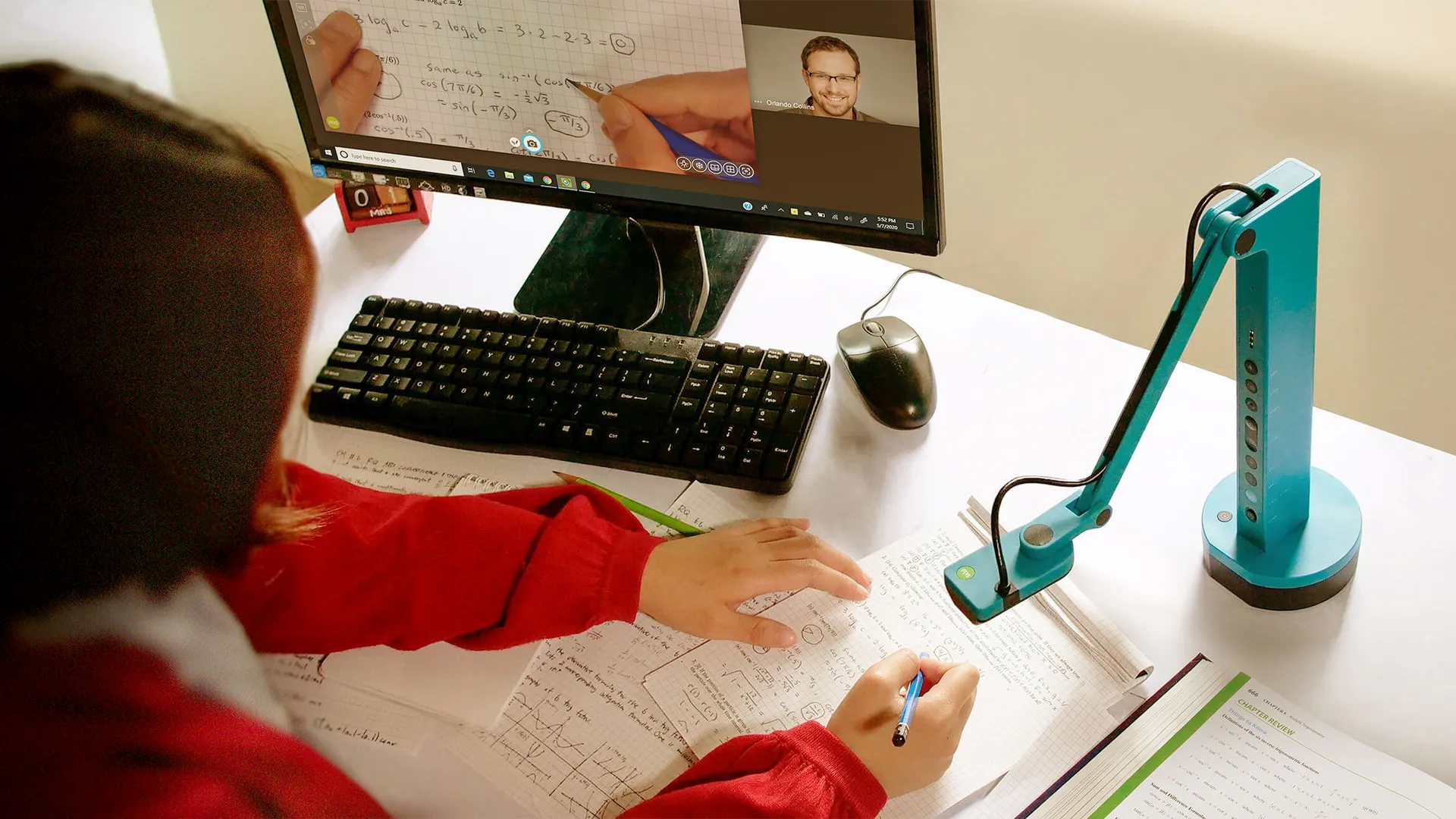
Teaching in an Age of ‘Militant Apathy’ — from chronicle.com by Beth McMurtrie
Immersive education offers a way to reach students. But can it ever become the norm?
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
But as many students continue to exhibit debilitating levels of anxiety, hopelessness, and disconnection — what one professor termed “militant apathy” — colleges are struggling to come up with a response beyond short-term solutions. The standard curricula in higher ed — and the way it’s discussed as primarily a path to economic success — can exacerbate those feelings. Students are told the main point of college is to move up the economic ladder, so no wonder it feels transactional. And the threat of failure must seem paralyzing given the high cost of a degree.
…
Colleges try to counter that by telling students that critical-thinking and communication skills are important as well. “But that’s a pretty vague argument that isn’t obvious for students to internalize and motivate their behavior. So what you see then is widespread disengagement from the curriculum,” says Arum. “For educators like me, what’s missing is what education is about. It’s about psychological well-being and flourishing and growth and human development and encouraging a set of dispositions, attitudes and behaviors that lead to fulfilling lives.”
“In every context, the student needs to feel like they are driving, they are the ones managing their own learning,” says Immordino-Yang. Instead, students have come to expect “‘you tell me what to do and I’ll do it,’” she says. “We need to take that away. That is a crutch. That is not real learning. That is compliance.”
From DSC:
The liberal arts are so important. But at what cost? What are people willing to pay for a more rounded education? The market is speaking — and the liberal arts are dying. I think that less expensive forms of online-based learning may turn out to be the best chance of the liberal arts surviving in the 21st century. The price must come waaaay down.
And speaking of the cost of getting a degree, this item is relevant as well:
Colleges Fear Cost of Doing Business Will Become Much Costlier — from chronicle.com by Lee Gardner
Inflation, enrollment woes, and increasing intolerance of tuition increases have made this budget season especially difficult.
Excerpts:
In decades past, colleges might have mitigated precarious budgets by raising tuition, but that’s a hard row to hoe in 2023.
…
The public colleges most feeling the financial squeeze from lowered enrollments are regional universities and community colleges, which typically receive less state support per student than public flagship universities.
…
Inflation remains high, at around 6 percent, and the biggest worry that it presents for college leaders comes from upward pressure on wages, says Staisloff.
While the sky may not be falling for higher education, Staisloff says “the cloud ceiling keeps dropping and dropping and dropping and dropping, and that’s getting harder to ignore.”
Speaking of the cost of getting a degree as well as higher education’s need to reinvent itself, also see:
College Doesn’t Need to Take Four Years — an opinion piece from the Wall Street Journal by Scott L. Wyatt and Allen C. Guelzo
For many students, the standard bachelor’s degree program has become a costly straitjacket.