Google, Facebook, and Microsoft are remaking themselves around AI — from wired.com by Cade Metz
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Alongside a former Stanford researcher—Jia Li, who more recently ran research for the social networking service Snapchat—the China-born Fei-Fei will lead a team inside Google’s cloud computing operation, building online services that any coder or company can use to build their own AI. This new Cloud Machine Learning Group is the latest example of AI not only re-shaping the technology that Google uses, but also changing how the company organizes and operates its business.
Google is not alone in this rapid re-orientation. Amazon is building a similar group cloud computing group for AI. Facebook and Twitter have created internal groups akin to Google Brain, the team responsible for infusing the search giant’s own tech with AI. And in recent weeks, Microsoft reorganized much of its operation around its existing machine learning work, creating a new AI and research group under executive vice president Harry Shum, who began his career as a computer vision researcher.
But Etzioni says this is also part of very real shift inside these companies, with AI poised to play an increasingly large role in our future. “This isn’t just window dressing,” he says.
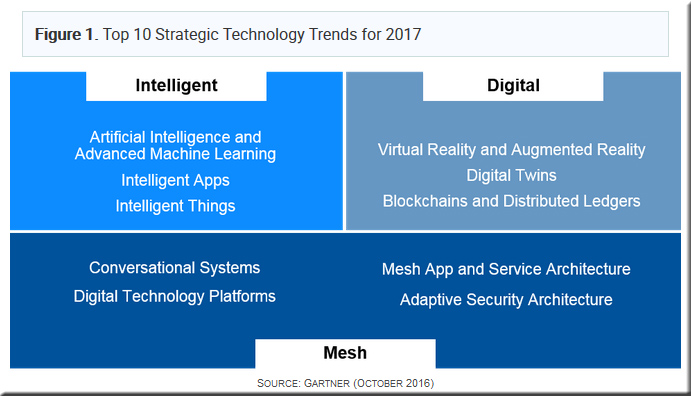
Intelligence everywhere! Gartner’s Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2017 — from which-50.com
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
AI and Advanced Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced machine learning (ML) are composed of many technologies and techniques (e.g., deep learning, neural networks, natural-language processing [NLP]). The more advanced techniques move beyond traditional rule-based algorithms to create systems that understand, learn, predict, adapt and potentially operate autonomously. This is what makes smart machines appear “intelligent.”
“Applied AI and advanced machine learning give rise to a spectrum of intelligent implementations, including physical devices (robots, autonomous vehicles, consumer electronics) as well as apps and services (virtual personal assistants [VPAs], smart advisors), ” said David Cearley, vice president and Gartner Fellow. “These implementations will be delivered as a new class of obviously intelligent apps and things as well as provide embedded intelligence for a wide range of mesh devices and existing software and service solutions.”
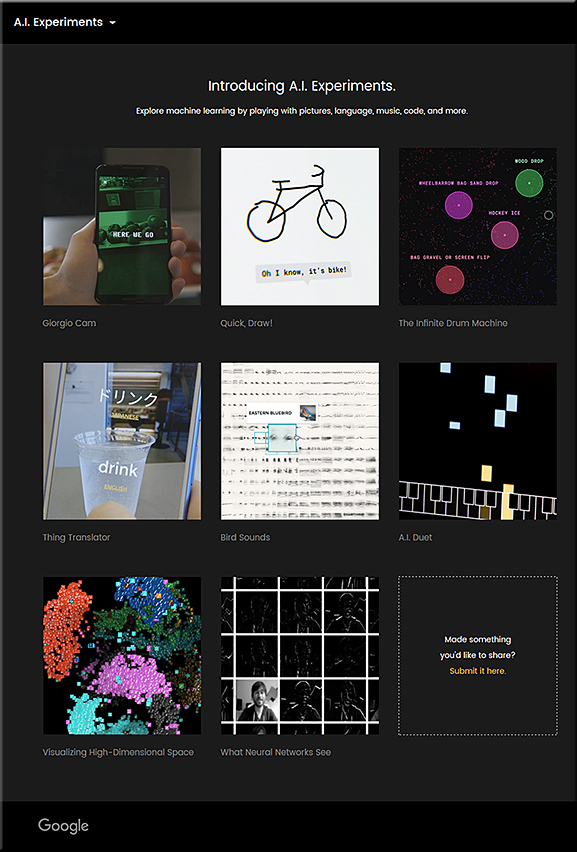
Google’s new website lets you play with its experimental AI projects — from mashable.com by Karissa Bell
Excerpt:
Google is letting users peek into some of its most experimental artificial intelligence projects.
The company unveiled a new website Tuesday called A.I. Experiments that showcases Google’s artificial intelligence research through web apps that anyone can test out. The projects include a game that guesses what you’re drawing, a camera app that recognizes objects you put in front of it and a music app that plays “duets” with you.
Google unveils a slew of new and improved machine learning APIs — from digitaltrends.com by Kyle Wiggers
Excerpt:
On Tuesday, Google Cloud chief Diane Greene announced the formation of a new team, the Google Cloud Machine Learning group, that will manage the Mountain View, California-based company’s cloud intelligence efforts going forward.
Found in translation: More accurate, fluent sentences in Google Translate — from blog.google by Barak Turovsky
Excerpt:
In 10 years, Google Translate has gone from supporting just a few languages to 103, connecting strangers, reaching across language barriers and even helping people find love. At the start, we pioneered large-scale statistical machine translation, which uses statistical models to translate text. Today, we’re introducing the next step in making Google Translate even better: Neural Machine Translation.
Neural Machine Translation has been generating exciting research results for a few years and in September, our researchers announced Google’s version of this technique. At a high level, the Neural system translates whole sentences at a time, rather than just piece by piece. It uses this broader context to help it figure out the most relevant translation, which it then rearranges and adjusts to be more like a human speaking with proper grammar. Since it’s easier to understand each sentence, translated paragraphs and articles are a lot smoother and easier to read. And this is all possible because of end-to-end learning system built on Neural Machine Translation, which basically means that the system learns over time to create better, more natural translations.
‘Augmented Intelligence’ for Higher Ed — from insidehighered.com by Carl Straumsheim
IBM picks Blackboard and Pearson to bring the technology behind the Watson computer to colleges and universities.
Excerpts:
[IBM] is partnering with a small number of hardware and software providers to bring the same technology that won a special edition of the game show back in 2011 to K-12 institutions, colleges and continuing education providers. The partnerships and the products that might emerge from them are still in the planning stage, but the company is investing in the idea that cognitive computing — natural language processing, informational retrieval and other functions similar to the ones performed by the human brain — can help students succeed in and outside the classroom.
Chalapathy Neti, vice president of education innovation at IBM Watson, said education is undergoing the same “digital transformation” seen in the finance and health care sectors, in which more and more content is being delivered digitally.
…
IBM is steering clear of referring to its technology as “artificial intelligence,” however, as some may interpret it as replacing what humans already do.
“This is about augmenting human intelligence,” Neti said. “We never want to see these data-based systems as primary decision makers, but we want to provide them as decision assistance for a human decision maker that is an expert in conducting that process.”
What a Visit to an AI-Enabled Hospital Might Look Like — from hbr.org by R “Ray” Wang
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
The combination of machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and cognitive computing will soon change the ways that we interact with our environments. AI-driven smart services will sense what we’re doing, know what our preferences are from our past behavior, and subtly guide us through our daily lives in ways that will feel truly seamless.
Perhaps the best way to explore how such systems might work is by looking at an example: a visit to a hospital.
…
The AI loop includes seven steps:
- Perception describes what’s happening now.
- Notification tells you what you asked to know.
- Suggestion recommends action.
- Automation repeats what you always want.
- Prediction informs you of what to expect.
- Prevention helps you avoid bad outcomes.
- Situational awareness tells you what you need to know right now.
Japanese artificial intelligence gives up on University of Tokyo admissions exam — from digitaltrends.com by Brad Jones
Excerpt:
Since 2011, Japan’s National Institute of Informatics has been working on an AI, with the end goal of having it pass the entrance exam for the University of Tokyo, according to a report from Engadget. This endeavor, dubbed the Todai Robot Project in reference to a local nickname for the school, has been abandoned.
It turns out that the AI simply cannot meet the exact requirements of the University of Tokyo. The team does not expect to reach their goal of passing the test by March 2022, so the project is being brought to an end.
“We are building not just Azure to have rich compute capability, but we are, in fact, building the world’s first AI supercomputer,” he said.
— from Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella spruiks power of machine learning,
smart bots and mixed reality at Sydney developers conference
Why it’s so hard to create unbiased artificial intelligence — from techcrunch.com by Ben Dickson
Excerpt:
As artificial intelligence and machine learning mature and manifest their potential to take on complicated tasks, we’ve become somewhat expectant that robots can succeed where humans have failed — namely, in putting aside personal biases when making decisions. But as recent cases have shown, like all disruptive technologies, machine learning introduces its own set of unexpected challenges and sometimes yields results that are wrong, unsavory, offensive and not aligned with the moral and ethical standards of human society.
While some of these stories might sound amusing, they do lead us to ponder the implications of a future where robots and artificial intelligence take on more critical responsibilities and will have to be held responsible for the possibly wrong decisions they make.
The Non-Technical Guide to Machine Learning & Artificial Intelligence — from medium.com by Sam DeBrule
Excerpt:
This list is a primer for non-technical people who want to understand what machine learning makes possible.
To develop a deep understanding of the space, reading won’t be enough. You need to: have an understanding of the entire landscape, spot and use ML-enabled products in your daily life (Spotify recommendations), discuss artificial intelligence more regularly, and make friends with people who know more than you do about AI and ML.
News: For starters, I’ve included a link to a weekly artificial intelligence email that Avi Eisenberger and I curate (machinelearnings.co). Start here if you want to develop a better understanding of the space, but don’t have the time to actively hunt for machine learning and artificial intelligence news.
Startups: It’s nice to see what startups are doing, and not only hear about the money they are raising. I’ve included links to the websites and apps of 307+ machine intelligence companies and tools.
People: Here’s a good place to jump into the conversation. I’ve provided links to Twitter accounts (and LinkedIn profiles and personal websites in their absence) of the founders, investors, writers, operators and researchers who work in and around the machine learning space.
Events: If you enjoy getting out from behind your computer, and want to meet awesome people who are interested in artificial intelligence in real life, there is one place that’s best to do that, more on my favorite place below.
How one clothing company blends AI and human expertise — from hbr.org by H. James Wilson, Paul Daugherty, & Prashant Shukla
Excerpt:
When we think about artificial intelligence, we often imagine robots performing tasks on the warehouse or factory floor that were once exclusively the work of people. This conjures up the specter of lost jobs and upheaval for many workers. Yet, it can also seem a bit remote — something that will happen in “the future.” But the future is a lot closer than many realize. It also looks more promising than many have predicted.
Stitch Fix provides a glimpse of how some businesses are already making use of AI-based machine learning to partner with employees for more-effective solutions. A five-year-old online clothing retailer, its success in this area reveals how AI and people can work together, with each side focused on its unique strengths.

Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
As the White House report rightly observes, the implications of an AI-suffused world are enormous — especially for the people who work at jobs that soon will be outsourced to artificially-intelligent machines. Although the report predicts that AI ultimately will expand the U.S. economy, it also notes that “Because AI has the potential to eliminate or drive down wages of some jobs … AI-driven automation will increase the wage gap between less-educated and more-educated workers, potentially increasing economic inequality.”
Accordingly, the ability of people to access higher education continuously throughout their working lives will become increasingly important as the AI revolution takes hold. To be sure, college has always helped safeguard people from economic dislocations caused by technological change. But this time is different. First, the quality of AI is improving rapidly. On a widely-used image recognition test, for instance, the best AI result went from a 26 percent error rate in 2011 to a 3.5 percent error rate in 2015 — even better than the 5 percent human error rate.
Moreover, as the administration’s report documents, AI has already found new applications in so-called “knowledge economy” fields, such as medical diagnosis, education and scientific research. Consequently, as artificially intelligent systems come to be used in more white-collar, professional domains, even people who are highly educated by today’s standards may find their livelihoods continuously at risk by an ever-expanding cybernetic workforce.
As a result, it’s time to stop thinking of higher education as an experience that people take part in once during their young lives — or even several times as they advance up the professional ladder — and begin thinking of it as a platform for lifelong learning.
Colleges and universities need to be doing more to move beyond the array of two-year, four-year, and graduate degrees that most offer, and toward a more customizable system that enables learners to access the learning they need when they need it. This will be critical as more people seek to return to higher education repeatedly during their careers, compelled by the imperative to stay ahead of relentless technological change.
From DSC:
That last bolded paragraph is why I think the vision of easily accessible learning — using the devices that will likely be found in one’s apartment or home — will be enormously powerful and widespread in a few years. Given the exponential pace of change that we are experiencing — and will likely continue to experience for some time — people will need to reinvent themselves quickly.
Higher education needs to rethink our offerings…or someone else will.
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)