Potentially-useful sites for developing writers out there:
Top ten podcasts every teacher needs to hear — from wiley.com; with thanks to Emily Liebtag for her posting on Twitter for this resource
Excerpt:
Listening to podcasts is an easy way to dive into a topic that interests you and learn something new from others who share your passion for education.
We’re highlighting the following ten podcast episodes featuring Jossey-Bass authors that you can listen to whenever, wherever to help you master your craft or reignite your love of teaching.
So, take some time for yourself, grab your earbuds, and press play on these…
Shakespearean Wisdom Appears on a Building in Las Vegas in New Sunlight-Activated Installation by DAKU — from thisiscolossal.com by Laura Staugaitis
Microsoft debuts Ideas in Word, a grammar and style suggestions tool powered by AI — from venturebeat.com by Kyle Wiggers; with thanks to Mr. Jack Du Mez for his posting on this over on LinkedIn
Excerpt:
The first day of Microsoft’s Build developer conference is typically chock-full of news, and this year was no exception. During a keynote headlined by CEO Satya Nadella, the Seattle company took the wraps off a slew of updates to Microsoft 365, its lineup of productivity-focused, cloud-hosted software and subscription services. Among the highlights were a new AI-powered grammar and style checker in Word Online, dubbed Ideas in Word, and dynamic email messages in Outlook Mobile.
Ideas in Word builds on Editor, an AI-powered proofreader for Office 365 that was announced in July 2016 and replaced the Spelling & Grammar pane in Office 2016 later that year. Ideas in Words similarly taps natural language processing and machine learning to deliver intelligent, contextually aware suggestions that could improve a document’s readability. For instance, it’ll recommend ways to make phrases more concise, clear, and inclusive, and when it comes across a particularly tricky snippet, it’ll put forward synonyms and alternative phrasings.
Also see:
- How Microsoft is shaping the future of your office — from finance.yahoo.com by Daniel Howley
Excerpt:
The new tech includes:- Augmented Reality meetings
- Advanced digital voice assistants
- Enhanced speech recognition technologies
- Microsoft Releases Blockchain Manager App
Excerpt:
The new blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) platform will purportedly allow users to build blockchain applications on preconfigured network.
From DSC:
I just found out about this and I wanted to pass it along to you aspiring young writers/playwrights out there! If it’s too late for this year, put it on your radar for next year!
Worldwide Plays Festival Submission Deadline: February 1, 2019
Announcing the judges of the 10th Annual Writopia Lab Worldwide Plays Festival Competition, an exciting, immersive festival of plays written by young playwrights ages 5-19, turning a multi-roomed theater space in midtown Manhattan into The Neighborhood, where audiences will be lead from place to place, play to play, plunged into the wacky and provoking minds of children and teens.
The Judges are:
- Gideon Glick (currently on Broadway in To Kill A Mockingbird),
- Abe Koogler (Obie Award Winner for Manhattan Theatre Club’s Fulfillment Center),
- Jordana Spiro (Netflix’ Ozark),
- Madhuri Shekar (writer on upcoming HBO’s The Nevers),
- Matthew Shapiro (Emmy Winning Co-Producer Marvelous Mrs. Maisel)
Named after David Letterman’s Worldwide Pants due to funding of earlier festivals, Writopia Lab’s Worldwide Plays Festival has produced hundreds of full productions of plays written by young playwrights over the past decade.
This year, we invite playwrights from 1st through 12th grade around the world to enter our competition. We will select winning plays in three age groups: Elementary School, Middle School and High School.
From hundreds of submissions from across the country, 36 will be selected for production and three will receive a cash prize as part of our festival in May of 2019 at TheaterLab, in the theater district of New York City. Prizes include $750 for best high school play, $500 for best middle school play, and $250 for best elementary school play.
Winners will be notified by March, 2019.
For more information about how to submit, please visit: https://www.writopialab.org/
This Year’s Theme:
The Neighborhood
“Life is so rich when you go off the logical path and embark on eccentric adventures,”
Steve Young, producer and writer of Bathrooms over Broadway, and former head writer at The Late Show with David Letterman.
In this spirit, we ask playwrights from all walks of life-from homeless shelters to townhouses-to embark on eccentric adventures in their own neighborhoods and share their discoveries with us on the stage. Plays take place in one of three locations: The Convenience Store or Bodega, The Community Center (Church, Mosque, Synagogue, Yoga Studio, etc.) or Outside Your Door. Most of our writers attend highly segregated school systems and find great comfort-and meaningful challenge-in working closely in workshops with peers from diverse backgrounds.
At showtime, actors playing a rich array of complex neighborhood characters (also written by young writers), lead groups of audiences from room to room, weaving together a multitude of plays by young playwrights–urban and suburban, gay and straight, binary and nonbinary, outside and in-celebrating a totality of experience around the corner, down the block, across the hall in your America.
Festival Performances:
Where: Theaterlab, 357 West 36th Street, 3rd floor
When: Wednesday May 1st, 2019 to Sunday May 5th, 2019
Media Contact:
Lance Laytner
Public Good Relations
(917)573-8960
lance@publicgoodrelations.com
Also per Inside VR & AR:
Google has teamed up with Boston-based Commonwealth Shakespeare Company to produce a VR version of Shakespeare’s “Hamlet.” Called “Hamlet 360: Thy Father’s Spirit,” the Bard’s classic tale of murder and revenge was tailored specifically for virtual reality, with some scenes lengthened and the overall run time pared way down. Director Steven Maler told the New York Times the production is a way “to show people how exciting it can be to be in the space where it’s happening.” The viewer sees the action from the point of view of the ghost of Hamlet’s father. Hamlet 360 was filmed on a Yi Halo 360 camera and is posted on WGBH-Boston’s YouTube channel. — NYTIMES
Awesome study hacks: 5 ways to remember more of what you read — from academiccoachingwithpat.com by Pat LaDouceur; with thanks to Julia Reed for her Tweet on this
Excerpts:
- Annotate as you read
- Skim
- Rewrite key ideas in your own words
- Write a critique
- List your questions
Reorganizing information helps you learn it more effectively, which is why Rewriting makes the list as one of the top 5 reading study hacks. It forces you to stay active and involved with the text (from DSC: the word “engaged” comes to mind here), to consider arguments and synthesize information, and thus remember more of what you read.
Social media as a learning tool: Five suggested sses for the classroom — from frontierinternet.com; with thanks to Laura Tscholl, Communications Specialist | The Gateway for this resource
From DSC:
I have often reflected on differentiation or what some call personalized learning and/or customized learning. How does a busy teacher, instructor, professor, or trainer achieve this, realistically?
It’s very difficult and time-consuming to do for sure. But it also requires a team of specialists to achieve such a holy grail of learning — as one person can’t know it all. That is, one educator doesn’t have the necessary time, skills, or knowledge to address so many different learning needs and levels!
- Think of different cognitive capabilities — from students that have special learning needs and challenges to gifted students
- Or learners that have different physical capabilities or restrictions
- Or learners that have different backgrounds and/or levels of prior knowledge
- Etc., etc., etc.
Educators and trainers have so many things on their plates that it’s very difficult to come up with _X_ lesson plans/agendas/personalized approaches, etc. On the other side of the table, how do students from a vast array of backgrounds and cognitive skill levels get the main points of a chapter or piece of text? How can they self-select the level of difficulty and/or start at a “basics” level and work one’s way up to harder/more detailed levels if they can cognitively handle that level of detail/complexity? Conversely, how do I as a learner get the boiled down version of a piece of text?
Well… just as with the flipped classroom approach, I’d like to suggest that we flip things a bit and enlist teams of specialists at the publishers to fulfill this need. Move things to the content creation end — not so much at the delivery end of things. Publishers’ teams could play a significant, hugely helpful role in providing customized learning to learners.
Some of the ways that this could happen:
Use an HTML like language when writing a textbook, such as:
<MainPoint> The text for the main point here. </MainPoint>
<SubPoint1>The text for the subpoint 1 here.</SubPoint1>
<DetailsSubPoint1>More detailed information for subpoint 1 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SubPoint2>The text for the subpoint 2 here.</SubPoint2>
<DetailsSubPoint2>More detailed information for subpoint 2 here.</DetailsSubPoint2>
<SubPoint3>The text for the subpoint 3 here.</SubPoint3>
<DetailsSubPoint3>More detailed information for subpoint 3 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SummaryOfMainPoints>A list of the main points that a learner should walk away with.</SummaryOfMainPoints>
<BasicsOfMainPoints>Here is a listing of the main points, but put in alternative words and more basic ways of expressing those main points. </BasicsOfMainPoints>
<Conclusion> The text for the concluding comments here.</Conclusion>
<BasicsOfMainPoints> could be called <AlternativeExplanations>
Bottom line: This tag would be to put things forth using very straightforward terms.
Another tag would be to address how this topic/chapter is relevant:
<RealWorldApplication>This short paragraph should illustrate real world examples
of this particular topic. Why does this topic matter? How is it relevant?</RealWorldApplication>
On the students’ end, they could use an app that works with such tags to allow a learner to quickly see/review the different layers. That is:
- Show me just the main points
- Then add on the sub points
- Then fill in the details
OR - Just give me the basics via an alternative ways of expressing these things. I won’t remember all the details. Put things using easy-to-understand wording/ideas.
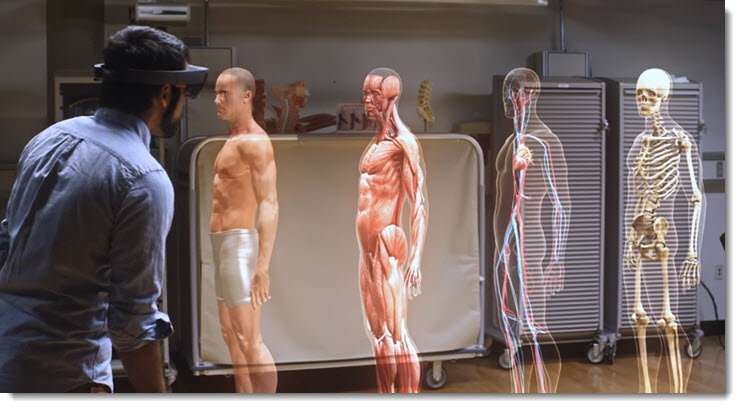
It’s like the layers of a Microsoft HoloLens app of the human anatomy:
Or it’s like different layers of a chapter of a “textbook” — so a learner could quickly collapse/expand the text as needed:
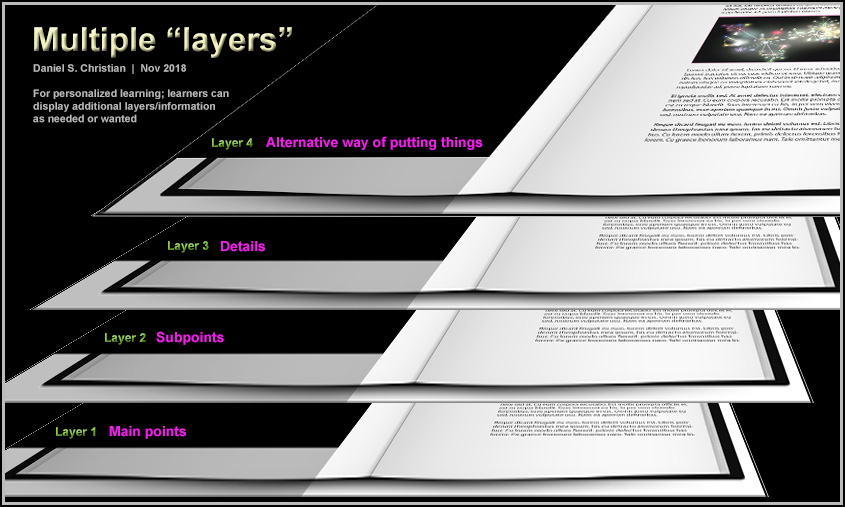
This approach could be helpful at all kinds of learning levels. For example, it could be very helpful for law school students to obtain outlines for cases or for chapters of information. Similarly, it could be helpful for dental or medical school students to get the main points as well as detailed information.
Also, as Artificial Intelligence (AI) grows, the system could check a learner’s cloud-based learner profile to see their reading level or prior knowledge, any IEP’s on file, their learning preferences (audio, video, animations, etc.), etc. to further provide a personalized/customized learning experience.
To recap:
- “Textbooks” continue to be created by teams of specialists, but add specialists with knowledge of students with special needs as well as for gifted students. For example, a team could have experts within the field of Special Education to help create one of the overlays/or filters/lenses — i.e., to reword things. If the text was talking about how to hit a backhand or a forehand, the alternative text layer could be summed up to say that tennis is a sport…and that a sport is something people play. On the other end of the spectrum, the text could dive deeply into the various grips a person could use to hit a forehand or backhand.
- This puts the power of offering differentiation at the point of content creation/development (differentiation could also be provided for at the delivery end, but again, time and expertise are likely not going to be there)
- Publishers create “overlays” or various layers that can be turned on or off by the learners
- Can see whole chapters or can see main ideas, topic sentences, and/or details. Like HTML tags for web pages.
- Can instantly collapse chapters to main ideas/outlines.
This Android app lets you search for specific words in books & documents via augmented reality — from mobile-ar.reality.news by Tommy Palladino
Excerpt:
One of the neatest tricks available in Google Lens, an app that can identify and interpret real world information, is the ability to copy text from the app’s camera view and paste it into a digital document.
And while the computer vision assistance of Google Lens takes care of the copy and paste function in augmented reality, a new mobile app from Find It Software fulfills the find function directly on printed documents in real time.

Production Values for Audio Podcasts, Part I — from learningsolutionsmag.com by Jeff D’Anza
Excerpts:
There are a number of production values that narrative podcasters find effective for grabbing listener attention and keeping their audiences engaged in the story; you could think of these as technical elements of professional audio quality. They range from techniques for improving content when applied to script writing to methods applied to audio recording and editing. The most successful professional podcasters use these elements to create immersion in the audio environment and to eliminate audio distraction. The result is the creation of a kind of audio theater. Here are four basic practices to embrace while creating your narrative podcasts.
- Set the scene first
- Hook the audience
- Vary character voices
- Talk like real people
Production Values for Audio Podcasts, Part II — from learningsolutionsmag.com by Jeff D’Anza
Excerpts:
In this article, I will continue with more production tricks that can substantially increase the quality of your narrative podcasts.
Use music to reset scenes
It’s not revolutionary to suggest that learners tend to have short attention spans, and the case is no different when it comes to narrative podcasts. Every so often you need to reset your learners’ brains in order to keep their attention level high.
One excellent way to accomplish this is through the use of musical breaks. Music breaks can function as a type of auditory palate cleanser, allowing the brain a few moments to stop focusing on information that is being presented and prepare the learner to be ready for the next section of content.
Also:
- Host/producer structure
- Get out of the studio
- Don’t fear insignificant details
From DSC:
Seems to me there’s some wisdom here for instructional designers as well as professors, teachers, and trainers who are creating learning/training related content and/or who are flipping their classrooms.
100 things students can create to demonstrate what they know — from teachthought.com
Excerpt:
[Here] is a diverse list adapted from resources found at fortheteachers.org of potential student products or activities learners can use to demonstrate their mastery of lesson content. The list also offers several digital tools for students to consider using in a technology-enriched learning environment.
Delaying the grade: How to get students to read feedback — from cultofpedagogy.com by Kristy Louden
Excerpt:
This meant that I could return papers with comments but without grades.
And from this a whole new system was born: Return papers to students with only feedback. Delay the delivery of the actual grade so student focus moves from the grade to the feedback.
The simple act of delaying the grade meant that students had to think about their writing. They had to read their own writing—after a few weeks away from it—and digest my comments, which allowed them to better recognize what they did well or not so well. The response from students was extremely positive; they understood the benefit of rereading their essays and paying attention to feedback. One boy said, “Mrs. Louden, you’re a genius. I’ve never read what a teacher writes on my essay before, and now I have to.”
From DSC:
I’m including higher ed in the tags here…as this could be effective for college students as well. College students who have long played the game of getting the grade…simply playing the system and putting the ownership and development of their learning much lower on the priority list. Let’s help students stop outsourcing their learning.
Writing Resources from the “State of Writing” — from stateofwriting.com with thanks to Mary Bennett who mentions that this site is an “incredibly useful resource with tips and its own collection of writing and grammar guides.”
Some of the useful sections include resources regarding:
- Dictionaries and Thesauruses
- Style Guides
- Grammar and Punctuation
- Etymology
- Quotations
- Writing various genres
- Foreign Languages
From DSC:
I vote that we change the color that we grade papers — whether on paper (harcopy) or whether via digitally/electronically-based annotations — from red to green. Why? Because here’s how I see the colors:
- RED:
- Failure.
- You got it wrong. Bad job.
- Danger
- Stop!
- Can be internalized as, “I’m no good at (writing, math, social studies, science, etc…..) and I’ll never be any good at it (i.e., the fixed mindset; I was born this way and I can’t change things).
- GREEN:
- Growth
- As in spring, flowers appearing, new leaves on the trees, new life
- As in support of a growth mindset
- It helps with more positive thoughts/internalized messages: I may have got it wrong, but I can use this as a teaching moment; this feedback helps me grow…it helps me identify my knowledge and/or skills gaps
- Health
- Go (not stop); i.e., keep going, keep learning
- May help develop more of a love of learning (or at least have more positive experiences with learning, vs feeling threatened or personally put down)
- Growth
From DSC:
This application looks to be very well done and thought out! Wow!
Check out the video entitled “Interactive Ink – Enables digital handwriting“ — and you may also wonder whether this could be a great medium/method of having to “write things down” for better information processing in our minds, while also producing digital work for easier distribution and sharing!
Wow! Talk about solid user experience design and interface design! Nicely done.
Below is an excerpt of the information from Bella Pietsch from anthonyBarnum Public Relations
Imagine a world where users interact with their digital devices seamlessly, and don’t suffer from lag and delayed response time. I work with MyScript, a company whose Interactive Ink tech creates that world of seamless handwritten interactivity by combining the flexibility of pen and paper with the power and productivity of digital processing.
According to a recent forecast, the global handwriting recognition market is valued at a trillion-plus dollars and is expected to grow at an almost 16 percent compound annual growth rate by 2025. To add additional context, the new affordable iPad with stylus support was just released, allowing users to work with the $99 Apple Pencil, which was previously only supported by the iPad Pro.
Check out the demo of Interactive Ink using an Apple Pencil, Microsoft Surface Pen, Samsung S Pen or Google Pixelbook Pen here.
Interactive Ink’s proficiencies are the future of writing and equating. Developed by MyScript Labs, Interactive Ink is a form of digital ink technology which allows ink editing via simple gestures and providing device reflow flexibility. Interactive Ink relies on real-time predictive handwriting recognition, driven by artificial intelligence and neural network architectures.