From DSC:
I’m posting this in an effort to:
- Help students learn how to learn
- Help students achieve the greatest possible returns on their investments (both their $$ and their time) when they are trying to learn about new things
I’d like to thank Mr. William Knapp, Executive Director at GRCC for Distance Learning & Instructional Technology, for sharing this resource on Twitter.
A better way to study through self-testing and distributed practice — from kqed.org by Claudia Wallis
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
As I prepared to write this column, I relied on some pretty typical study techniques. First, as I’ve done since my student days, I generously highlighted key information in my background reading. Along the way, I took notes, many of them verbatim, which is a snap with digital copying and pasting. (Gotta love that command-C, command-V.) Then I reread my notes and highlights. Sound familiar? Students everywhere embrace these techniques and yet, as it turns out, they are not particularly good ways to absorb new material. At least not if that’s all you do.
Researchers have devoted decades to studying how to study. The research literature is frankly overwhelming. Luckily for all of us, the journal Psychological Science in the Public Interest published a review article a few years ago that remains the most comprehensive guide out there. Its 47 pages hold valuable lessons for learners of any age and any subject — especially now, with end-of-semester exams looming.
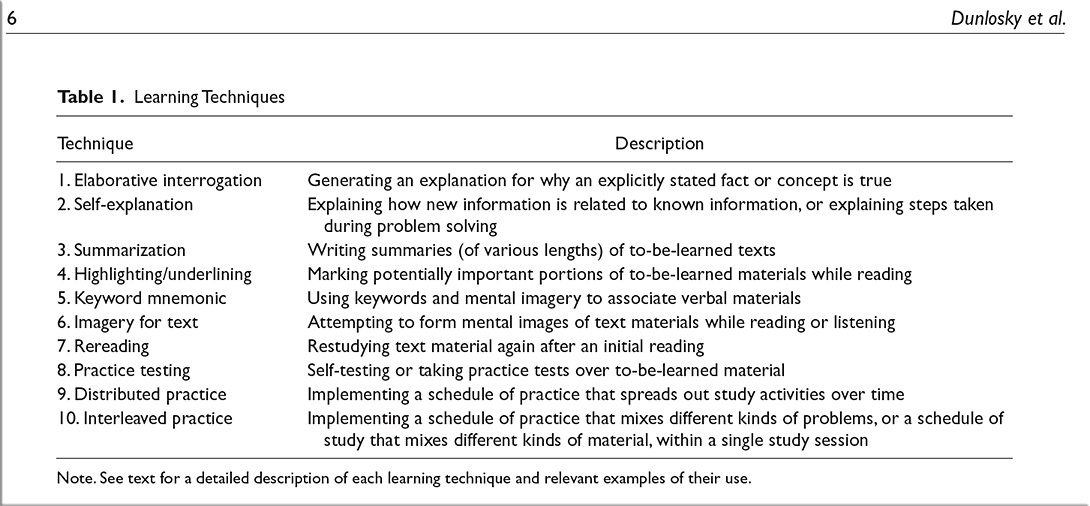
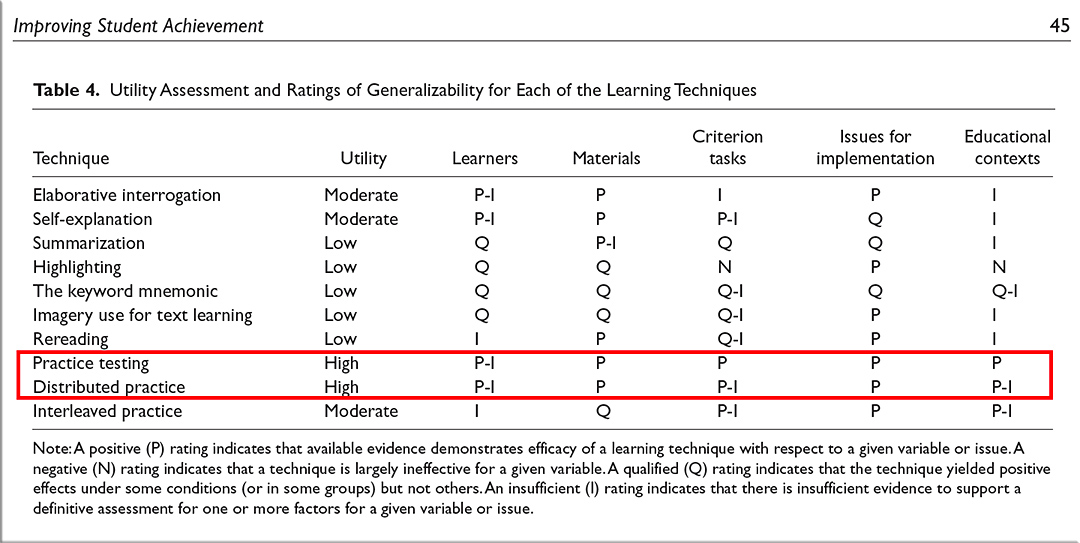
The authors examined ten different study techniques, including highlighting, rereading, taking practice tests, writing summaries, explaining the content to yourself or another person and using mnemonic devices. They drew on the results of nearly 400 prior studies. Then, in an act of boldness not often seen in academic research, they actually awarded ratings: high, low or moderate utility.
The study strategies that missed the top rating weren’t necessarily ineffective, explains the lead author John Dunlosky, a psychology professor at Kent State University, but they lacked sufficient evidence of efficacy, or were proven useful only in certain areas of study or with certain types of students. “We were trying to find strategies that have a broad impact across all domains for all students,” Dunlosky says, “so it was a pretty tough rating scale.”
In fact, only two techniques got the top rating: practice testing and “distributed practice,” which means scheduling study activities over a period of time — the opposite of cramming.
Practice testing can take many forms: flashcards, answering questions at the end of a textbook chapter, tackling review quizzes online. Research shows it works well for students from preschool through graduate and professional education.
Testing yourself works because you have to make the effort to pull information from your memory — something we don’t do when we merely review our notes or reread the textbook.
…
As for distributed practice vs. cramming, Dunlosky and his fellow authors write that “cramming is better than not studying at all,” but if you are going to devote four or five hours to studying for your biology mid-term, you would you be far better off spacing them out over a several days or weeks. “You get much more bang for your buck if you space,” Dunlosky told me.
Also see:
Improving Students’ Learning With Effective Learning Techniques — from journals.sagepub.com by John Dunlosky, Katherine A. Rawson, Elizabeth J. Marsh, Mitchell J. Nathan, and Daniel T. Willingham
Promising Directions From Cognitive and Educational Psychology
Excerpt:
In this monograph, we discuss 10 learning techniques in detail and offer recommendations about their relative utility. We selected techniques that were expected to be relatively easy to use and hence could be adopted by many students. Also, some techniques (e.g., highlighting and rereading) were selected because students report relying heavily on them, which makes it especially important to examine how well they work. The techniques include elaborative interrogation, self-explanation, summarization, highlighting (or underlining), the keyword mnemonic, imagery use for text learning, rereading, practice testing, distributed practice, and interleaved practice.
In fact, only two techniques got the top rating: practice testing and “distributed practice,” which means scheduling study activities over a period of time — the opposite of cramming.
From DSC:
This is yet another reason that I like the approach of using streams of content to help people learn something new. Because you can implement distributed practice, encourage recall, etc. when you put the content out there at regular intervals.











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)