Alexa, Tell Me Where You’re Going Next — from backchannel.com by Steven Levy
Amazon’s VP of Alexa talks about machine learning, chatbots, and whether industry is strip-mining AI talent from academia.
Excerpt:
Today Prasad is giving an Alexa “State of the Union” address at the Amazon Web Services conference in Las Vegas, announcing an improved version of the Alexa Skills Kit, which helps developers create the equivalent of apps for the platform; a beefed-up Alexa Voice Service, which will make it easier to transform third-party devices like refrigerators and cars into Alexa bots; a partnership with Intel; and the Alexa Accelerator that, with the startup incubator Techstars, will run a 13-week program to help newcomers build Alexa skills. Prasad and Amazon haven’t revealed sales numbers, but industry experts have estimated that Amazon has sold over five million Echo devices so far.
Prasad, who joined Amazon in 2013, spent some time with Backchannel before his talk today to illuminate the direction of Alexa and discuss how he’s recruiting for Jeff Bezos’s arsenal without drying up the AI pipeline.
What DeepMind brings to Alphabet — from economist.com
The AI firm’s main value to Alphabet is as a new kind of algorithm factory
Excerpt:
DeepMind’s horizons stretch far beyond talent capture and public attention, however. Demis Hassabis, its CEO and one of its co-founders, describes the company as a new kind of research organisation, combining the long-term outlook of academia with “the energy and focus of a technology startup”—to say nothing of Alphabet’s cash.
…
Were he to succeed in creating a general-purpose AI, that would obviously be enormously valuable to Alphabet. It would in effect give the firm a digital employee that could be copied over and over again in service of multiple problems. Yet DeepMind’s research agenda is not—or not yet—the same thing as a business model. And its time frames are extremely long.
Artificial Intelligence: Silicon Valley’s Next Frontier — from toptechnews.com by Ethan Baron
Excerpt:
Silicon Valley needs its next big thing, a focus for the concentrated brain power and innovation infrastructure that have made this region the world leader in transformative technology. Just as the valley’s mobile era is peaking, the next frontier of growth and innovation has arrived: It’s Siri in an Apple iPhone, Alexa in an Amazon Echo, the software brain in Google’s self-driving cars, Amazon’s product recommendations and, someday, maybe the robot surgeon that saves your life.
It’s artificial intelligence, software that can “learn” and “think,” the latest revolution in tech.
“It’s going to be embedded in everything,” said startup guru Steve Blank, an adjunct professor at Stanford. “We’ve been talking about artificial intelligence for 30 years, maybe longer, in Silicon Valley. It’s only in the last five years, or maybe even the last two years, that this stuff has become useful.”
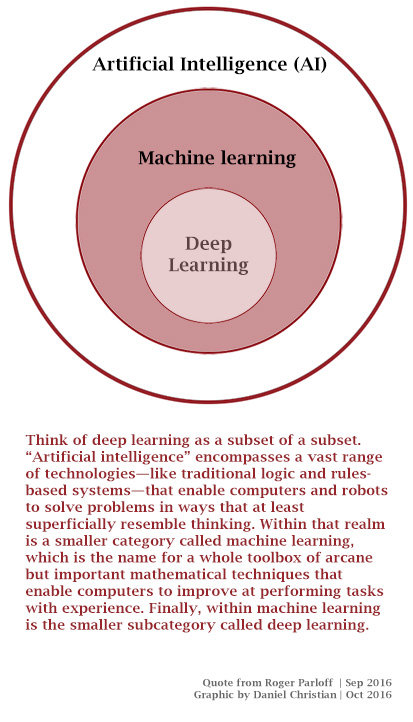
What Is The Difference Between Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning? — from forbes.com by Bernard Marr
Excerpt:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two very hot buzzwords right now, and often seem to be used interchangeably. They are not quite the same thing, but the perception that they are can sometimes lead to some confusion. So I thought it would be worth writing a piece to explain the difference.
…
In short, the best answer is that:
Artificial Intelligence is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider “smart”.
And,
Machine Learning is a current application of AI based around the idea that we should really just be able to give machines access to data and let them learn for themselves.
Why we are still light years away from full artificial intelligence — from techcrunch.com by Clara Lu
Excerpt:
Yet, the truth is, we are far from achieving true AI — something that is as reactive, dynamic, self-improving and powerful as human intelligence.
…
Full AI, or superintelligence, should possess the full range of human cognitive abilities. This includes self-awareness, sentience and consciousness, as these are all features of human cognition.
Udacity adds 14 hiring partners as AI, VR and self-driving talent wars heat up — from techcrunch.com by Darrell Etherington
Excerpt:
Udacity is positioned perfectly to benefit from the rush on talent in a number of growing areas of interest among tech companies and startups. The online education platform has added 14 new hiring partners across its Artificial Intelligence Engineer, Self-Driving Car Engineer and Virtual Reality Developer Nanodegree programs, as well as in its Predictive Analytics Nanodegree, including standouts like Bosch, Harma, Slack, Intel, Amazon Alexa and Samsung.
That brings the total number of hiring partners for Udacity to over 30, which means a lot of potential soft landings for graduates of its nanodegree programs. The nanodegree offered by Udacity is its own original form of accreditation, which is based on a truncated field of study that spans months, rather than years, and allows students to direct the pace of their own learning. It also all takes place online, so students can potentially learn from anywhere.
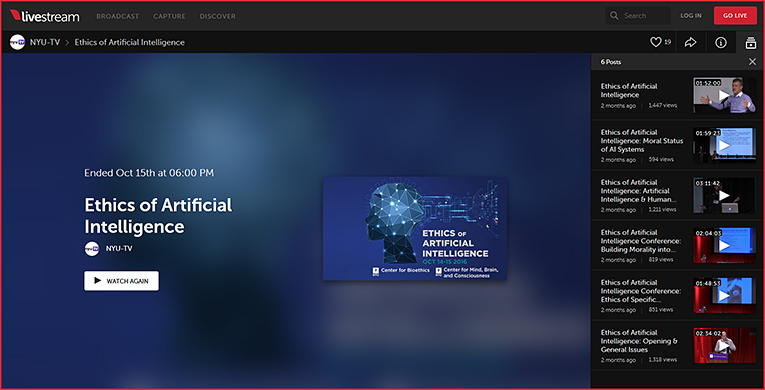
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence – from livestream.com
The Great A.I. Awakening — from nytimes.com by Gideo Lewis-Kraus
How Google used artificial intelligence to transform Google Translate, one of its more popular services — and how machine learning is poised to reinvent computing itself.
Excerpt:
Google’s decision to reorganize itself around A.I. was the first major manifestation of what has become an industrywide machine-learning delirium. Over the past four years, six companies in particular — Google, Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Microsoft and the Chinese firm Baidu — have touched off an arms race for A.I. talent, particularly within universities. Corporate promises of resources and freedom have thinned out top academic departments. It has become widely known in Silicon Valley that Mark Zuckerberg, chief executive of Facebook, personally oversees, with phone calls and video-chat blandishments, his company’s overtures to the most desirable graduate students. Starting salaries of seven figures are not unheard-of. Attendance at the field’s most important academic conference has nearly quadrupled. What is at stake is not just one more piecemeal innovation but control over what very well could represent an entirely new computational platform: pervasive, ambient artificial intelligence.
Microsoft bets on AI — from businessinsider.com
Excerpt:
On [December 12th, 2016], Microsoft announced a new Microsoft Ventures fund dedicated to artificial intelligence (AI) investments, according to TechCrunch. The fund, part of the company’s investment arm that launched in May, will back startups developing AI technology and includes Element AI, a Montreal-based incubator that helps other companies embrace AI. The fund further supports Microsoft’s focus on AI. The company has been steadily announcing major initiatives in support of the technology. For example, in September, it announced a major restructuring and formed a new group dedicated to AI products. And in mid-November, it partnered with OpenAI, an AI research nonprofit backed by Elon Musk, to further its AI research and development efforts.
The Growth of Artificial Intelligence in E-commerce — from redstagfulfillment.com by Jake Rheude
Excerpt:
Whether Artificial Intelligence (AI) is something you’ve just come across or it’s something you’ve been monitoring for a while, there’s no denying that it’s starting to influence many industries. And one place that it’s really starting to change things is e-commerce. Below you’ll find some interesting stats and facts about how AI is growing in e-commerce and how it’s changing the way we do things. From personalizing the shopping experience for customers to creating personal buying assistants, AI is something retailers can’t ignore. We’ll also take a look at some examples of how leading online stores have used AI to enrich the customer buying experience.
Will AI built by a ‘sea of dudes’ understand women? AI’s inclusivity problem — from digitaltrends.com by Dyllan Furness
Excerpt:
Only 26 percent of computer professionals were women in 2013, according to a recent review by the American Association of University Women. That figure has dropped 9 percent since 1990.
Explanations abound. Some say the industry is masculine by design. Others claim computer culture is unwelcoming — even hostile — to women. So, while STEM fields like biology, chemistry, and engineering see an increase in diversity, computing does not. Regardless, it’s a serious problem.
Artificial intelligence is still in its infancy, but it’s poised to become the most disruptive technology since the Internet. AI will be everywhere — in your phone, in your fridge, in your Ford. Intelligent algorithms already track your online activity, find your face in Facebook photos, and help you with your finances. Within the next few decades they’ll completely control your car and monitor your heart health. An AI may one day even be your favorite artist.
The programs written today will inform the systems built tomorrow. And if designers all have one worldview, we can expect equally narrow-minded machines.






















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)