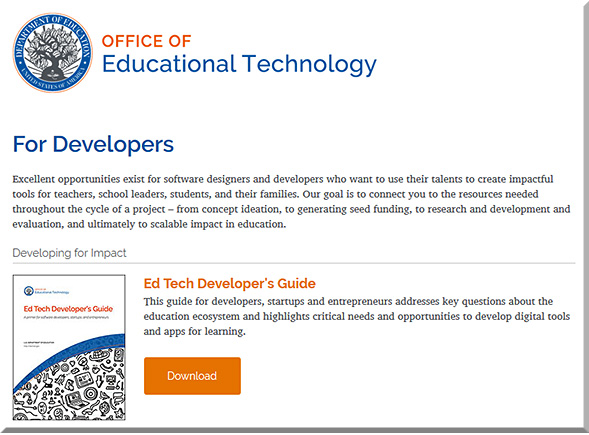
Ten Trends in Data Science 2015 — from linkedin.com by Kurt Cagle
Excerpt:
Data Science Teams
I see the emergence within organizations of data science teams. Typically, such teams will be made up of a number of different specialties:
- Integrator. A programmer or DBA that specializes in data ingestion and ETL from multiple different sources. Their domain will tend to be services and databases, and as databases become data application platforms, their role primarily shifts from being responsible for schemas to being responsible for building APIs. Primary focus: Data Acquisition
- Data Translation Specialist. This will typically be a person focused on Hadoop, Map/Reduce and similar intermediate processing necessary to take raw data and clean it, transform it, and simplify it. They will work with both integrators and ontologists, Primary Focus: Data Acquiisition
- Ontologist. The ontologist is a data architect specializing in building canonical models, working with different models, and establishing relationships between data sets. They will often have semantics or UML backgrounds. Primary focus: Data Awareness.
- Curators. These people are responsible for the long term management, sourcing and provenance of data. This role is often held by librarians or archivists. They will often work closely with the ontologists. Primary Focus: Data Awareness.
- Stochastic Analyst (Data Scientist?). This role is becoming a specialist one, in which people versed with increasingly sophisticated stochastic and semantic analysis tools take the contextual data and extraction trends, patterns and anti-patterns from this. They usually have a strong mathematical or statistical background, and will typically work with domain experts. Primary Focus: Data Analysis
- Domain Expert. Typically these are analysts who know their particular domain, but aren’t necessarily expert on informatics. These may be financial specialists, business analysts, researchers, and so forth, depending upon the specific enterprise focus. Primary Focus: Data Analysis
- Visualizers. These are typically going to be web interface developers with skills in areas such as SVG or Canvas and the suites of visualization tools that are emerging in this area. Their role is typically to take the data at hand and turn it into usable, meaningful information. They will work closely with both domain experts and stochastic analysts, as well as with the ontologist to better coerce the information coming from the data systems into meaningful patterns. Primary Focus:Data Analysis
- Data Science Manager. This person is responsible for managing the team, understanding all of the domains reasonably well enough to interface with the client, and coordinating efforts. This person also is frequently the point person for establishing governance. Primary Focus: All.
Infographic: What’s Hot in Data Science in 2015 — from data-informed.com; with thanks to Michael Caveretta’s tweet on this
Michigan State Wants a Big Data Professor on Campus — from edtechmagazine.com by D. Frank Smith; back from Nov 2014
Explosive growth in the data science field is pushing higher education to extend its analytics expertise.
Excerpt:
There is a torrent of information flooding today’s higher education institutions. Michigan State University is hoping to find Big Data experts to turn it into results.
Putting Big Data to use in an educational setting takes a special set of skills. MSU’s College of Communication Arts and Sciences recently held a search for an assistant professor of Big Data and health, a position that will lead courses on data analytics and IT in the Department of Media and Information.
“We seek a scholar conducting cutting-edge social and/or technical research utilizing big data approaches — including theory-building, analytics, applications, and effects,” according to MSU’s job listing, which has expired, but is still available on LinkedIn.
Is Data Science a buzzword? Modern Data Scientist defined — from marketingdistillery.com by Krzysztof Zawadzki
.
From DSC: Those working in higher ed – take note of this 12 week bootcamp:
.
..  .
.
.
Should Big Data Skills Be Taught in K–12 Classrooms? — from by D. Frank Smith
A new report recommends that schools begin preparing students to think like data scientists at an earlier age.
Excerpt:
The skills necessary for the data analytics jobs of tomorrow aren’t being taught in K–12 schools today, according to a new report released by the Education Development Center, Inc.’s (EDC) Oceans of Data Institute. The Profile of the Big-Data Enabled Specialist projects a workforce shortage for data-driven positions. Based on a 2011 McKinsey & Co. report cited by the Oceans of Data Institute, ”By 2018, the United States alone could face a shortage of 140,000 to 190,000 people with deep analytical skills as well as 1.5 million managers and analysts with the know-how to use the analysis of big data to make effective decisions.”
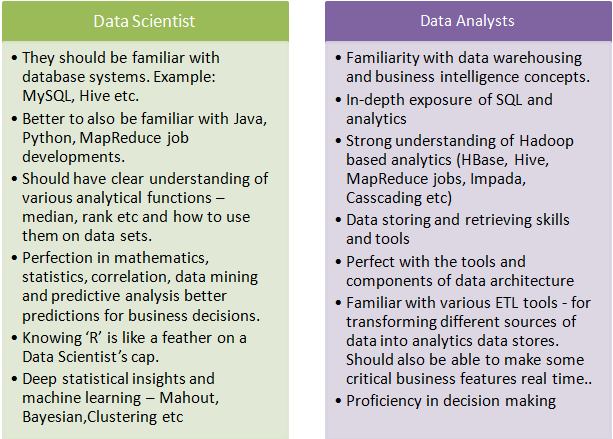
Difference between Data Scientist and Data Analyst — from edureka.co; again, with thanks to Michael Caveretta’s tweet on this
Excerpt: .
. 
.
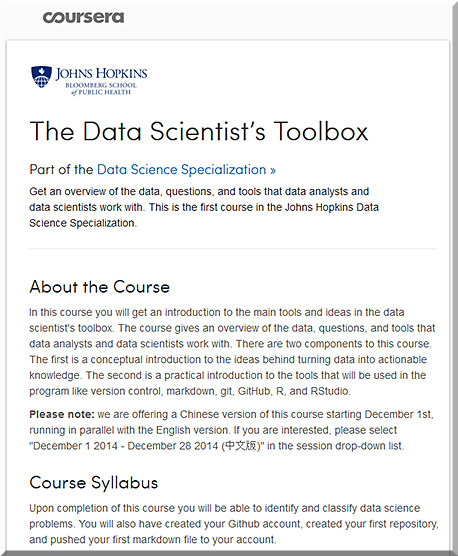
The Data Scientist’s Toolbox — course from coursera.org
The 25 Hottest Skills That Got People Hired in 2014 — from linkedin.com
Excerpts:
- Statistical analysis and data mining
- Business intelligence
- Data engineering and data warehousing
16 analytic disciplines compared to data science — from datasciencecentral.com by Vincent Granville
Excerpt:
What are the differences between data science, data mining, machine learning, statistics, operations research, and so on?
Here I compare several analytic disciplines that overlap, to explain the differences and common denominators. Sometimes differences exist for nothing else other than historical reasons. Sometimes the differences are real and subtle. I also provide typical job titles, types of analyses, and industries traditionally attached to each discipline. Underlined domains are main sub-domains. It would be great if someone can add an historical perspective to my article.
Tech 2015: Deep Learning And Machine Intelligence Will Eat The World — from forbes.com by Anthony Wing Kosner; with thanks to Pedro for his tweet on this
Excerpt:
Despite what Stephen Hawking or Elon Musk say, hostile Artificial Intelligence is not going to destroy the world anytime soon. What is certain to happen, however, is the continued ascent of the practical applications of AI, namely deep learning and machine intelligence. The word is spreading in all corners of the tech industry that the biggest part of big data, the unstructured part, possesses learnable patterns that we now have the computing power and algorithmic leverage to discern—and in short order.
The effects of this technology will change the economics of virtually every industry.
The rise of machines that learn — from infoworld.com by Eric Knorr; with thanks to Oliver Hansen for his tweet on this
A new big data analytics startup, Adatao, reminds us that we’re just at the beginning of a new phase of computing when systems become much, much smarter

Data Science Dojo — @DataScienceDojo
Stanford startup focused on all things data science.
The 2 Types Of Data Scientists Everyone Should Know About — from datasciencecentroal.com by Bernard Marr
Excerpt:
It depends entirely on how broadly you categorize them. In reality, of course – there are as many “types” of data scientist as there are people working in data science. I’ve worked with a lot, and have yet to meet two who are identical.
But what I have done here is separate data scientists into groups, containing individuals who share similar skills, methods, outlooks and responsibilities. Then I grouped those groups together, again and again, until I was left with just two quite distinctly different groups.
I’ve decided to call these two types strategic data scientists and operational data scientists.
Deep learning Reading List — from jmozah.github.io