If equity is a priority, UDL is a must — from cultofpedagogy.com by Katie Novak
Once you identify the firm goal, ask yourself, “Based on the variability in my class, what barriers may prevent learners from working toward that goal and how can I eliminate those barriers through design?”
Excerpt:
When we design the same learning pathways for all learners, we might tell ourselves we are being fair, but in fact, single pathways are exclusionary. Beverly Daniel Tatum, author of the critically acclaimed book, Why Are All The Black Kids Sitting Together in the Cafeteria? And Other Conversations About Race, challenges us to focus on impact over intentions. It may not be our intent to exclude our learners, but the reality is that many students do not have opportunities to learn at high levels or to access curriculum and instruction that is accessible, engaging, culturally sustaining, and linguistically appropriate.
Luckily, there is a framework that rejects these one-size-fits-all solutions and empowers educators to proactively design learning experiences so all students can increase their brainpower and accelerate and own their learning. The framework is Universal Design for Learning (UDL).
UDL is a framework for designing learning experiences so students have options for how they learn, what materials they use, and how they demonstrate their learning.
From DSC:
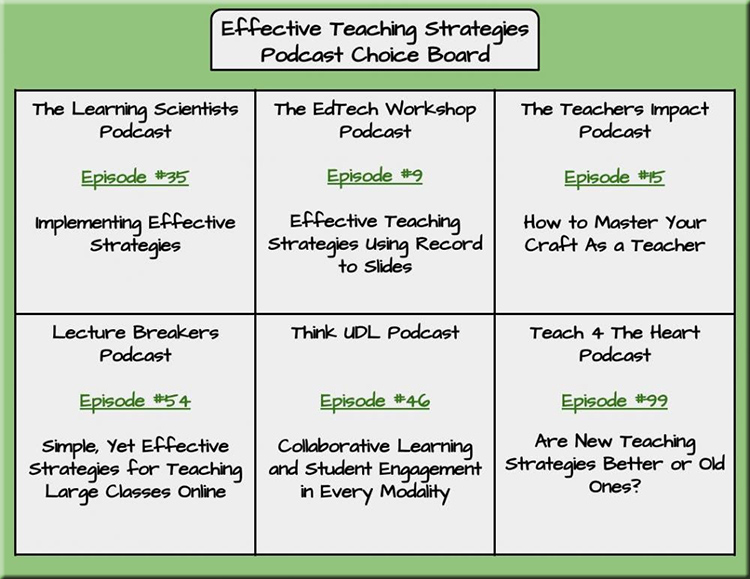
I put together this graphic as I’m working on a Module (for Canvas) to address the topic of accessibility: