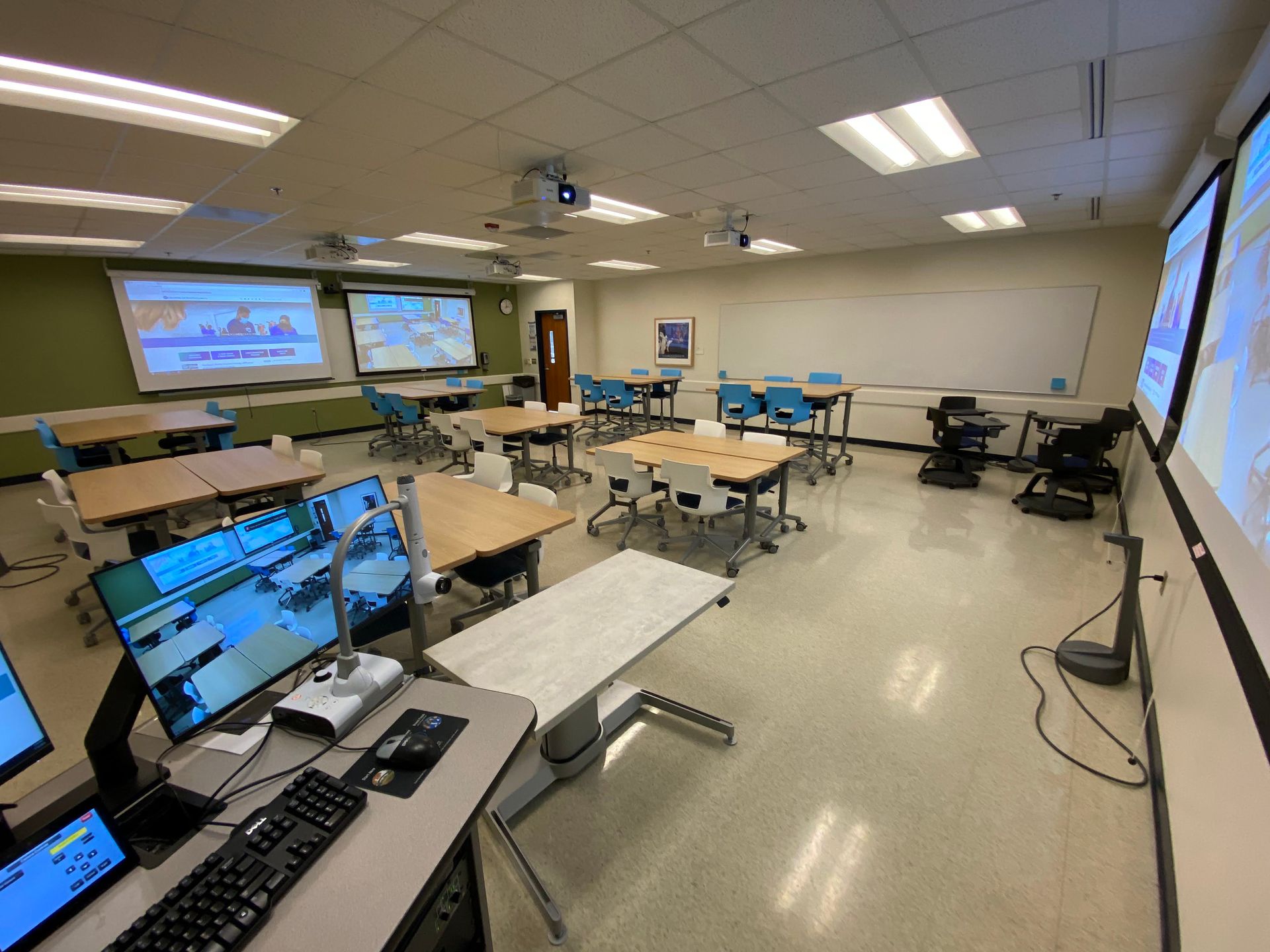
A New Generation Of Mastery-Based Learning Platforms Has Arrived — from joshbersin.com by Josh Bersin
Excerpt:
The $330 billion corporate training market is enormous, fragmented, and complex. For years it was dominated by Learning Management Systems (LMS) and content providers, each pioneered in the early 2000s. These systems served well, but the needs of employees and organizations moved ahead.
Today companies want not only a place to find and administer learning, they want a “Learning Platform” that creates mastery. And this market, that of “Learning Delivery Platforms,” is far more complex than you think. Let me put it straight: video-based chapter by chapter courses don’t teach you much. Companies want a solution that is expert-led, engaging, includes assignments and coaching, and connects employees to experts and peers.
Well there’s a new breed of platforms focused in this area, and I call them Capability Academy systems.
These are platforms explicitly to bring together expert teachers, AI-enabled collaboration, assignments, and coaching to drive mastery. They can train thousands of people in small cohorts, offering hands-on support for technical or PowerSkills topics. And the results are striking: these vendors achieve 90% completion rates and netPromoter scores above 60 (far above traditional content libraries).
6 Ed Tech Tools to Try in 2023 — from cultofpedagogy.com by Jennifer Gonzalez
Excerpt:
The guide is packed with tools that can meet so many of your needs as a teacher, and many of them are already well established and widely used. But every January, we like to choose six that we think deserve a little extra attention. Most are not actually brand-new to the world, but each one has something special about it. So here we go!
6 Google Scholar Tips From Its Co-Creator — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
Google Scholar can be a great tool for teachers and their students. Here’s how to get the most out of it.
Excerpt:
Anurag Acharya co-created Google Scholar in 2004. The Google engineer and former professor of computer science at the University of California at Santa Barbara was inspired to create the free search tool after being frustrated by being unable to access research articles as a student at the Kharagpur campus of the Indian Institute of Technology.
Today, Acharya is head of Google Scholar and an authority on how the scholarly search engine can best be used by teachers and their students. He offers these tips and best practices for teachers to use and share with their students.
Instructional Designer: Tools of the Trade Webinar 3/8 (from Teaching: A Path to L&D) and tools of the trade
Teaching: A Path to L&D aims to provide free guidance to teachers looking to move into the world of Learning and Development, specifically Instructional Design. Check out our website at www.teachlearndev.org for free coaching, webinars, and resources to help you on your journey!