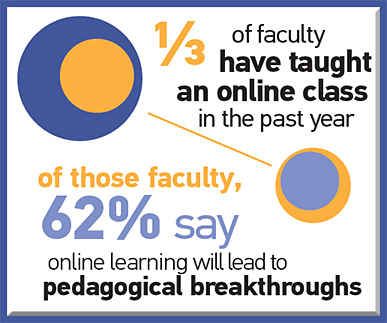
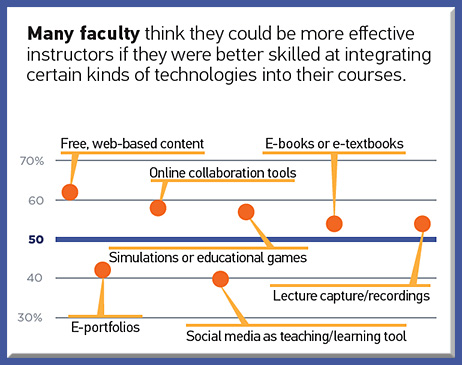
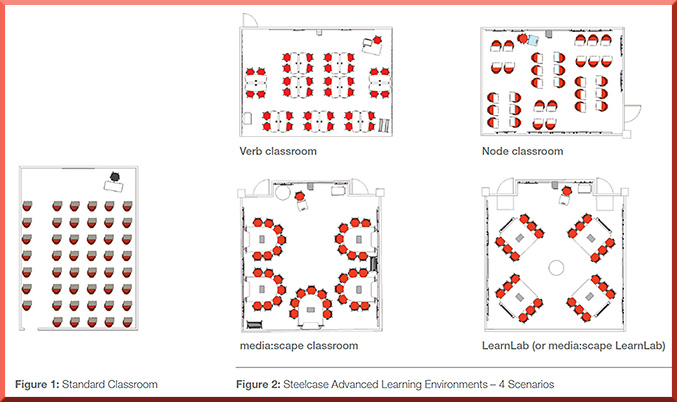
Last week I attended the 20th Annual Online Learning Consortium International Conference. While there, I was inspired by an excellent presentation entitled, “A Disruptive Innovation: MSU’s Surviving the Coming Zombie Apocalypse – Are You Ready to Survive a New Way of Learning?“ The four team members from Michigan State University included:
- Glenn R. Stutzky | Course Instructor
- Keesa V. Muhammad | Instructional Designer
- Christopher Irvin | Instructional Designer
- Hailey Mooney | Course Librarian
Check out the intro clip on the website about the course:
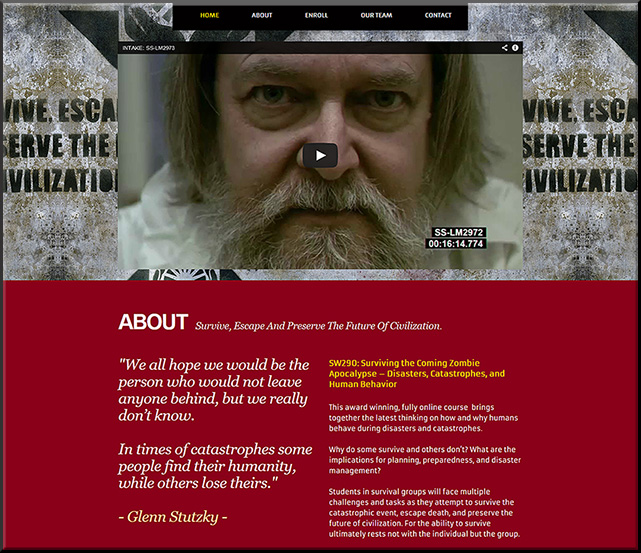
From the description for the presentation:
This session highlights MSU’s award winning, groundbreaking online course that fuses social theory, filmmaking, social media, and viral marketing while students survive an apocalyptic event. http://zombie.msu.edu/
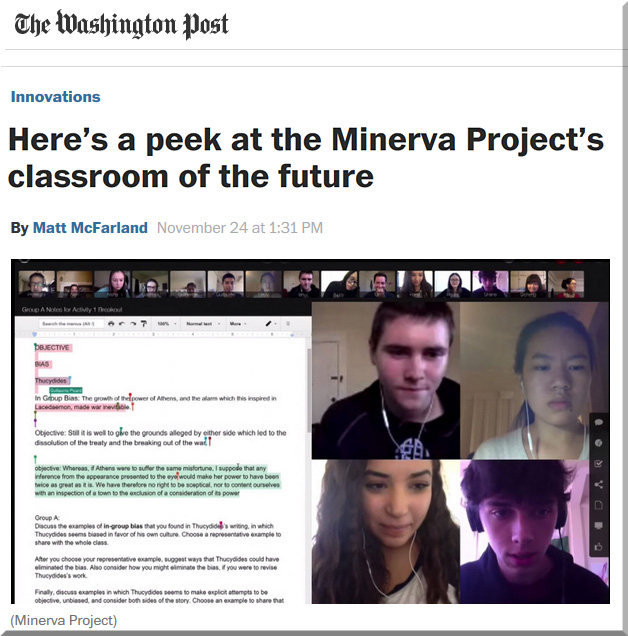
MSU created and used powerful digital storytelling and multimedia to overlay real, experiential, immersive learning. Important content was relayed, but in a way that drew upon your emotions, your ability to solve problems and navigate in a world where you didn’t have all of the information, your ability to work with others, and more.
“This innovative course integrates current research and science on catastrophes and human behavior together with the idea of a zombie apocalypse. In doing so, we actively engage with students as they think about the nature, scope, and impact of catastrophic events on individuals, families, societies, civilizations, and the Earth itself.”
“Our innovative approach to teaching and learning features: students as active participants, the instructor becomes the facilitator, storytelling replaces lectures, zombies become the catalyst of teaching, a “zombrarian” (librarian) drives research, and the students emerge as digital storytellers as a way of assessing their own learning.”
Others outside MUS have found out about the course and have requested access to it. As a result of this, they’ve opened it up to non-credit seeking participants and now various people from police forces, Centers for Disease Control, and others are able to take the course. To make this learning experience even more accessible, the cost has been greatly reduced: from $1600+ to just $500. (So this talented team is not only offering powerful pedagogies, but also significant monetary contributions to the university as well.)
For me, the key thing here is that this course represents what I believe is the direction that’s starting to really pull ahead of the pack and, if done well, will likely crush most of the other directions/approaches. And that is the use of teams to create, deliver, teach, and assess content – i.e., team-based learning approaches.
So many of the sessions involved professional development for professors and teachers – and much of this is appropriate. However, in the majority of cases, individual efforts aren’t enough anymore. Few people can bring to the table what a talented, experienced group of specialists are able to bring. Individual efforts aren’t able to compete with team-based content creation and delivery anymore — and this is especially true online, whereby multiple disciplines are immediately invoked once content hits the digital realm.
In this case, the team was composed of:
- The professor
- Two Instructional Designers
- and a librarian
The team:
- Developed websites
- Designed their own logo
- Marketed the course w/ a zombie walking around campus w/ brochures and a walking billboard
- Used a Twitter stream
- Used a tool called Pensu for their students’ individual journals
- Made extensive use of YouTube and digital storytelling
- Coined a new acronym called MOLIE – multimedia online learning immersive experience
- Used game-like features, such as the development of a code that was found which revealed key information (which was optional, but was very helpful to those who figured it out). The team made it so that the course ended differently for each group, depending upon what the teams’ decisions were through the weeks
- Used some 3D apps to make movies more realistic and to create new environments
- Continually presented new clues for students to investigate. Each team had a Team Leader that posted their team’s decisions on YouTube.
They encouraged us to:
THINK BIG! Get as creative as you can, and only pull back if the “suits” make you! Step outside the box! Take risks! “If an idea has life, water it. Others will check it out and get involved.”
In their case, the idea originated with an innovative, risk-taking professor willing to experiment – and who started the presentation with the following soliloquy:
Syllabi are EVIL
Syllabi are EVIL and they must die!
Listen to me closely and I’ll tell you why.
Just want students to know what is known?
See what’s been seen?
Go – where we’ve been going?
Then the Syllabus is your friend,
cuz you know exactly where you’ll end.
But if you want to go somewhere new,
see colors beyond Red, Green, and Blue.
Then take out your Syllabus and tear-it-in-half,
now uncertainty has become your path.
Be not afraid because you’ll find,
the most amazing things from Creative Minds,
who have been set free to FLY,
once untethered from the Syllabi.
Glenn Stutzky
Premiered at the 2014
Online Learning Consortium International Conference
October 29, 2014
They started with something that wasn’t polished, but it’s been an iterative approach over the semesters…and they continue to build on it.
I congratulated the team there — and do so again here. Excellent, wonderful work!
By the way, what would a creative movie-like trailer look like for your course?
















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)