We dabble with it, we try to make money out of it, but we don’t embrace it as part of our core mission.
Inside Amazon’s Artificial Intelligence Flywheel — from wired.com by Steven Levy
How deep learning came to power Alexa, Amazon Web Services, and nearly every other division of the company.
Excerpt:
Amazon loves to use the word flywheel to describe how various parts of its massive business work as a single perpetual motion machine. It now has a powerful AI flywheel, where machine-learning innovations in one part of the company fuel the efforts of other teams, who in turn can build products or offer services to affect other groups, or even the company at large. Offering its machine-learning platforms to outsiders as a paid service makes the effort itself profitable—and in certain cases scoops up yet more data to level up the technology even more.