Next Generation K-12: 10 Implications for HigherEd — from gettingsmart.com by Tom Vander Ark and Guest Author
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
There are a growing number of next generation models in K-12 as a result of new thinking about learning design and deeper understandings of college and career readiness, enabled by cheap devices, better tools, and foundation support. They personalize learning in blended and competency-based environments. These models revolve around students and learning, rather than teachers and direct instruction as the primary pedagogy.
We’ve chronicled the development of next-gen schools (here and here) and see hundreds of districts and networks adopting next-gen strategies. We’re optimistic that broader adoption of these strategies will produce better student outcomes. Following are 10 examples of next-gen learning in K-12.
…
These examples are not single course innovations, they are engineered solutions. The first half are districts or networks; the other half are schoolwide models. There are hundreds of examples and they have big implications for HigherEd.
We see 10 implications for HigherEd; some directly as a result of next-gen models, some resulting from next-gen policies, some from EdTech and consumer variables impacting both K-12 and HigherEd.
From DSC:
I post this valuable item from Tom Vander Ark because I’m constantly shouting “Heads up!” “Heads-up!” I shout it to those of us working within higher education, and I shout it to those working within the corporate world.
Why?
Because those of us working within higher education operate in a continuum — and so do you working within the corporate world (especially those of you working within corporate training and corporate universities, as well as those of you producing elearning-based materials).
What happens in the prior stages of a student’s/employee’s life directly impacts us/you. Expectations are at play here; which impacts engagement; which impacts learning.
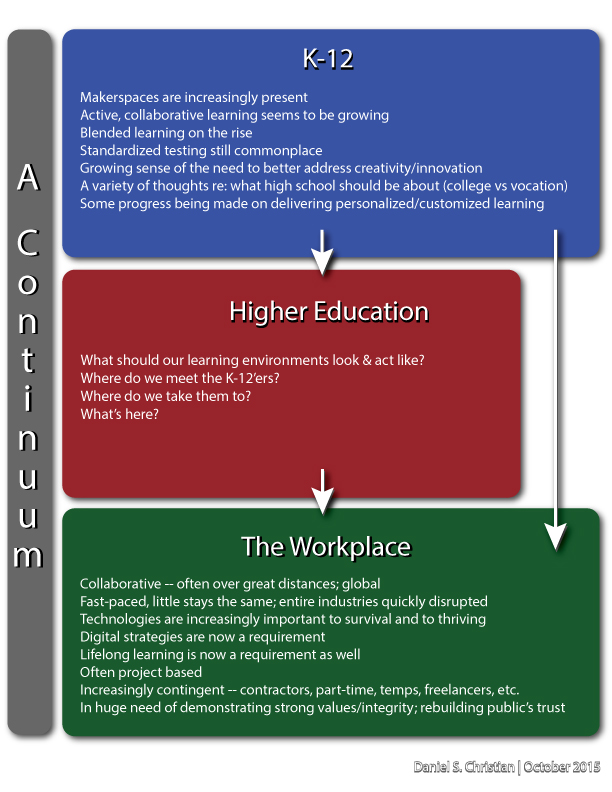
Why there isn’t greater collaboration between these spheres is troublesome to me. So I want to lift up those people — like Tom Vander Ark — who are trying to do something about it.
————
Addendum on 11/5/15 that nicely illustrates my point:
2 things you should know about Google ed evangelist’s vision [Educause 2015] — from educationdive.com by Roger Riddell
Jaime Casap says schools aren’t broken, but they do need to adapt
Excerpt:
While that topic was certainly touched on during Casap’s keynote at Educause, the issue at hand on Thursday was a much more generational one. The discussion was, after all, titled “The Digitally Native Generation Z Is Going to College: Are You Ready?”
“There’s a generation of students coming to college that are a little bit different from the ones that they’re used to, and they’re learning in a different way,” Casap said, adding that a lot of the innovation in education is occurring in K-12 and will likely have some impact on higher ed.


















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)