Are we ready to navigate the complex ethics of advanced AI assistants? — from futureofbeinghuman.com by Andrew Maynard
An important new paper lays out the importance and complexities of ensuring increasingly advanced AI-based assistants are developed and used responsibly
Last week a behemoth of a paper was released by AI researchers in academia and industry on the ethics of advanced AI assistants.
It’s one of the most comprehensive and thoughtful papers on developing transformative AI capabilities in socially responsible ways that I’ve read in a while. And it’s essential reading for anyone developing and deploying AI-based systems that act as assistants or agents — including many of the AI apps and platforms that are currently being explored in business, government, and education.
The paper — The Ethics of Advanced AI Assistants — is written by 57 co-authors representing researchers at Google Deep Mind, Google Research, Jigsaw, and a number of prominent universities that include Edinburgh University, the University of Oxford, and Delft University of Technology. Coming in at 274 pages this is a massive piece of work. And as the authors persuasively argue, it’s a critically important one at this point in AI development.
Key questions for the ethical and societal analysis of advanced AI assistants include:
- What is an advanced AI assistant? How does an AI assistant differ from other kinds of AI technology?
- What capabilities would an advanced AI assistant have? How capable could these assistants be?
- What is a good AI assistant? Are there certain values that we want advanced AI assistants to evidence across all contexts?
- Are there limits on what AI assistants should be allowed to do? If so, how are these limits determined?
- What should an AI assistant be aligned with? With user instructions, preferences, interests, values, well-being or something else?
- What issues need to be addressed for AI assistants to be safe? What does safety mean for this class of technologies?
- What new forms of persuasion might advanced AI assistants be capable of? How can we ensure that users remain appropriately in control of the technology?
- How can people – especially vulnerable users – be protected from AI manipulation and unwanted disclosure of personal information?
- Is anthropomorphism for AI assistants morally problematic? If so, might it still be permissible under certain conditions?
- …
AI for the physical world — from superhuman.ai by Zain Kahn
Excerpt: (emphasis DSC)
A new company called Archetype is trying to tackle that problem: It wants to make AI useful for more than just interacting with and understanding the digital realm. The startup just unveiled Newton — “the first foundation model that understands the physical world.”
What’s it for?
A warehouse or factory might have 100 different sensors that have to be analyzed separately to figure out whether the entire system is working as intended. Newton can understand and interpret all of the sensors at the same time, giving a better overview of how everything’s working together. Another benefit: You can ask Newton questions in plain English without needing much technical expertise.
How does it work?
- Newton collects data from radar, motion sensors, and chemical and environmental trackers
- It uses an LLM to combine each of those data streams into a cohesive package
- It translates that data into text, visualizations, or code so it’s easy to understand
Apple’s $25-50 million Shutterstock deal highlights fierce competition for AI training data — from venturebeat.com by Michael Nuñez; via Tom Barrett’s Prompcraft e-newsletter
Apple has entered into a significant agreement with stock photography provider Shutterstock to license millions of images for training its artificial intelligence models. According to a Reuters report, the deal is estimated to be worth between $25 million and $50 million, placing Apple among several tech giants racing to secure vast troves of data to power their AI systems.
AWS, Educause partner on generative AI readiness tool — from edscoop.com by Skylar Rispens
Amazon Web Services and the nonprofit Educause announced a new tool designed to help higher education institutions gauge their readiness to adopt generative artificial intelligence.
Amazon Web Services and the nonprofit Educause on Monday announced they’ve teamed up to develop a tool that assesses how ready higher education institutions are to adopt generative artificial intelligence.
Through a series of curated questions about institutional strategy, governance, capacity and expertise, AWS and Educause claim their assessment can point to ways that operations can be improved before generative AI is adopted to support students and staff.
“Generative AI will transform how educators engage students inside and outside the classroom, with personalized education and accessible experiences that provide increased student support and drive better learning outcomes,” Kim Majerus, vice president of global education and U.S. state and local government at AWS, said in a press release. “This assessment is a practical tool to help colleges and universities prepare their institutions to maximize this technology and support students throughout their higher ed journey.”
Speaking of AI and our learning ecosystems, also see:
Gen Z Wants AI Skills And Businesses Want Workers Who Can Apply AI: Higher Education Can Help — from forbes.com by Bruce Dahlgren
At a moment when the value of higher education has come under increasing scrutiny, institutions around the world can be exactly what learners and employers both need. To meet the needs of a rapidly changing job market and equip learners with the technical and ethical direction needed to thrive, institutions should familiarize students with the use of AI and nurture the innately human skills needed to apply it ethically. Failing to do so can create enormous risk for higher education, business and society.
What is AI literacy?
To effectively utilize generative AI, learners will need to grasp the appropriate use cases for these tools, understand when their use presents significant downside risk, and learn to recognize abuse to separate fact from fiction. AI literacy is a deeply human capacity. The critical thinking and communication skills required are muscles that need repeated training to be developed and maintained.
The University Student’s Guide To Ethical AI Use — from studocu.com; with thanks to Jervise Penton at 6XD Media Group for this resource
This comprehensive guide offers:
- Up-to-date statistics on the current state of AI in universities, how institutions and students are currently using artificial intelligence
- An overview of popular AI tools used in universities and its limitations as a study tool
- Tips on how to ethically use AI and how to maximize its capabilities for students
- Current existing punishment and penalties for cheating using AI
- A checklist of questions to ask yourself, before, during, and after an assignment to ensure ethical use
Some of the key facts you might find interesting are:
- The total value of AI being used in education was estimated to reach $53.68 billion by the end of 2032.
- 68% of students say using AI has impacted their academic performance positively.
- Educators using AI tools say the technology helps speed up their grading process by as much as 75%.
[Report] The Top 100 AI for Work – April 2024 — from flexos.work; with thanks to Daan van Rossum for this resource
AI is helping us work up to 41% more effectively, according to recent Bain research. We review the platforms to consider for ourselves and our teams.
Following our AI Top 150, we spent the past few weeks analyzing data on the top AI platforms for work. This report shares key insights, including the AI tools you should consider adopting to work smarter, not harder.
While there is understandable concern about AI in the work context, the platforms in this list paint a different picture. It shows a future of work where people can do what humans are best suited for while offloading repetitive, digital tasks to AI.
This will fuel the notion that it’s not AI that takes your job but a supercharged human with an army of AI tools and agents. This should be a call to action for every working person and business leader reading this.
How Generative AI Owns Higher Education. Now What? — from forbes.co by Steve Andriole
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
What about course videos? Professors can create them (by lecturing into a camera for several hours hopefully in different clothes) from the readings, from their interpretations of the readings, from their own case experiences – from anything they like. But now professors can direct the creation of the videos by talking – actually describing – to a CustomGPTabout what they’d like the video to communicate with their or another image. Wait. What? They can make a video by talking to a CustomGPT and even select the image they want the “actor” to use? Yes. They can also add a British accent and insert some (GenAI-developed) jokes into the videos if they like. All this and much more is now possible. This means that a professor can specify how long the video should be, what sources should be consulted and describe the demeanor the professor wants the video to project.
From DSC:
Though I wasn’t crazy about the clickbait type of title here, I still thought that the article was solid and thought-provoking. It contained several good ideas for using AI.
Excerpt from a recent EdSurge Higher Ed newsletter:
There are darker metaphors though — ones that focus on the hazards for humanity of the tech. Some professors worry that AI bots are simply replacing hired essay-writers for many students, doing work for a student that they can then pass off as their own (and doing it for free).
From DSC:
Hmmm…the use of essay writers was around long before AI became mainstream within higher education. So we already had a serious problem where students didn’t see the why in what they were being asked to do. Some students still aren’t sold on the why of the work in the first place. The situation seems to involve ethics, yes, but it also seems to say that we haven’t sold students on the benefits of putting in the work. Students seem to be saying I don’t care about this stuff…I just need the degree so I can exit stage left.
My main point: The issue didn’t start with AI…it started long before that.
And somewhat relevant here, also see:
I Have Bigger Fish to Fry: Why K12 Education is Not Thinking About AI — from medium.com by Maurie Beasley, M.Ed. (Edited by Jim Beasley)
This financial stagnation is occurring as we face a multitude of escalating challenges. These challenges include but are in no way limited to, chronic absenteeism, widespread student mental health issues, critical staff shortages, rampant classroom behavior issues, a palpable sense of apathy for education in students, and even, I dare say, hatred towards education among parents and policymakers.
…
Our current focus is on keeping our heads above water, ensuring our students’ safety and mental well-being, and simply keeping our schools staffed and our doors open.
Meet Ed: Ed is an educational friend designed to help students reach their limitless potential. — from lausd.org (Los Angeles School District, the second largest in the U.S.)
What is Ed?
An easy-to-understand learning platform designed by Los Angeles Unified to increase student achievement. It offers personalized guidance and resources to students and families 24/7 in over 100 languages.
Also relevant/see:
- Los Angeles Unified Bets Big on ‘Ed,’ an AI Tool for Students — from by Lauraine Langreo
The Los Angeles Unified School District has launched an AI-powered learning tool that will serve as a “personal assistant” to students and their parents.The tool, named “Ed,” can provide students from the nation’s second-largest district information about their grades, attendance, upcoming tests, and suggested resources to help them improve their academic skills on their own time, Superintendent Alberto Carvalho announced March 20. Students can also use the app to find social-emotional-learning resources, see what’s for lunch, and determine when their bus will arrive.
Could OpenAI’s Sora be a big deal for elementary school kids? — from futureofbeinghuman.com by Andrew Maynard
Despite all the challenges it comes with, AI-generated video could unleash the creativity of young children and provide insights into their inner worlds – if it’s developed and used responsibly
Like many others, I’m concerned about the challenges that come with hyper-realistic AI-generated video. From deep fakes and disinformation to blurring the lines between fact and fiction, generative AI video is calling into question what we can trust, and what we cannot.
And yet despite all the issues the technology is raising, it also holds quite incredible potential, including as a learning and development tool — as long as we develop and use it responsibly.
I was reminded of this a few days back while watching the latest videos from OpenAI created by their AI video engine Sora — including the one below generated from the prompt “an elephant made of leaves running in the jungle”
…
What struck me while watching this — perhaps more than any of the other videos OpenAI has been posting on its TikTok channel — is the potential Sora has for translating the incredibly creative but often hard to articulate ideas someone may have in their head, into something others can experience.
Can AI Aid the Early Education Workforce? — from edsurge.com by Emily Tate Sullivan
During a panel at SXSW EDU 2024, early education leaders discussed the potential of AI to support and empower the adults who help our nation’s youngest children.
While the vast majority of the conversations about AI in education have centered on K-12 and higher education, few have considered the potential of this innovation in early care and education settings.
At the conference, a panel of early education leaders gathered to do just that, in a session exploring the potential of AI to support and empower the adults who help our nation’s youngest children, titled, “ChatECE: How AI Could Aid the Early Educator Workforce.”
Hau shared that K-12 educators are using the technology to improve efficiency in a number of ways, including to draft individualized education programs (IEPs), create templates for communicating with parents and administrators, and in some cases, to support building lesson plans.
Again, we’ve never seen change happen as fast as it’s happening.
Enhancing World Language Instruction With AI Image Generators — from eduoptia.org by Rachel Paparone
By crafting an AI prompt in the target language to create an image, students can get immediate feedback on their communication skills.
Educators are, perhaps rightfully so, cautious about incorporating AI in their classrooms. With thoughtful implementation, however, AI image generators, with their ability to use any language, can provide powerful ways for students to engage with the target language and increase their proficiency.
AI in the Classroom: A Teacher’s Toolkit for Transformation — from esheninger.blogspot.com by Eric Sheninger
While AI offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to remember that it is a tool to empower educators, not replace them. The human connection between teacher and student remains central to fostering creativity, critical thinking, and social-emotional development. The role of teachers will shift towards becoming facilitators, curators, and mentors who guide students through personalized learning journeys. By harnessing the power of AI, educators can create dynamic and effective classrooms that cater to each student’s individual needs. This paves the way for a more engaging and enriching learning experience that empowers students to thrive.
Teachers Are Using AI to Create New Worlds, Help Students with Homework, and Teach English — from themarkup.org by Ross Teixeira; via Matthew Tower
Around the world, these seven teachers are making AI work for them and their students
In this article, seven teachers across the world share their insights on AI tools for educators. You will hear a host of varied opinions and perspectives on everything from whether AI could hasten the decline of learning foreign languages to whether AI-generated lesson plans are an infringement on teachers’ rights. A common theme emerged from those we spoke with: just as the internet changed education, AI tools are here to stay, and it is prudent for teachers to adapt.
Teachers Desperately Need AI Training. How Many Are Getting It? — from edweek.org by Lauraine Langreo
Even though it’s been more than a year since ChatGPT made a big splash in the K-12 world, many teachers say they are still not receiving any training on using artificial intelligence tools in the classroom.
More than 7 in 10 teachers said they haven’t received any professional development on using AI in the classroom, according to a nationally representative EdWeek Research Center survey of 953 educators, including 553 teachers, conducted between Jan. 31 and March 4.
From DSC:
This article mentioned the following resource:
Artificial Intelligence Explorations for Educators — from iste.org
NVIDIA just released FREE online courses in AI.
Here are 9 courses you can’t afford to miss: pic.twitter.com/4vkwX6SU07
— Shruti Mishra (@heyshrutimishra) March 22, 2024
How Early Adopters of Gen AI Are Gaining Efficiencies — from knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu by Prasanna (Sonny) Tambe and Scott A. Snyder; via Ray Schroeder on LinkedIn
Enterprises are seeing gains from generative AI in productivity and strategic planning, according to speakers at a recent Wharton conference.
Its unique strengths in translation, summation, and content generation are especially useful in processing unstructured data. Some 80% of all new data in enterprises is unstructured, he noted, citing research firm Gartner. Very little of that unstructured data that resides in places like emails “is used effectively at the point of decision making,” he noted. “[With gen AI], we have a real opportunity” to garner new insights from all the information that resides in emails, team communication platforms like Slack, and agile project management tools like Jira, he said.
6 YouTube Channels to Stay Up to Date with AI — from heaigirl.substack.com by Diana Dovgopol
Here are some cool AI YouTube channels.
Here are 6 YouTube channels I watch to stay up to date with AI. This list will be useful whether you’re a casual AI enthusiast or an experienced programmer.
1. Matt Wolfe: AI for non-coders
This is a fast-growing YouTube channel focused on artificial intelligence for non-coders. On this channel, you’ll find videos about ChatGPT, Midjourney, and any AI tool that it’s gaining popularity.
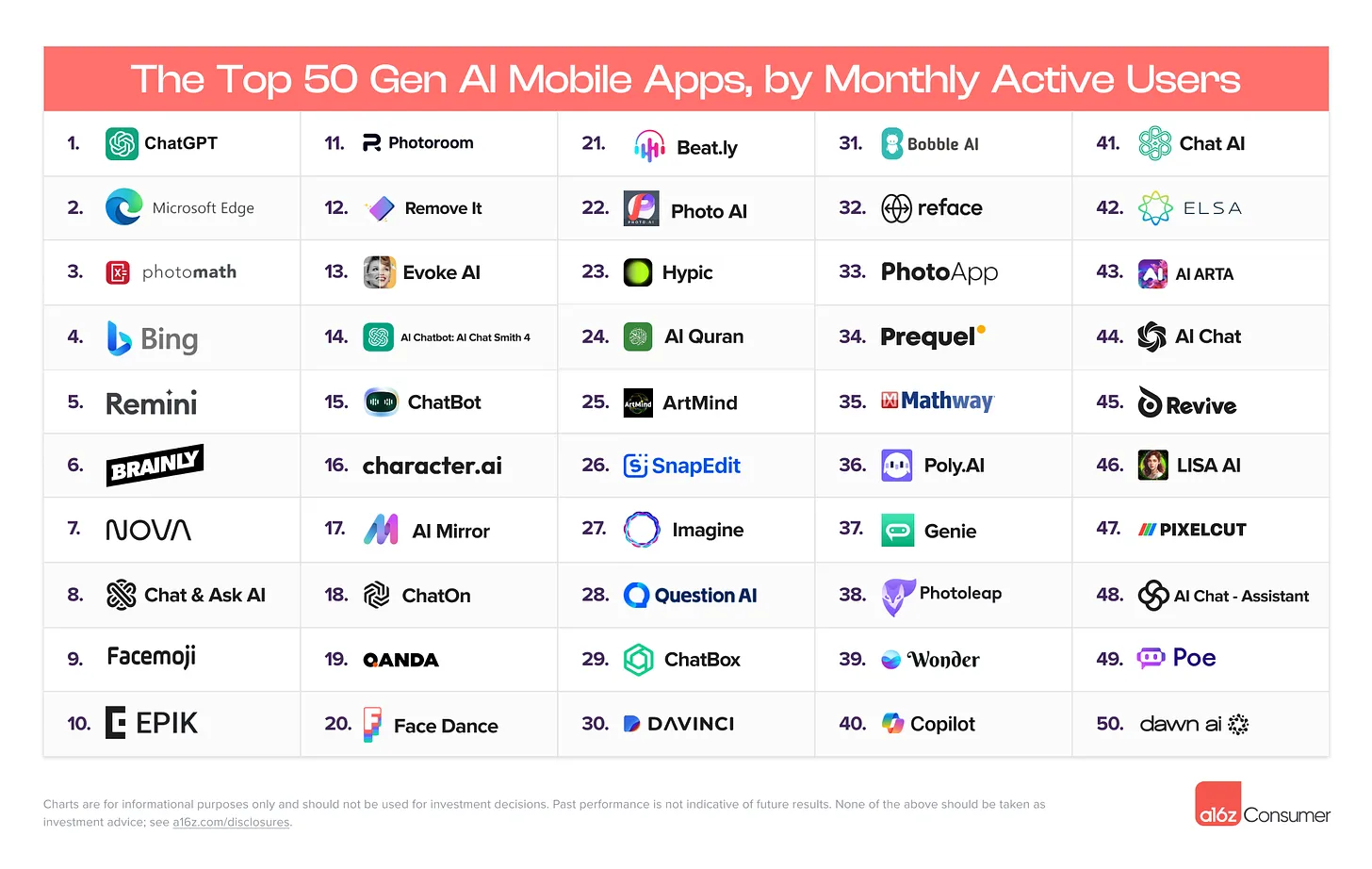
Top AI mobile apps, Stable Video 3D, & my AI film workflow — from by Heather Cooper
Plus 1-Click 3D animation and other cool AI tools
#3 Photomath
Photomath is a comprehensive math help app that provides step-by-step explanations for a wide range of math problems, from elementary to college level. Photomath is only available as a mobile app. (link)
Features:
- Get step-by-step solutions with multiple methods to choose from
- Scan any math problem, including word problems, using the app’s camera
- Access custom visual aids and extra “how” and “why” tips for deeper understanding
Google researchers unveil ‘VLOGGER’, an AI that can bring still photos to life — from venturebeat.com by Michael Nuñez
Google researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence system that can generate lifelike videos of people speaking, gesturing and moving — from just a single still photo. The technology, called VLOGGER, relies on advanced machine learning models to synthesize startlingly realistic footage, opening up a range of potential applications while also raising concerns around deepfakes and misinformation.
Google just dropped VLOGGER and it’s insane
This is ChatGPT for Image to Talking Video
Here are 7 Powerful AI features you can’t afford to miss out pic.twitter.com/84gcWbQ4cG
— Poonam Soni (@CodeByPoonam) March 20, 2024
What We Risk By Automating Tasks We Loathe — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
I’m fascinated by the potential of these tools to augment and enhance our work and creativity. There’s no denying the impressive capabilities we’re already seeing with text generation, image creation, coding assistance, and more. Used thoughtfully, AI can be a powerful productivity multiplier.
At the same time, I have significant concerns about the broader implications of this accelerating technology, especially for education and society at large. We’re traversing new ground at a breakneck pace, and it’s crucial that we don’t blindly embrace AI without considering the potential risks.
My worry is that by automating away too many tasks, even seemingly rote ones like creating slide decks, we risk losing something vital—humanity at the heart of knowledge work.
Nvidia Introduce AI Nurses — from wireprompt.substack.com | Weekkly AI Report from WirePrompt
Nvidia has announced a partnership with Hippocratic AI to introduce AI “agents” aimed at replacing nurses in hospitals. These AI “nurses” come at a significantly low cost compared to human nurses and are purportedly intended to address staffing issues by handling “low-risk,” patient-facing tasks via video calls. However, concerns are raised regarding the ethical implications and effectiveness of replacing human nurses with AI, particularly given the complex nature of medical care.
A glimpse of the future of AI at work:
I got early access to Devin, the “AI developer” – it is slow & breaks often, but you can start to see what an AI agent can do.
It makes a plan and executes it autonomously, doing research, writing code & debugging, without you watching. pic.twitter.com/HHBQQDQZ9q
— Ethan Mollick (@emollick) March 15, 2024
16 Changes to the Way Enterprises Are Building and Buying Generative AI — from a16z.com by Sarah Wang and Shangda Xu
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Resourcing: budgets are growing dramatically and here to stay
- Models: enterprises are trending toward a multi-model, open source world
- Use cases: more migrating to production
- Size of total opportunity: massive and growing quickly
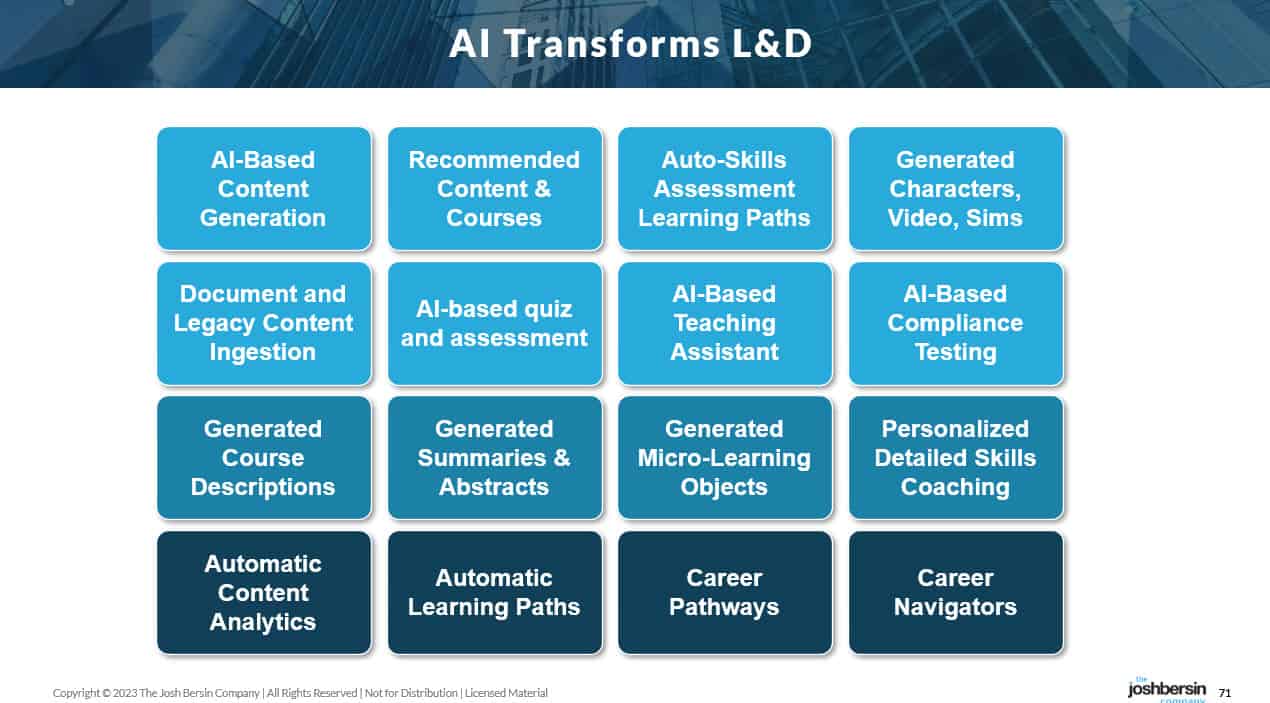
The $340 Billion Corporate Learning Industry Is Poised For Disruption — from joshbersin.com by Josh Bersin
What if, for example, the corporate learning system knew who you were and you could simply ask it a question and it would generate an answer, a series of resources, and a dynamic set of learning objects for you to consume? In some cases you’ll take the answer and run. In other cases you’ll pour through the content. And in other cases you’ll browse through the course and take the time to learn what you need.
And suppose all this happened in a totally personalized way. So you didn’t see a “standard course” but a special course based on your level of existing knowledge?
This is what AI is going to bring us. And yes, it’s already happening today.
GTC March 2024 Keynote with NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang
Also relevant/see:
- NVIDIA Launches Blackwell-Powered DGX SuperPOD for Generative AI Supercomputing at Trillion-Parameter Scale
Scales to Tens of Thousands of Grace Blackwell Superchips Using Most Advanced NVIDIA Networking, NVIDIA Full-Stack AI Software, and Storage Features up to 576 Blackwell GPUs Connected as One With NVIDIA NVLink NVIDIA System Experts Speed Deployment for Immediate AI Infrastructure

- NVIDIA Unveils Digital Blueprint for Building Next-Gen Data Centers
Omniverse digital twin supported by Ansys, Cadence, PATCH MANAGER, Schneider Electric, Vertiv and more, setting foundation for highly efficient AI infrastructure. - NVIDIA Digital Human Technologies Bring AI Characters to Life
Leading AI Developers Use Suite of NVIDIA Technologies to Create Lifelike Avatars and Dynamic Characters for Everything From Games to Healthcare, Financial Services and Retail Applications - NVIDIA Announces Omniverse Cloud APIs to Power Wave of Industrial Digital Twin Software Tools
Ansys, Cadence, Hexagon, Microsoft, Rockwell Automation, Siemens, Trimble Adopt Omniverse Technologies to Help Customers Design, Simulate, Build and Operate Physically Based Digital Twins - Climate Pioneers: 3 Startups Harnessing NVIDIA’s AI and Earth-2 Platforms
NVIDIA Inception members Tomorrow.io, ClimaSens and north.io specialize in extreme weather prediction, advance climate action across the globe.
Today is the beginning of our moonshot to solve embodied AGI in the physical world. I’m so excited to announce Project GR00T, our new initiative to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robot learning.
The GR00T model will enable a robot to understand multimodal… pic.twitter.com/EqN19Z3cXH
— Jim Fan (@DrJimFan) March 18, 2024
NVIDIA just announced GR00T.
It will enable a robot to understand multimodal instructions like language, video, and motion.
Very soon we will see them cooking, preparing coffee, in supermarkets, changing tires, etc.pic.twitter.com/3PptgNS1Yi
— Barsee ? (@heyBarsee) March 19, 2024
Immersive virtual reality tackles depression stigma says study — from inavateonthenet.net
A new study from the University of Tokyo has highlighted the positive effect that immersive virtual reality experiences have for depression anti-stigma and knowledge interventions compared to traditional video.
…
The study found that depression knowledge improved for both interventions, however, only the immersive VR intervention reduced stigma. The VR-powered intervention saw depression knowledge score positively associated with a neural response in the brain that is indicative of empathetic concern. The traditional video intervention saw the inverse, with participants demonstrating a brain-response which suggests a distress-related response.
From DSC:
This study makes me wonder why we haven’t heard of more VR-based uses in diversity training. I’m surprised we haven’t heard of situations where we are put in someone else’s mocassins so to speak. We could have a lot more empathy for someone — and better understand their situation — if we were to experience life as others might experience it. In the process, we would likely uncover some hidden biases that we have.
Addendum on 3/12/24:
Augmented reality provides benefit for Parkinson’s physical therapy — from inavateonthenet.net
How a Hollywood Director Uses AI to Make Movies — from every.to by Dan Shipper
Dave Clarke shows us the future of AI filmmaking
Dave told me that he couldn’t have made Borrowing Time without AI—it’s an expensive project that traditional Hollywood studios would never bankroll. But after Dave’s short went viral, major production houses approached him to make it a full-length movie. I think this is an excellent example of how AI is changing the art of filmmaking, and I came out of this interview convinced that we are on the brink of a new creative age.
We dive deep into the world of AI tools for image and video generation, discussing how aspiring filmmakers can use them to validate their ideas, and potentially even secure funding if they get traction. Dave walks me through how he has integrated AI into his movie-making process, and as we talk, we make a short film featuring Nicolas Cage using a haunted roulette ball to resurrect his dead movie career, live on the show.
Adobe Brings Conversational AI to Trillions of PDFs with the New AI Assistant in Reader and Acrobat — from news.adobe.com; via AI Secret

.
SAN JOSE, Calif. – [On 2/20/23], Adobe (Nasdaq:ADBE) introduced AI Assistant in beta, a new generative AI-powered conversational engine in Reader and Acrobat.
…
Simply open Reader or Acrobat and start working with the new capabilities, including:
- AI Assistant: AI Assistant recommends questions based on a PDF’s content and answers questions about what’s in the document – all through an intuitive conversational interface.
- Generative summary: Get a quick understanding of the content inside long documents with short overviews in easy-to-read formats.
- Intelligent citations: Adobe’s custom attribution engine and proprietary AI generate citations so customers can easily verify the source of AI Assistant’s answers.
- Easy navigation:
- Formatted output:
- Respect for customer data:
- Beyond PDF: Customers can use AI Assistant with all kinds of document formats (Word, PowerPoint, meeting transcripts, etc.)
Along these lines, also see:
- Adobe Acrobat gets an AI assistant. — from bensbites.beehiiv.com
- Adobe Acrobat — from adobe.com
5 ways Sora AI will change the creator economy and how to take advantage of that — from techthatmatters.beehiiv.com by Harsh Makadia
Essential skills to thrive with Sora AI
The realm of video editing isn’t about cutting and splicing.
A Video Editor should learn a diverse set of skills to earn money, such as:
- Prompt Writing
- Software Mastery
- Problem-solving skills
- Collaboration and communication skills
- Creative storytelling and visual aesthetics
Invest in those skills that give you a competitive edge.
The text file that runs the internet — from theverge.com by David Pierce
For decades, robots.txt governed the behavior of web crawlers. But as unscrupulous AI companies seek out more and more data, the basic social contract of the web is falling apart.
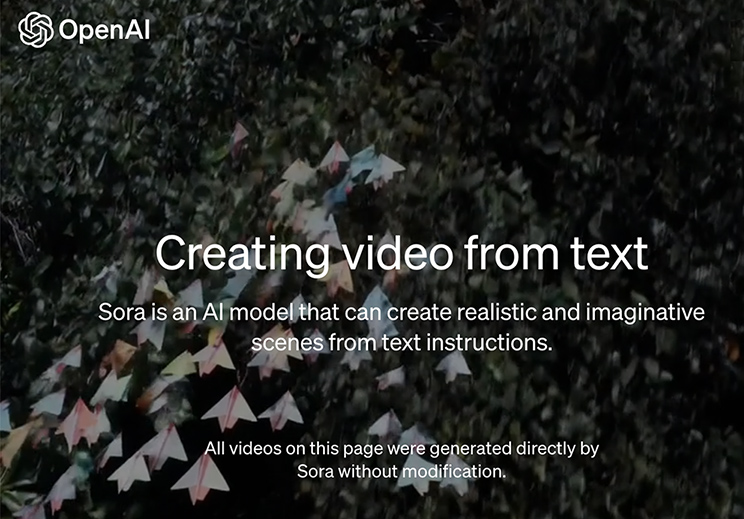
Text to video via OpenAI’s Sora. (I had taken this screenshot on the 15th, but am posting it now.)
We’re teaching AI to understand and simulate the physical world in motion, with the goal of training models that help people solve problems that require real-world interaction.
Introducing Sora, our text-to-video model. Sora can generate videos up to a minute long while maintaining visual quality and adherence to the user’s prompt.
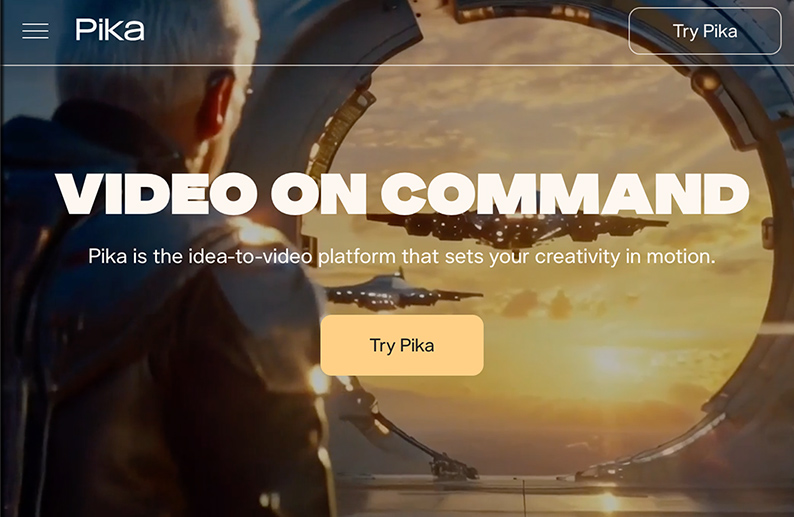
Along these lines, also see:
Pika; via Superhuman AI
? BREAKING: OpenAI just announced their new Text-To-Video model called Sora.
Look at these 10 insane examples:
1. Space movie trailer featuring a man wearing a red wool knitted motorcycle helmet pic.twitter.com/Z8ezF69Tar
— Alvaro Cintas (@dr_cintas) February 15, 2024
An Ivy League school just announced its first AI degree — from qz.com by Michelle Cheng; via Barbara Anna Zielonka on LinkedIn
It’s a sign of the times. At the same time, AI talent is scarce
At the University of Pennsylvania, undergraduate students in its school of engineering will soon be able to study for a bachelor of science degree in artificial intelligence.
What can one do with an AI degree? The University of Pennsylvania says students will be able to apply the skills they learn in school to build responsible AI tools, develop materials for emerging chips and hardware, and create AI-driven breakthroughs in healthcare through new antibiotics, among other things.
Google Pumps $27 Million Into AI Training After Microsoft Pledge—Here’s What To Know — from forbes.com by Robert Hart
Google on Monday announced plans to help train people in Europe with skills in artificial intelligence, the latest tech giant to invest in preparing workers and economies amid the disruption brought on by technologies they are racing to develop.
The Exhausting Pace of AI: Google’s Ultra Leap — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
The acceleration of AI deployments has gotten so absurdly out of hand that a draft post I started a week ago about a new development is now out of date.
…
The Pace is Out of Control
A mere week since Ultra 1.0’s announcement, Google has now introduced us to Ultra 1.5, a model they are clearly positioning to be the leader in the field. Here is the full technical report for Gemini Ultra 1.5, and what it can do is stunning.
Maryville Announces $21 Million Investment in AI and New Technologies Amidst Record Growth — from maryville.edu; via Arthur “Art” Fredrich on LinkedIn
[St. Louis, MO, February 14, 2024] – In a bold move that counters the conventions of more traditional schools, Maryville University has unveiled a substantial $21 million multi-year investment in artificial intelligence (AI) and cutting-edge technologies. This groundbreaking initiative is set to transform the higher education experience to be powered by the latest technology to support student success and a five-star experience for thousands of students both on-campus and online.
From DSC:
I recently ran into the following item:
UK university opens VR classroom — from inavateonthenet.net
Students at the University of Nottingham will be learning through a dedicated VR classroom, enabling remote viewing and teaching for students and lecturers.
Based in the university’s Engineering Science and Learning Centre (ELSC), this classroom, believed to be the first in the UK to use a dedicated VR classroom, using 40 VR headsets, 35 of which are tethered overhead to individual PCs, with five available as traditional, desk-based systems with display screens.
I admit that I was excited to see this article and I congratulate the University of Nottingham on their vision here. I hope that they can introduce more use cases and applications to provide evidence of VR’s headway.
As I look at virtual reality…
- On the plus side, I’ve spoken with people who love to use their VR-based headsets for fun workouts/exercises. I’ve witnessed the sweat, so I know that’s true. And I believe there is value in having the ability to walk through museums that one can’t afford to get to. And I’m sure that the gamers have found some incredibly entertaining competitions out there. The experience of being immersed can be highly engaging. So there are some niche use cases for sure.
- But on the negative side, the technologies surrounding VR haven’t progressed as much as I thought they would have by now. For example, I’m disappointed Apple’s taken so long to put a product out there, and I don’t want to invest $3500 in their new product. From the reviews and items on social media that I’ve seen, the reception is lukewarm. At the most basic level, I’m not sure people want to wear a headset for more than a few minutes.
So overall, I’d like to see more use cases and less nausea.
Addendum on 2/27/24:
Leyard ‘wall of wonder’ wows visitors at Molecular Biology Lab — from inavateonthenet.net











.webp)