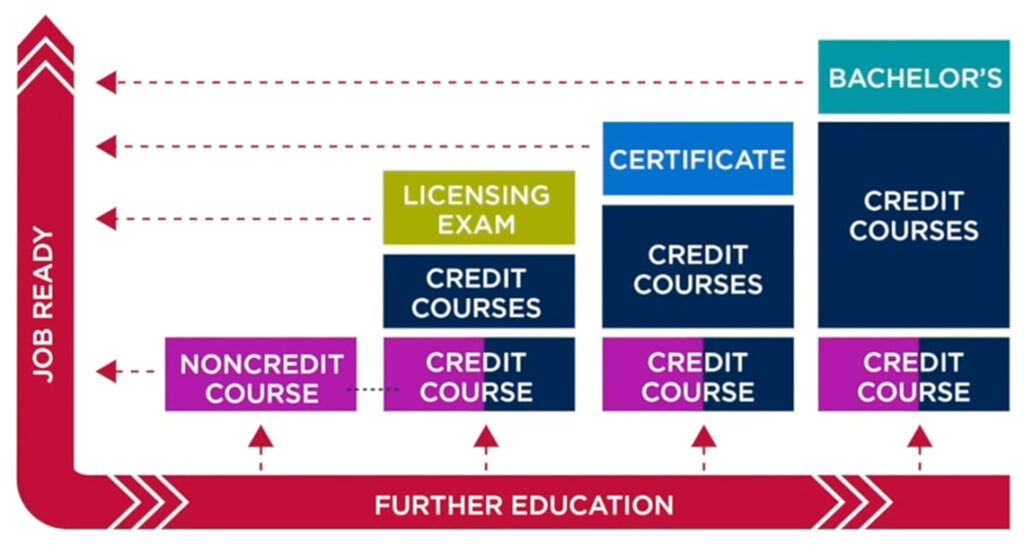
From DSC:
Below are several observations re: our learning ecosystems — and some ideas on how we can continue to improve them.
It takes years to build up the knowledge and skills in order to be a solid teacher, faculty member, instructional designer, and/or trainer. It takes a lot of studying to effectively research how the brain works and how we learn. Then we retire…and the knowledge is often lost or not passed along. And the wheel gets reinvented all over again. And again. And again.
Along these lines — and though we’re making progress in this area — too often we separate the research from the practical application of that research. So we have folks working primarily in learning science, neuroscience, cognitive psychology, and related fields. But their research doesn’t always get practically applied within our learning spaces. We have researchers…and then we have practitioners. So I greatly appreciate the likes of Pooja Agarwal and Patrice Bain out at RetrievalPractice.org, Daniel Willingham, Eva Keiffenheim, The Learning Scientists, James Lang, and several others who bridge this gap.

Perhaps more researchers, faculty members, teachers, trainers, instructional designers, principals, provosts, etc. could blog or be active out on social media.
***
Along these lines, we need to spend more time helping people know how best to study and to learn.
If that type of thing is ever to be learned, it seems like it’s often learned or discussed in the mid- to later years of one’s life…often after one’s primary and secondary days are long gone.
Instead, we should consider putting these easy-to-understand posters from the Learning Scientists in every K-12 school, college, and university in the nation — or something like them.
***
To provide the most effective engaging learning experiences, we should consider using more team-based approaches. As appropriate, that could include the students themselves.
***
We put way too much emphasis on grades — which produces gameplayers who seek only to do the minimum amount of work necessary to get the A’s. Doing so creates systems whereby learning is not the goal — getting a 4.0+ is.
***
As we are now required to be lifelong learners, our quality of life as a whole goes waaaay up if we actually enjoy learning. Many people discover later in life that they like to learn…they just didn’t like school. Perhaps we could place greater emphasis within K-16 on whether students enjoyed their learning experiences or not. And if not, what might have made that topic more enjoyable to them? Or what other topics would they like to dive into (that weren’t’ on the original learning menu)?
This could also apply in the corporate training/L&D space as well. Such efforts could go a long way in helping establish stronger learning cultures.
***
We don’t provide enough choice to our students. We need to do a better job of turning over more control to them in their learning journey. We turn students off to learning because we try to cram information that they don’t care about down their throats. So then we have to use the currency of grades to force them into doing the work that they could care less about doing. Their experience with learning/school can easily get soured.

We need to be more responsive with our curricula. And we need to explain how the information we’re trying to relay is relevant in the real world and will be relevant in their futures.
***
So those are some ideas that I wanted to relay. Thanks for your time and for your shared interests here!















 Podcasting studio at FUSE Workspace in Houston, TX.
Podcasting studio at FUSE Workspace in Houston, TX.