7 legaltech trends to watch in 2024 — from lexology.com by Sacha Kirk
Legal technology, or ‘legaltech’, is transforming the legal sector by automating processes and enhancing the provision of legal services. As we approach 2024, several trends within this field are particularly worth keeping an eye on. These not only promise to streamline legal operations but will also help increase the in-house legal department’s visibility and value to the organisation.
Here are seven legaltech trends poised to make an impact in the coming year.
1. Artificial intelligence and machine learning
AI and machine learning remain pivotal in legaltech, especially for in-house lawyers who deal with vast quantities of contracts and complex legal matters. In 2024, these technologies will be integral for legal research, contract review, and the drafting of legal documents. Statistics from the Tech & the Law 2023 Report state more than three in five corporate legal departments (61%) have adopted generative AI in some capacity, with 7% actively using generative AI in their day-to-day work. With constant improvements to LLM (Large Language Models) by the big players, i.e. OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft (via OpenAI), 2024 will see more opportunities open and efficiencies gained for legal teams.
Our top 5 legal technology trends predicted for 2024 — from legalfutures.co.uk
5. ID verification software
With identity fraud on the increase there is a growing demand from the Government for people to be identified with accuracy and they are proposing to pass legislation in February 2024 that will tighten the requirements for the professional organisations involved. They will promote the use of technology to reduce the risk of fraudulent transactions including mortgage fraud where according to Experian’s Report “the greatest jump in fraud cases has been seen …. with fraud increasing from around 41 cases to around 52 cases per 10,000 applications.”
Guest Post: The Year in Justice Tech: 2023 Report and News Roundup — from lawnext.com by Maya Markovich, executive director of the Justice Technology Association
In 2023, the justice tech ecosystem continued to grow rapidly, with a significant increase in solutions addressing access to justice-related challenges for consumers. Justice tech caught the interest of both impact investors, as well as those seeking opportunities to fund the disruption of antiquated systems via technology.
Consulting Giants See AI Shaving Years Off the Path to Partner — from bloomberg.com by Irina Anghel
- To make it to partner level typically takes at least a decade
- AI seen freeing up junior staffers to do more meaningful work
Consulting giants and law firms are looking to artificial intelligence to speed up the time it takes junior staffers to make it to the prestigious partner level as the technology eliminates vast swaths of the repetitive, time-consuming tasks that typically filled up their first few years on the job.
Stock Up 10% in December; Unveils Groundbreaking Initiatives — from in.investing.com by Aayush Khanna (India)
Excerpt from DSC — and I’m not out to give legal or investing advice. I just really appreciated the list of legaltech-related innovations:
In the LegalTech realm, QiLegal emerges as a robust cloud-based platform, aiming to digitize the legal framework. Envisaged to propel the justice system with Virtual Courts, Online Dispute Resolution, and AI-enabled Drafting, QiLegal responds to the estimated USD 100 billion global LegalTech market.
The essential role of creator and customer collaboration in legal tech — from legaldive.com by Relativity (sponsored content; emphasis below from DSC)
However, with these high stakes and wide margins for error in hand, the accuracy, defensibility, and reliability of that AI is subject to intense professional and judicial scrutiny. And for good reason: anything less than the thoughtful, intentional development of specifically fit-for-purpose AI applications in this realm can contribute to the loss of millions of dollars, the livelihoods of countless individuals, and deeply damaging miscarriages of justice.
Generative AI and the small law firm: The value of legal domain expertise — from thomsonreuters.com by Mark Haddad
In our new blog series, we continue to discuss how small law firms can leverage their natural advantages with generative artificial intelligence to compete at a higher level
Gen AI presents unprecedented opportunities for small law firms to compete.
The idea that legal Gen AI means turning over legal decision-making to a machine overlooks the importance of the data portion of the Venn diagram above. A properly trained and targeted Gen AI application for legal use will build on the work of lawyers in the form of cases, statutes, briefs and memoranda, how-to guides, contracts, client advisories, templates — all the esoteric and robust data that results from lawyers’ expertise and knowledge.
All law firms, even smaller ones, have an opportunity to leverage their own data assets against competitors at scale once their lawyers identify and curate the appropriate critical data sets from within their firm and embed them within the AI solution. This proprietary data can be combined with larger pools of data from authoritative external sources like trusted legal content sources to further strengthen the responses that the Gen AI tool provides.
AAA® Launches New AAAi Lab Offering Products, Education, Guidance & News Resources — from prnewswire.com by American Arbitration Assocation
Latest Technology Innovation Seeks to Support AAA Users, Arbitrators & Broader Legal Community with Incorporating Generative AI into ADR Processes
NEW YORK, Dec. 6, 2023 /PRNewswire/ — The American Arbitration Association® (AAA) and its international division, the International Centre for Dispute Resolution® (ICDR®), announces the launch of the AAAi Lab, a web center supporting AAA users, arbitrators, in-house counsel and law firms with policy guidance, educational webinars and tools for embracing generative AI in alternative dispute resolution.
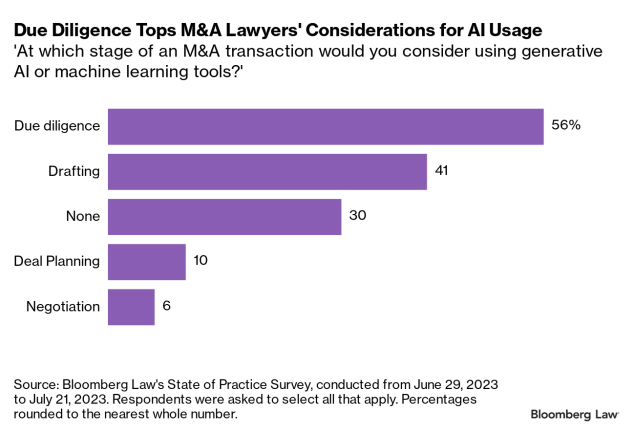
ANALYSIS: Most M&A Attorneys Would Use AI for Due Diligence — from news.bloomberglaw.com by Abena Opong-Fosu
Artificial intelligence (AI) has infiltrated almost every facet of daily life. For M&A lawyers, exposure to AI and machine learning tools likely comes from deals involving the buying and selling of AI companies as well as through the software the lawyers use on a daily basis.
Most deal lawyers who responded to a recent Bloomberg Law survey said that they’re open to using AI at some point in dealmaking.