Michigan flags 112 low-performing schools for intensive intervention — from mlive.com by Matthew Miller
Excerpt:
“These are the urban high minority districts, right? So they were the ones that had the highest death rates, the highest case rates, the highest income and economic hits because of the pandemic,” she said. “We know that all of this goes into what we label as school quality even though it’s about so much more than the school or the district.”
The full list is here >>
From DSC:
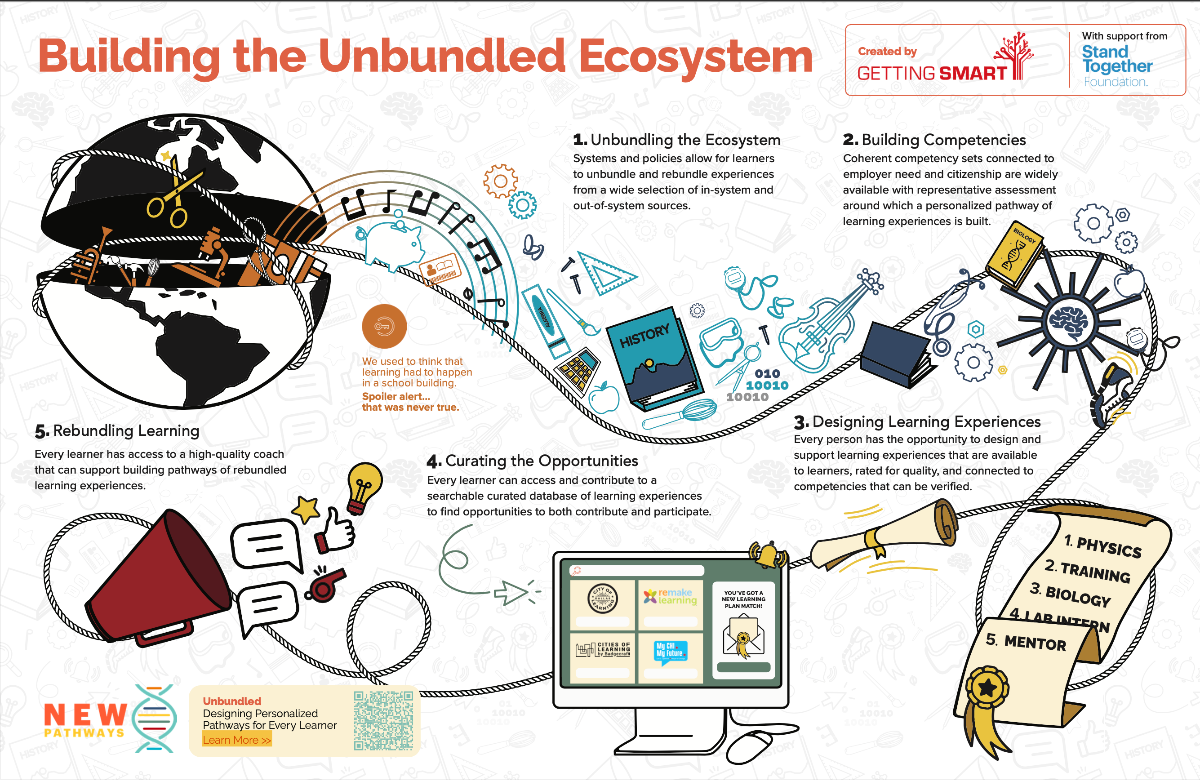
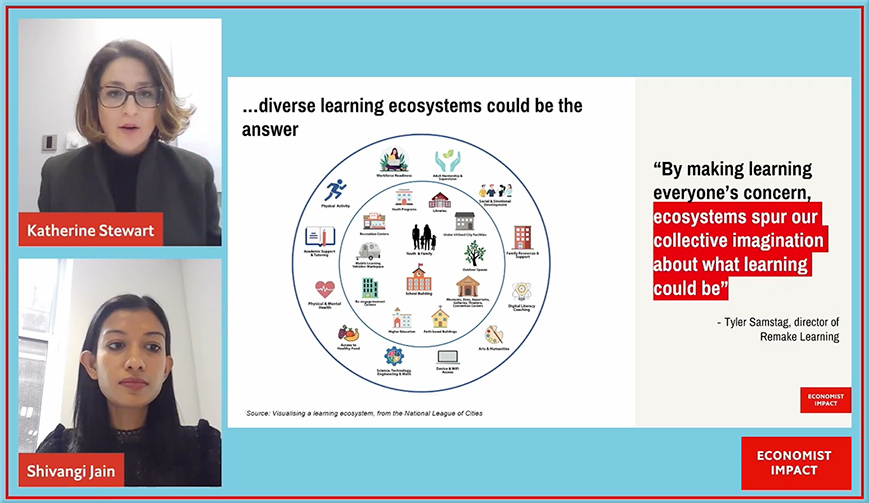
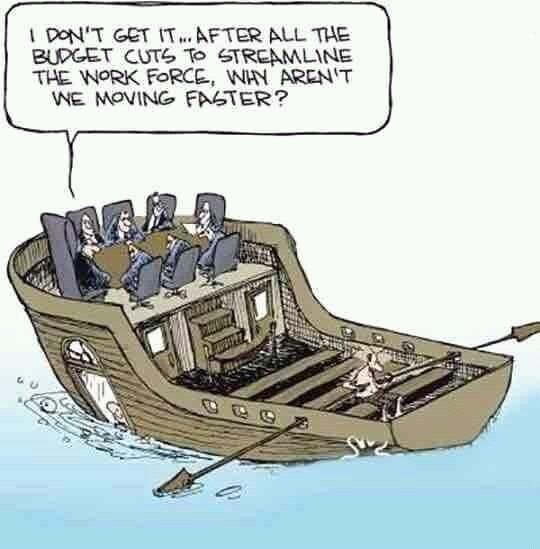
I surely hope that what’s going on in the image below isn’t what’s going on within the state of Michigan (as well as other states) — but I have my fears/concerns in that regard. Though admittedly, my focus here isn’t so much about the financial pictures, but rather it has to do with the straight-jacketing of the teachers and students by legislators in Lansing (and other state capitals). If I were to redraw this image, I would have legislators in (far-away) Lansing seated in comfortable chairs and offices while frazzled/overworked educators are straight-jacketed in the classrooms.
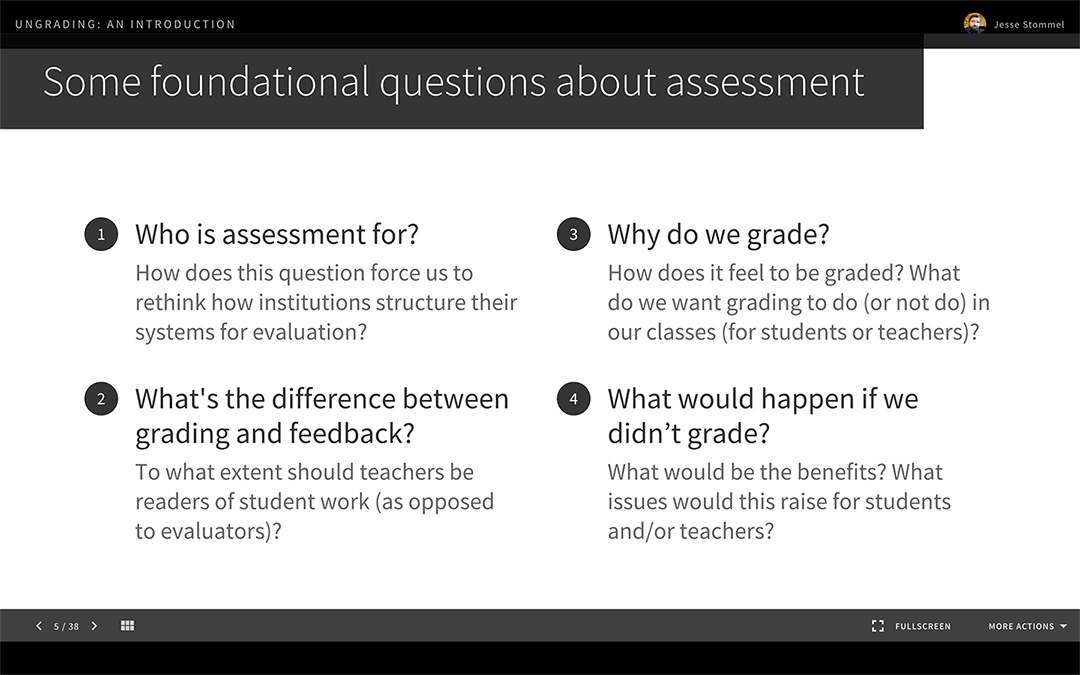
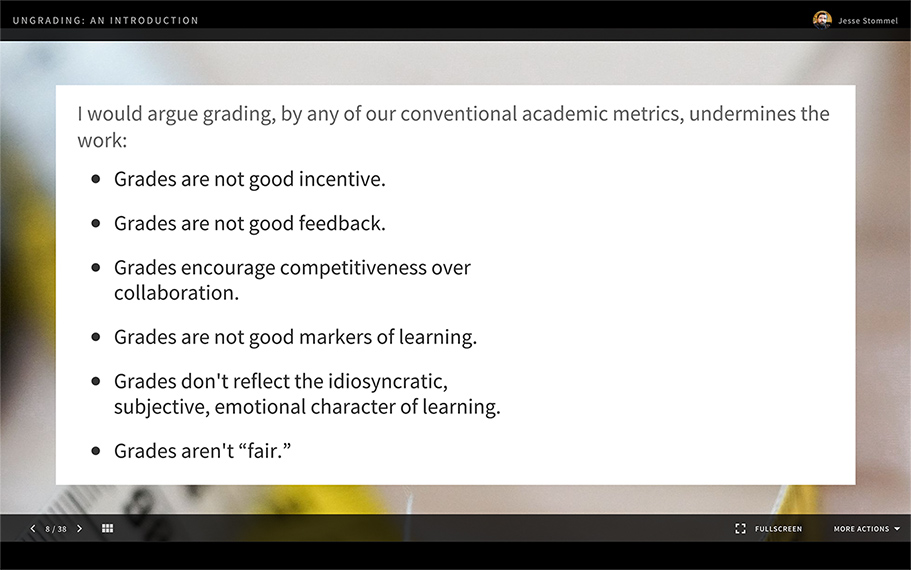
We have too many standardized tests and too many one-size-fits-all methods of “doing school” that aren’t coming from the people on the front lines. Those same people, given the right environment, could unleash a far greater amount of joy, wonder, relevance, creativity, and counsel — for themselves as well as for their students.
.

.
The ‘Digital Equity’ Students Need to Learn May Not Come Without Community Outreach — from edsurge.com by Daniel Mollenkamp
Excerpt:
And that means, more than ever, getting an education requires access to fast, reliable internet. But while the infrastructure to make sure that everyone can use the internet has improved in the last couple of years, the process isn’t complete.
If we want to keep the digital divide from growing, experts say, it’ll mean districts thinking about themselves as just one part of the larger community composed of families, nonprofits, businesses—all of them potential partners in expanding internet access for students.
.
Missing an Opportunity: Ed Dept. Criticized by GAO for Teacher Shortage Strategy — from the74million.org by Marianna McMurdock
In recent report, GAO finds key recruitment, retention challenges impacting the profession, and why current federal strategy lacks teeth to succeed
Excerpt:
The challenge of cost of entry into the profession and concerns of return on investment, the GAO report found, is also significantly straining the country’s supply of teachers. Compounding the financial reality, many candidates fear being overworked and mistreated.
“The COVID-19 pandemic laid bare teachers’ discontent with aspects of their jobs, including a lack of support for their safety and value as professionals and an increasingly disrespectful and demanding workplace culture—and exacerbated teacher shortages nationwide,” the GAO stated, pulling data from focus groups held throughout the pandemic.
Addendum on 12/10/22:
 Chimere Stephens, the director of NYC Men Teach at the NYC Department of Education, reads a book to a class of 1st grade students in January at PS 55 elementary school.
Chimere Stephens, the director of NYC Men Teach at the NYC Department of Education, reads a book to a class of 1st grade students in January at PS 55 elementary school.