From DSC:
After reading the following item from Jeremy Caplan’s most recent e-newsletter entitled, “Tiny Stuff I Love“…
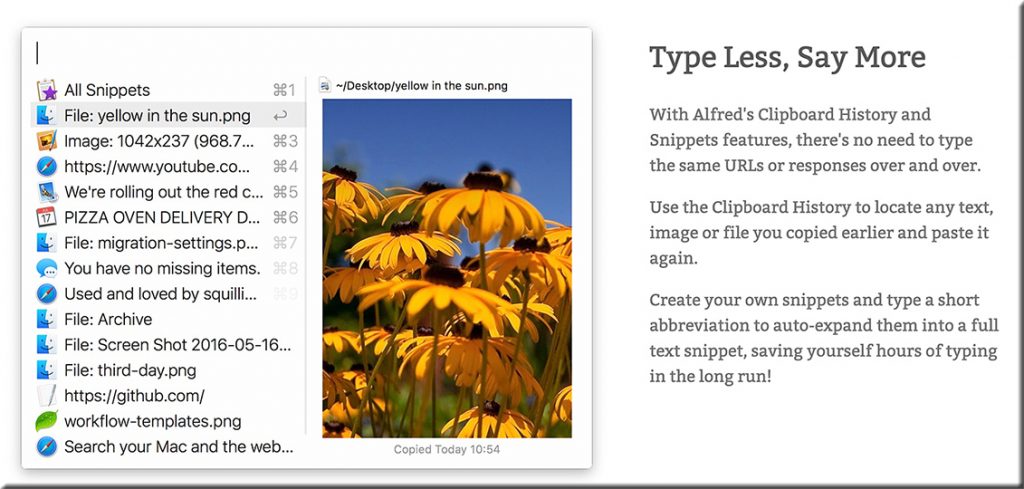
Alfred = Saves me time on copying and pasting
If you copy and paste stuff frequently, get a clipboard manager. I use Alfred throughout every workday. It keeps the last 100+ things I’ve copied in a neat list so I can paste anything I’ve used recently into a browser, document, or wherever else.
This is super-handy when I’m copying and pasting things repeatedly from one place to another. Sometimes I’m moving a bunch of stuff from a document into an email. Or putting several links or notes into a Zoom chat window.
Lots of tools do something similar. I also like the Copied App, $8 on the Mac App store. It has a companion iPhone app.
…I instantly thought of how useful this type of tool would be for teachers, professors, and perhaps trainers as well — especially when grading!
From this page (emphasis DSC):
What Does a Clipboard Manager Do?
The default clipboard in Windows works well, but it’s quite basic. The biggest limitation is that it can only hold one item at a time. If you copy a piece of text, forget to use it, then copy an image later, the text will be gone. Another hassle is that you can’t view what you’ve copied without pasting it.
For anyone who copies and pastes all the time, these are big problems. Thankfully, this is where clipboard managers come in. They greatly expand the functionality of your clipboard by remembering dozens of entries, allowing you to pin frequently used snippets for easy access, and much more.

Readers of this blog might also be interested in some of the other tools that Jeremy mentions, including:
- Toby = Save and share my browser tabs