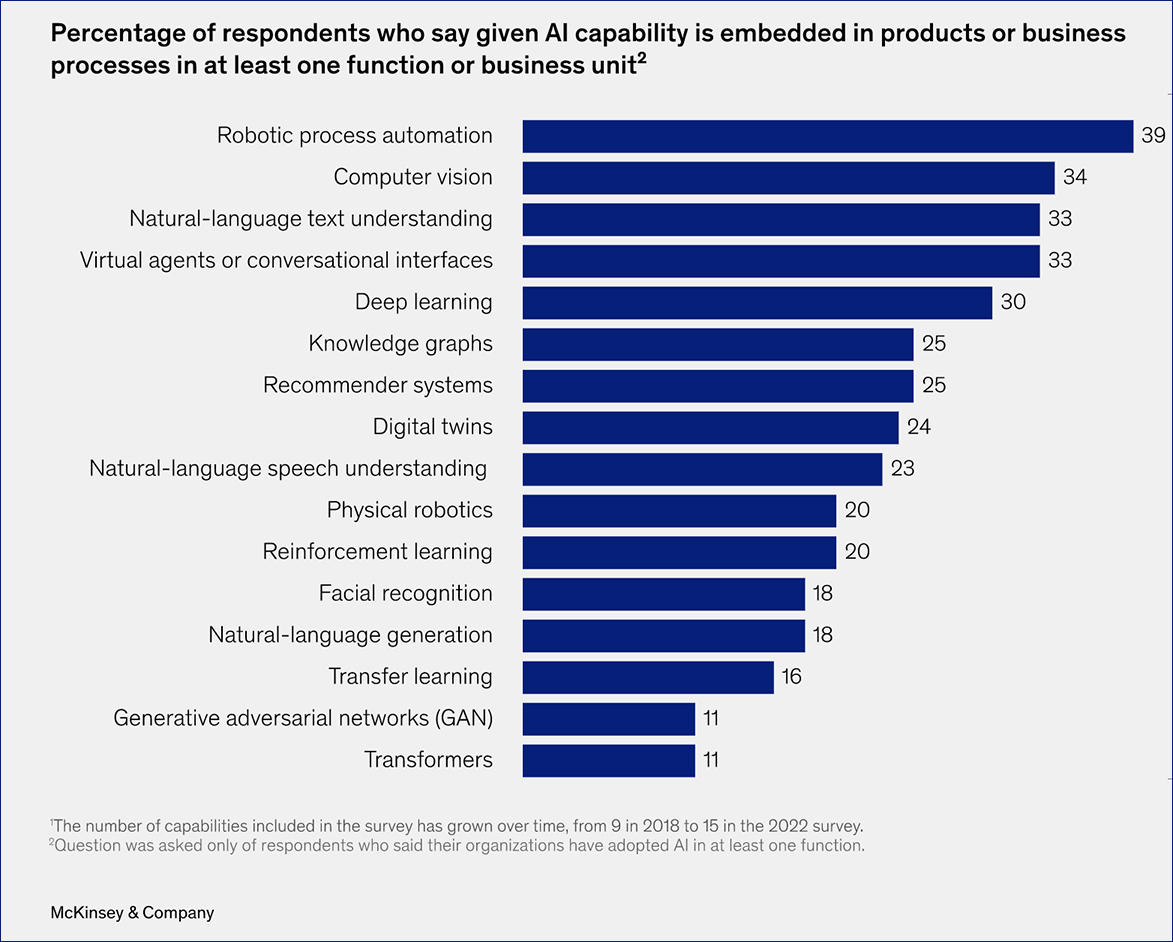
? I’m in love with this instructional routine: Slow Reveal Graphs! Start with a graph stripped of context and gradually reveal its labels, numbers, and title as students talk about what they see. Genius!
Thanks @jennalaib! (via @ericcurts)https://t.co/4WsI87EQWF
— Tony Vincent (@tonyvincent) February 9, 2023
Along the lines of tools, also see:
6 Apps and Websites to Make Video Journals — from classtechtips.com by Monica Burns
Excerpt:
Have you made video journals with your students? Earlier this year on the blog, I shared some of the reasons why this medium is worth considering. Today on the blog, we’ll look at six apps and websites to make video journals alongside a few more reasons why video journals are worth considering.
There are several reasons why a teacher might introduce video journals to their students. First, video journals can be a powerful tool for self-reflection and personal growth. By creating and reflecting on videos of themselves, students can better understand their own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and identify areas for improvement.
Video journals can also provide a creative outlet for students to express themselves. Students may enjoy experimenting with different video-editing techniques and sharing their work with their peers. This experience using video tools can transfer to additional learning experiences, especially because video journals can help students practice their communication skills in speaking and visual storytelling.
And speaking of tools and technologies, also see:
A Valentine for Education Technology — from campustechnology.com by Mary Grush and Gardner Campbell
Excerpt:
However, in making some adjustments for an online experience, I soon realized that I was able, actually, to enhance aspects of the Read-a-thon and thus the course as well. For the first time, I could choose to invite the wider Milton community to the event, encouraging people to join from many different points across the country and potentially around the globe!
I like certain kinds of management technologies that help me with record keeping and organization. But I don’t love them. I love technologies of communication because, I think, they’re at the heart of teaching and learning — creating opportunities for human beings to think together, to study something together.