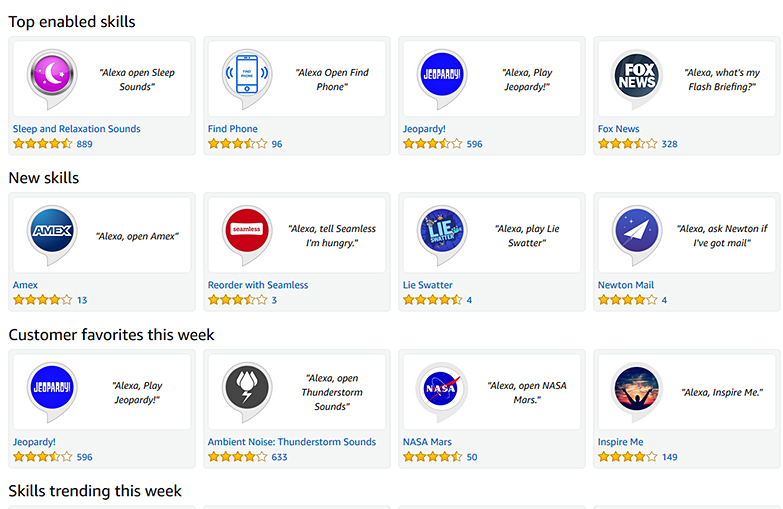
The Business of Artificial Intelligence — from hbr.org by Erik Brynjolfsson & Andrew McAfee
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
The most important general-purpose technology of our era is artificial intelligence, particularly machine learning (ML) — that is, the machine’s ability to keep improving its performance without humans having to explain exactly how to accomplish all the tasks it’s given. Within just the past few years machine learning has become far more effective and widely available. We can now build systems that learn how to perform tasks on their own.
Why is this such a big deal? Two reasons. First, we humans know more than we can tell: We can’t explain exactly how we’re able to do a lot of things — from recognizing a face to making a smart move in the ancient Asian strategy game of Go. Prior to ML, this inability to articulate our own knowledge meant that we couldn’t automate many tasks. Now we can.
Second, ML systems are often excellent learners. They can achieve superhuman performance in a wide range of activities, including detecting fraud and diagnosing disease. Excellent digital learners are being deployed across the economy, and their impact will be profound.
In the sphere of business, AI is poised have a transformational impact, on the scale of earlier general-purpose technologies. Although it is already in use in thousands of companies around the world, most big opportunities have not yet been tapped. The effects of AI will be magnified in the coming decade, as manufacturing, retailing, transportation, finance, health care, law, advertising, insurance, entertainment, education, and virtually every other industry transform their core processes and business models to take advantage of machine learning. The bottleneck now is in management, implementation, and business imagination.
…
The machine learns from examples, rather than being explicitly programmed for a particular outcome.
Let’s start by exploring what AI is already doing and how quickly it is improving. The biggest advances have been in two broad areas: perception and cognition. …For instance, Aptonomy and Sanbot, makers respectively of drones and robots, are using improved vision systems to automate much of the work of security guards.
Machine learning is driving changes at three levels: tasks and occupations, business processes, and business models.
You may have noticed that Facebook and other apps now recognize many of your friends’ faces in posted photos and prompt you to tag them with their names.












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)