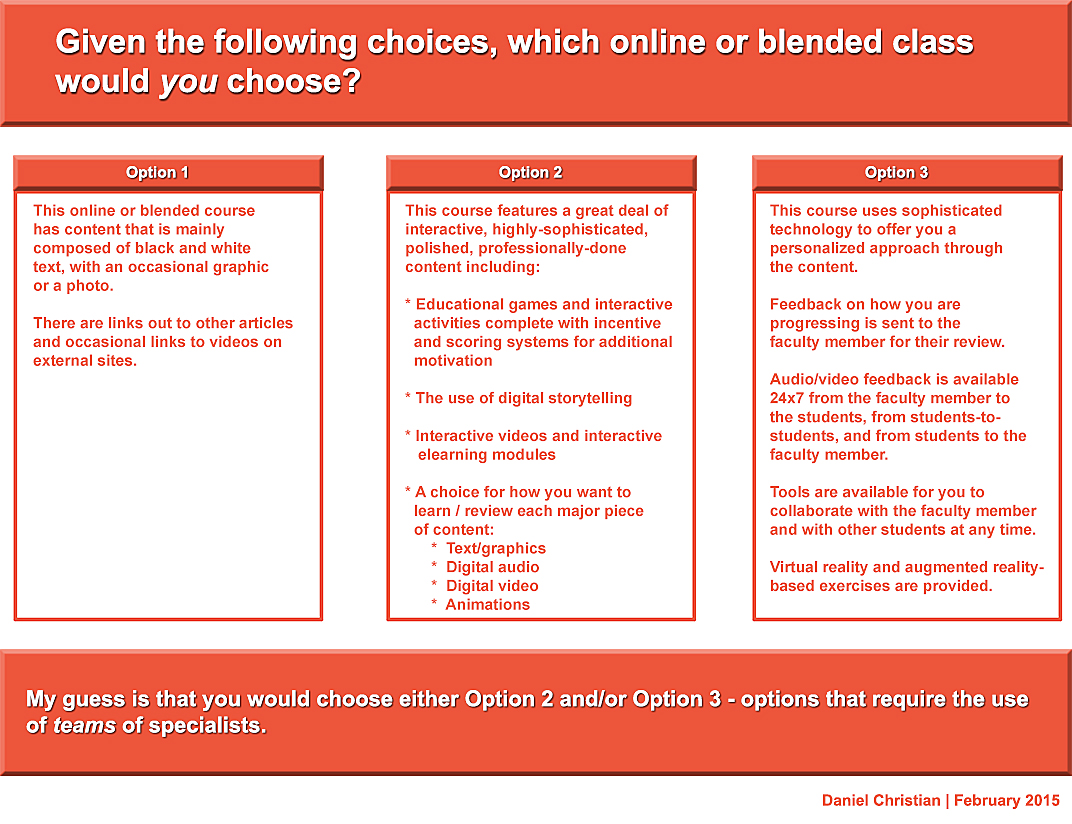
Interview: Kevin Carey, author of ‘The End Of College’ — from NPR Ed
Excerpt:
But author Kevin Carey argues that those problems might be overcome in the future with online higher education. Carey directs the Education Policy Program at the New America Foundation. In his new book, The End of College: Creating the Future of Learning and the University of Everywhere, Carey envisions a future in which “the idea of ‘admission’ to college will become an anachronism, because the University of Everywhere will be open to everyone” and “educational resources that have been scarce and expensive for centuries will be abundant and free.”
…
On the term “University of Everywhere”
The University of Everywhere is the university that I think my children and future generations will attend when they go to college. … They will look very different in some ways, although not in other ways, from the colleges that I went to and that many of us have become familiar with. This will be driven by advances in information technology: So whereas historically you went to college in a specific place and only studied with the other people who could afford to go [to] that place, in the future we’re going to study with people all over the world, interconnected over global learning networks and in organizations that in some cases aren’t colleges as we know them today, but rather 21st-century learning organizations that take advantage of all of the educational tools that are rapidly becoming available to offer great college experiences for much less money.
From DSC:
Though Kevin discusses various items in this interview, I wanted to focus on the topic of online learning and leveraging the Internet for lifelong learning.
Whether out of fear, self-preservation, or for some other reasons, there continues to exist within higher education a group of people who still discount the power of the Internet to offer opportunities for learning throughout one’s lifetime. They poo-poo online learning for example, looking down upon it and assert that such methods can’t measure up to the traditional face-to-face based learning experiences. Never mind that the majority of these folks — it not all of them — have never taught online nor have they taken a well-executed, formal online-based course. They don’t realize how far various technologies have come to provide powerful, effective, highly-convenient learning experiences. They just continue to poo-poo it:
Only 27.6% of chief academic officers reported that their faculty accepted online instruction in 2003. This proportion showed some improvement over time, reaching a high of 33.5% in 2007. The slow increase was short-lived, however. Today, the rate is nearly back to where it began; 28.0% of academic leaders say that their faculty accept the “value and legitimacy of online education.”
Grade Level: Tracking Online Education in the
United States by I. Elaine Allen and Jeff Seaman (2015)
Meanwhile, the world continues to change, pressing needs continue to amass, technologies continue to emerge and morph, and many outside of higher ed are starting to care less and less about what those stuck in traditional higher ed even have to say. They’re beginning to design other alternatives. See below for some examples.
With that said, there’s also a sizable group of us who are working hard to innovate and to leverage the power of the Internet — who seek to reduce the price of obtaining a degree, to make quality education more affordable and accessible to the masses, and who seek to provide a balance of the liberal arts/foundational skills with the skills that are needed out in the workplace. Also see below for examples of this.
DSC: I write these reflections down to urge those of us working within higher education NOT to be like the Smith Coronas of the world, NOT to be like the Blockbusters and Kodaks of the world — who, to their very dying day, clutched tightly to their beliefs/strategies/business plans, not seeing the tidal waves that were approaching them.
————–
The New Normal — from edtechdigest.wordpress.com by Victor Rivero
A dearth in practical technology skills calls for an online boot camp approach.
Excerpt:
The ecosystems of many companies are changing as baby boomers retire and workplaces are filled with a strange and not fully functioning blend of digital immigrants, with fresh new academic graduates. In many cases these graduates have invested considerable time and money in traditional offline learning and have come out overqualified yet drastically under skilled.
…
Many people who make the switch are ready for change and want it to happen quickly. Online training through technology boot camps for example, means they can pick up key technology skills, and as a result make a total career change; transitioning from being unemployed to becoming a busy productive freelancer in a matter of months. As a result, offline learning is losing ground while online learning is gaining traction by the second.
From DSC:
Can those of us working within higher ed offer such bootcamps?
Doing so would not only help learners of all ages but would also create new sources of (sorely-needed) revenue. Perhaps these sorts of bootcamps shouldn’t have to be vetted through the normal committees and mechanisms — as doing so will surely keep us from providing the level of responsiveness as the increasingly-fast-paced world now requires. Perhaps we leave those decisions up to the relevant, knowledgeable faculty members who can then team up with innovative staff and administrators to create and deliver these offerings.
————–
Udacity kicks off enrollment for its Swift-focused iOS developer ‘nanodegree’ — from techcrunch.com by Darrell Etherington
Excerpt:
If you’re looking for a way to gain the skills necessary to get a gig developing for iPhone and iPad, but unwilling to commit to a full-time college or university schedule, Udacity might have the answer. The online education platform debuted something called a “nanodegree” last year, and enrollment for the iOS developer edition of the same just opened to applicants today. Enrollment is open to anyone willing to spend $200 per month to participate (with a one-week free trial included) and closes at the end of March 10.
————–
IDEO Futures
C-Suite TV
Yyieldr
Lessons Go Where
Class Do
NYC Data Science Bootcamp
Hands-On Data Science & Engineering: A 5-Day Bootcamp
User Experience Design Immersive — A 10-Week, Full-Time Career Accelerator in Boston
Flatiron School
Python Programming for Beginners — set your own price
Eleven Fifty
Cybrary.it
————–
Re-imagining Learning & Credentialing in a Connected World — from etale.org by Bernard Bull
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
What happens when we don’t think of these as three disconnected and unrelated learning pathways? What if we see this as representative of a city or region in which one travels on a lifelong learning journey? What possibilities does that create for us? Consider a model where credentials can be provided as people demonstrate competence through any of these stops along the way, whether it is the weekend workshop, the self-guided tour, the self-study stop, or a formal course. This is one of the interesting and exciting possibilities of micro-credentials and digital badges. Their affordances give us a greater ability to imagine such contexts, as evidenced by the cities of learning initiatives.


————–
ACE and Blackboard unveil research on alternative pathways to degree completion — from acenet.edu
Papers on Credit for Prior Learning and Competency-Based Education Practices to be Released
Excerpts:
New research released [on 2/20/15] will shed light on how two approaches to creating alternative pathways to college graduation for post-traditional students are working.
…
The first paper is “Credit for Prior Learning: Charting Institutional Practice for Sustainability,” which identifies and addresses some of the cultural barriers and successful strategies to institutions incorporating CPL.
…
The second paper is “The Currency of Higher Education: Credits and Competencies,” which explores the challenges in adapting the traditional credit hour to an information-age economy that relies on greater flexibility and productivity.
————–
Harvard Business School hopes to fundamentally change online education with its new $1,500 pre-MBA program — from businessinsider.com.au by Richard Feloni
Excerpt:
This week, Harvard Business School launched an innovative new online education program to the public that it thinks is so far ahead of free online courses that it’s worthy of a $US1,500 price tag.
The 11-week pre-MBA program called CORe accepts about 500 students and is taught in the school’s signature case-study method. The first official session started on Feb. 25, and applications are open for spring and summer sessions.
CORe is the flagship offering from HBS’s new digital platform, HBX, which aims to become a full-fledged branch of the school rather than a place to dump video recordings of classroom lectures.
————–
Constructionism 3.0 — from steve-wheeler.blogspot.com
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Listening to MIT’s Vijay Kumar speaking is always informative. Kumar has vast experience in research in online and digital learning environments, and he conveys his knowledge in an accessible style. He was keen to argue that the future of education has two fundamental characteristics – open and digital. His previously published book Opening Up Education explains the first in plenty of detail, but the second, digital, was uppermost in his keynote presentation at ELI 2015, the Saudi Arabian premier e-learning event. He said that it is at the intersection of digital and open that learning innovation occurs, and that education will be transformed if attention is paid to them both.
————–
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
There are 37 million Americans like Joe who have some college but no degree. Many of them, like Joe, need to re-skill to be able to make a living. Many of them don’t have the time or money to be able to access a traditional certificate or degree program, even if it is online. In the language of disruption, they are non-consumers of traditional certificate and degree programs.
…
This emerging class of asynchronous online courses, both paid and free, is doing something similar by targeting primarily non-consumers—those not considering formal higher education (either again or for the first time). But these non-consumers are now improving their skills one competency at a time and certainly consuming education.
…
Traditional institutions of higher education are unlikely to fill this demand. Their institutions were not built to update and develop curriculum and short-term programs rapidly. Those best equipped to teach may be practitioners and real-world experts using online platforms that allow them to reach anyone instantly.
…
This is the sharing economy of education. Adults can choose the competencies they need, from pivot tables in Excel to training a new puppy, and learn them when they need them online, no longer tied to academic calendars or seminar dates.
————–
HEDLINE: Udemy’s Online Course Millionaires — from edukwest.com by Kirsten Winkler
Excerpt:
The top three Udemy instructors are currently:
Web Development – Rob Percival
Earnings: $2.8 million
Students: 120,000
Web Development – Victor Bastos
Earnings: $900,000
Students: 52,000
Personal Development – Alun Hill
Earnings: $650,000
Students: 47,000
————–
————–
LoudCloud Systems and FASTRAK: A non walled-garden approach to CBE — from mfeldstein.com by Phil Hill
Excerpt:
As competency-based education (CBE) becomes more and more important to US higher education, it would be worth exploring the learning platforms in use. While there are cases of institutions using their traditional LMS to support a CBE program, there is a new market developing specifically around learning platforms that are designed specifically for self-paced, fully-online, competency-framework based approaches.
…
…my interest here is not merely to review one company’s products, but rather to illustrate aspects of the growing CBE movement using the demo.
————–
As a whole new kind of college emerges, critics fret over standards — from hechingerreport.org by Matt Krupnick
Competency education offers credit for experience, but who decides? Critics worry whether competency-based education is growing too fast for standards to be set.
————–
Are prestigious private colleges worth the cost? — from The Wall Street Journal by Douglas Belkin
A high-school senior, a recruiting manager from Deloitte and a college professor weigh in
From DSC:
Even the very presence of this article in the Wall Street Journal should greatly concern those of us within higher education and this increasingly-common question should elicit a response at each of our institutions. It illustrates the pendulum swinging away from the strong public support of higher ed. Such support is weakening, as the price of higher ed has increased. And similar to the line in Jurassic Park, people will find a way. If they can’t afford traditional higher education, alternatives are sure to appear. Several of the aforementioned items bear witness to this fact.
————–