Personalized Learning Meets AI With Watson Classroom — from gettingsmart.com by Erin Gohl
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Teaching is truly a Herculean challenge. Even the very best teachers can keep only so many of these insights in their heads and make only so many connections between expectations and circumstances. They can be aware of only a fraction of the research on best practices. They have only so much time to collaborate and communicate with the other adults in a particular student’s life to share information and insights. To be the best of themselves, teachers need to have access to a warehouse of information, a research assistant to mine best practices, note takers to gather and record information on each student, a statistician to gauge effective practices, and someone to collaborate with to distill the next best step with each student. In recent years, a plethora of vendors have developed software solutions that promise to simplify this process and give schools and teachers the answers to understand and address the individual needs of each student. One of the most promising, which I recently had a chance to learn about, is IBM’s Watson Classroom.
…
IBM is clear about what makes Watson different than existing solutions. First of all, it is a cognitive partner; not a solution. Secondly, it does not require proprietary or additional assessments, curriculum, or content. It uses whatever a district has in place. But it goes beyond the performance of tiering difficulty, pace, and reading level that is now standard fare for the solutions promising individualized, adaptive and personalized learning. Watson takes the stew of data from existing systems (including assessments, attendance records, available accommodations), adds the ability to infer meaning from written reports, and is able to connect the quality of the result to the approach that was taken. And then adjust the next recommendation based on what was learned. It is artificial intelligence (AI) brought to education that goes far beyond the adaptive learning technologies of today.
…
Watson Classroom is currently being piloted in 12 school districts across the country. In those classrooms, Watson Classroom is utilizing cutting-edge computing power to give teachers a full range of support to be the best versions of themselves. Watson is facilitating the kind of education the great teachers strive for every day–one where learning is truly personalized for each and every student. Bringing the power of big data to the interactions between students and teachers can help assure that every student reaches beyond our expectations to achieve their full potential.
Learn with Google AI: Making ML education available to everyone — from blog.google
Excerpt:
To help everyone understand how AI can solve challenging problems, we’ve created a resource called Learn with Google AI. This site provides ways to learn about core ML concepts, develop and hone your ML skills, and apply ML to real-world problems. From deep learning experts looking for advanced tutorials and materials on TensorFlow, to “curious cats” who want to take their first steps with AI, anyone looking for educational content from ML experts at Google can find it here.
Learn with Google AI also features a new, free course called Machine Learning Crash Course (MLCC). The course provides exercises, interactive visualizations, and instructional videos that anyone can use to learn and practice ML concepts.
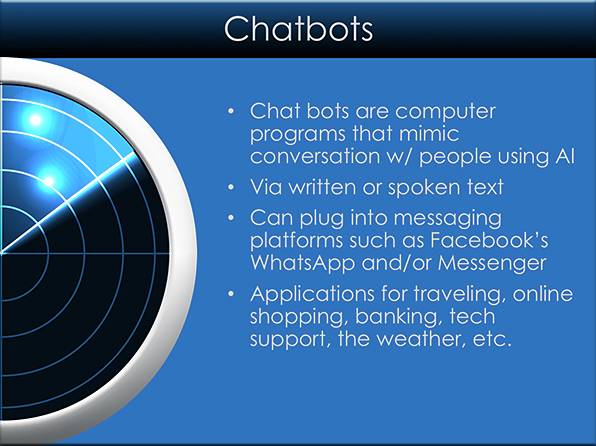
7 Ways Chatbots and AI are Disrupting HR — from chatbotsmagazine.com
Enterprises are embracing AI for automating human resources
Excerpt:
Chatbots and AI have become household names and enterprises are taking notice. According to a recent Forrester survey, roughly “85% of customer interactions within an enterprise will be with software robots in five years’ time” and “87% of CEOs are looking to expand their AI workforce” using AI bots.
In an effort to drive increased labor efficiencies, reduce costs, and deliver better customer/employee experiences enterprises are quickly introducing AI, machine learning, and natural language understanding as core elements of their digital transformation strategy in 2018.
Human resources (HR) is one area ripe for intelligent automation within an enterprise. AI-powered bots for HR are able to streamline and personalize the HR process across seasonal, temporary, part-time, and full-time employees.
…
There are 7 ways in which enterprises can use HR bots to drive increased labors efficiencies, reduced costs, and better employee experiences:
- Recruitment
- Onboarding
- Company Policy FAQs
- Employee Training
- Common Questions
- Benefits Enrollment
- Annual Self-Assessment/Reviews
From DSC:
Again, this article paint a bit too rosy of a picture for me re: the use of AI and HR, especially in regards to recruiting employees.
Implementation of AI into eLearning. Interview with Christopher Pappas — from joomlalms.com by Darya Tarliuk
Excerpt:
Every day we hear more and more about the impact that Artificial Intelligence gains in every sphere of our life. In order to discover how AI implementation is going to change the eLearning we decided to ask Christopher Pappas to share his views and find out what he thinks about it. Christopher is an experienced eLearning specialist and the Founder of the eLearning Industry’s Network.
…
How to get ready preparing course materials now, while considering the future impact of AI?
Christopher: Regardless of whether you plan to adopt an AI system as soon as they’re available to the mass market or you opt to hold off (and let others work out the glitches), infrastructure is key. You can prepare your course materials now by developing course catalogs, microlearning online training repositories, and personalized online training paths that fall into the AI framework. For example, the AI system can easily recommend existing resources based on a learners’ assessment scores or job duties. All of the building blocks are in place, allowing the system to focus on content delivery and data analysis.
Can You Trust Intelligent Virtual Assistants? — from nojitter.com by Gary Audin
From malicious hackers to accidental voice recordings, data processed through virtual assistants may open you to security and privacy risks.
Excerpt:
Did you know that with such digital assistants your voice data is sent to the cloud or another remote location for processing? Is it safe to talk in front of your TV remote? Are you putting your business data at risk of being compromised by asking Alexa to start your meeting?

Thanks, Robots! Now These Four Non-Tech Job Skills Are In Demand — from fastcompany.com by Christian Madsbjerg
The more we rely on AI and machine learning, the more work we need social scientists and humanities experts to do.
Excerpt:
Automation isn’t a simple struggle between people and technology, with the two sides competing for jobs. The more we rely on robots, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, the clearer it’s become just how much we need social scientists and humanities experts–not the reverse.
These four skills in particular are all unique to us humans, and will arguably rise in value in the coming years, as more and more companies realize they need the best of both worlds to unleash the potential from both humans and machines.


















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)