From DSC:
Before we get to the announcements in more detail….
can you imagine being a teacher, a professor, or a trainer — with all of the required applications
launched — if you were the presenter in this video at say the 12:45 mark?
If you are at all interesting in emerging technologies and what several pieces
of our future learning ecosystems — and meeting spaces — could easily look like,
you NEED to watch the entire presentation.
Also, they announced
Microsoft’s purchase of AltspaceVR…in virtual reality!
This clip shows them meeting in a virtual space.
The era of Windows Mixed Reality begins October 17 — from blogs.windows.com by Alex Kipman
Samsung unveils Windows Mixed Reality headset, AltSpaceVR joins Microsoft, SteamVR catalog coming to Windows Mixed Reality this holiday.
At an event in San Francisco we unveiled our vision for Windows Mixed Reality, announced SteamVR and AltSpaceVR are coming to Windows Mixed Reality, introduced the new Samsung Odyssey HMD, and kicked off the holiday shopping season by announcing the availability of pre-orders for Windows Mixed Reality headsets at the Microsoft Store.
Also see:

Oct 4th, 2017
Microsoft held its long-awaited launch of Windows 10 Mixed Reality yesterday, and while most of the new devices and products had been leaked earlier, there were still some big takeaways. Here are some of them:
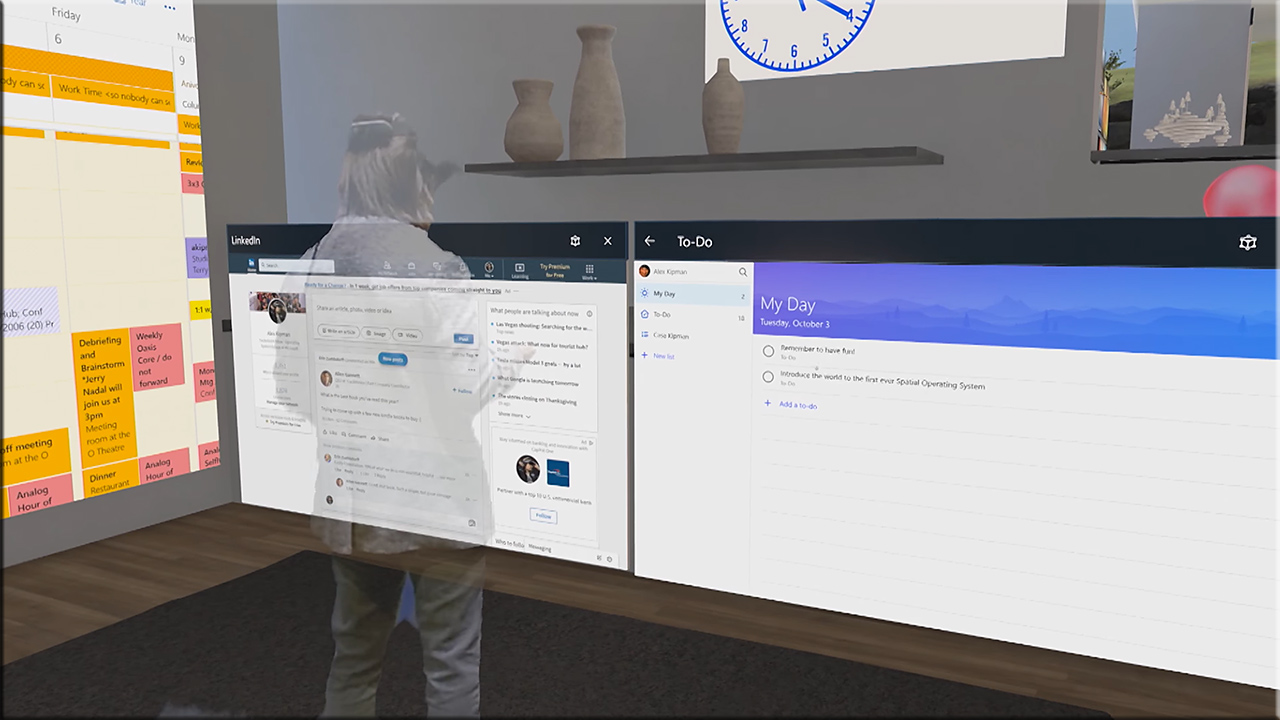
- Mixed Reality: Microsoft gave a demo of what its new platform will do, covering the AR/VR spectrum with games, apps, and experiences. One such experience is Cliff House, a virtual work space and entertainment room.
- Altspace VR: When the pioneering social VR app shut down this summer and was rescued by a “third party,” people wondered who that was. Turns out it was Microsoft, which acquired Altspace VR for an undisclosed amount. The acquisition was announced yesterday.
- Steam VR and Halo: Microsoft had previously announced that its new Mixed Reality headsets would support Steam VR titles. Developers can now access that support, and consumers will be able to access it later this year. In addition to the hundreds of VR titles available on Steam, on Oct. 17, Microsoft will offer free downloads of Halo Recruit.
- Odyssey and other headsets: The new Windows 10 platform is launching alongside a host of new headsets. In addition to the new Odyssey, which was made in partnership with Samsung, there are other headsets forthcoming from Acer, HP, Dell, Lenovo, and Asus.
- 2018 Olympics: This was announced previously in June, but yesterday Microsoft briefed the press that Intel is partnering with the International Olympic Committee to bring Windows Mixed Reality experiences to the 2018 games.
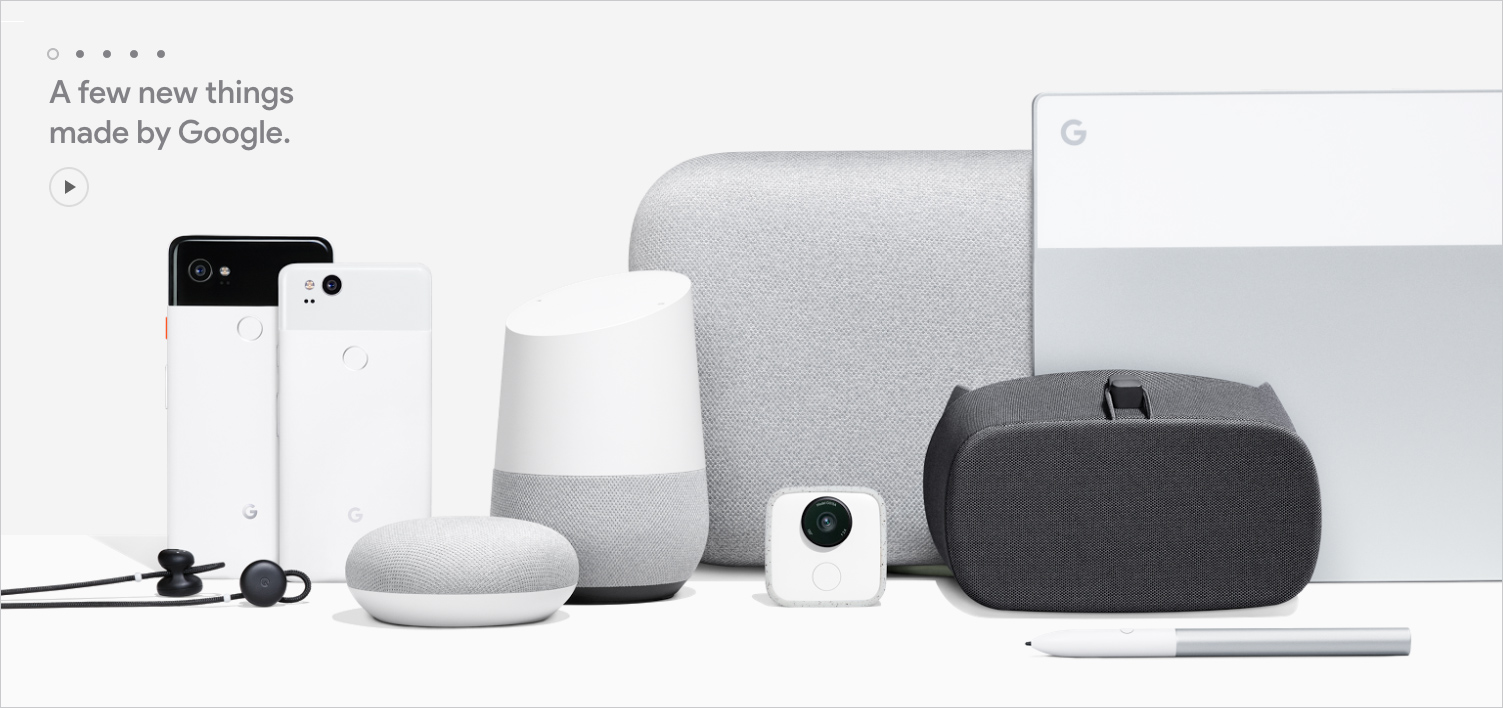
- Watch the Google Pixel 2 event in 19 minutes — from the verge.com by The Google Pixel event has wrapped and we got a good look at a bunch of new hardware lineup this year: the second generation of Pixel smartphones, new Google Homes, a Pixelbook, and a surprise new Google camera that uses artificial intelligence to snap pictures and videos of your family. Is it as weird as it sounds? If you missed the keynote where Google presented everything, here’s a recap of everything Google announced in about two hours cut into a 19-minute video so you can see for yourself if these new products will make it to your shopping list this holiday season.
- Google Upgrades Virtual-Reality Headset, Debuts Augmented-Reality Features — from bloomberg.com by Mark Gurman
- Google is turning Stranger Things characters into adorable augmented reality stickers — from the verge.com by
- Google Pixel 2 and 2 XL announced with water resistance, ‘dual-pixel’ camera, and always-on display — from theverge.com by
- The 5 biggest announcements from Google’s Pixel 2 event — from theverge.com by Shannon Liao
- Google Launches PixelBook Laptop Embedded With its Services — from bloomberg.com by Mark Gurman












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)