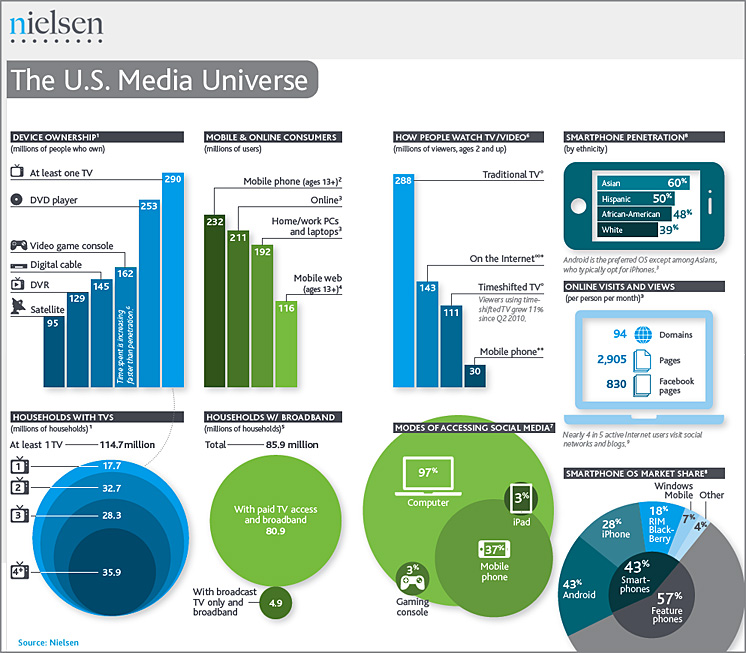
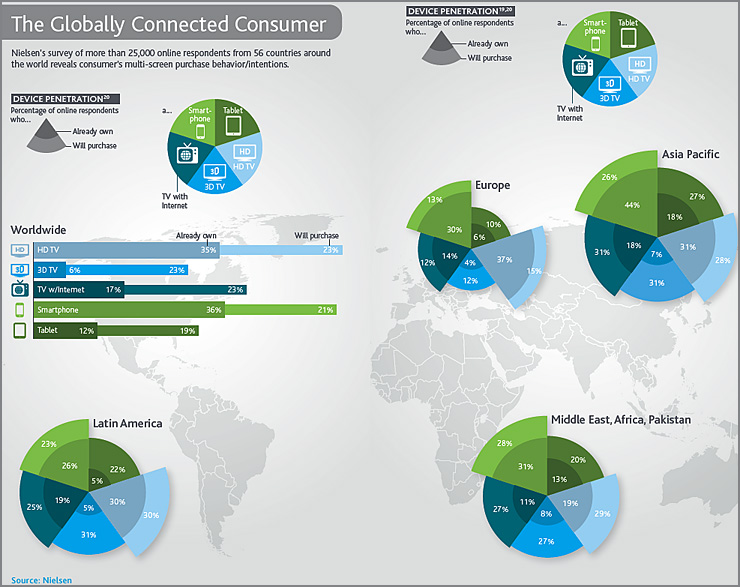
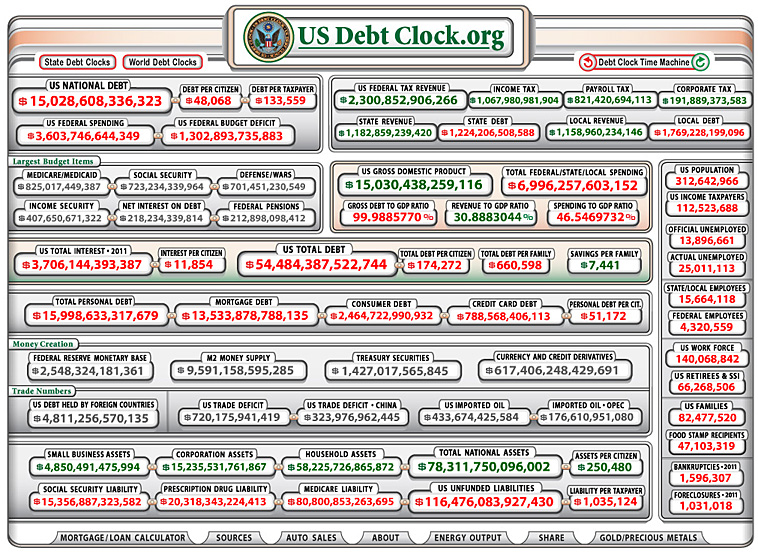
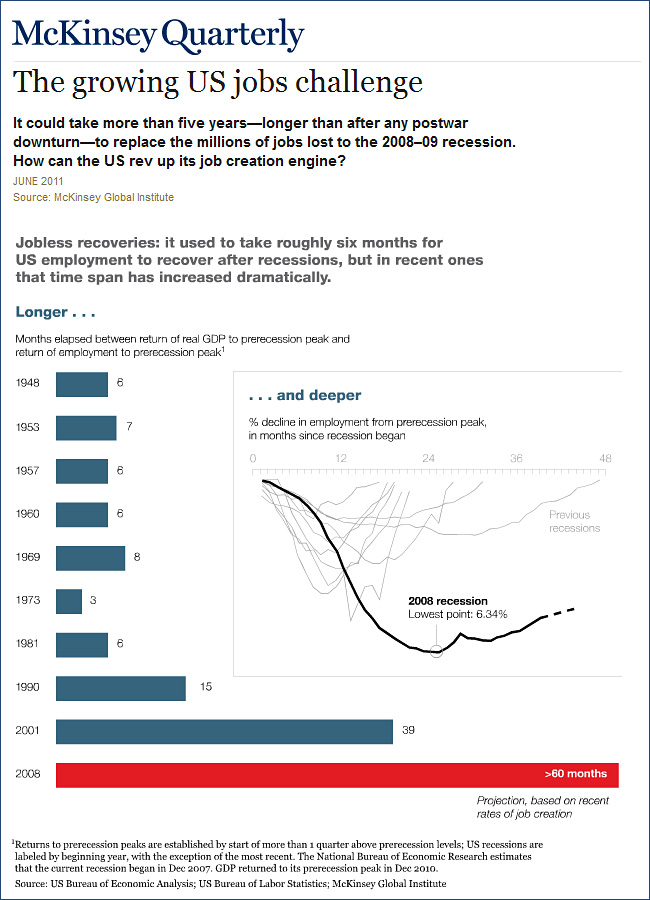
.
Official calls for urgency on college costs— from the New York Times by Tamar Lewin
Excerpts:
As Occupy movement protests helped push spiraling college costs into the national spotlight, Education Secretary Arne Duncan urged higher-education officials Tuesday to “think more creatively — and with much greater urgency” about ways to contain costs and reduce student debt.
…
“Three in four Americans now say that college is too expensive for most people to afford,” Mr. Duncan said. “That belief is even stronger among young adults — three-fourths of whom believe that graduates today have more debt than they can manage.”
Also see:
- Outrage: New York Times Reports that Ohio State’s Football Coach to Earn up to $4 Million a Year — from StraighterLine.com
Addendum later on 11/30/11:
- Our Students Deserve No Less – from ed.gov by Cameron Brenchley
.
“My chief message today is a sobering one,” said Secretary Duncan yesterday at the annual Federal Student Aid conference in Las Vegas, Nev. “I want to ask you, and the entire higher education community, to look ahead and start thinking more creatively—and with much greater urgency—about how to contain the spiraling costs of college and reduce the burden of student debt on our nation’s students.”
As of 11/20/11 (~2:00pm EST)
.
As of 8/24/11:
.
From DSC:
With the increase in globalization — and from what I’ve seen happening in the financial systems (i.e. how what happens in Europe affects the financial systems in the U.S./Asia/other and vice versa) — it seems clear that we are all in this boat together. If that’s true, what does that mean for:
- Businesses and economies around the world?
- The ability of families and individuals to afford the increasing cost of getting a degree?
- Higher educational systems — and business models — around the world?
- How do we resolve such massive problems?
- What does all of this mean for how we should be educating our students?
Addendum on 11/21/11:
- Debt committee: Why $1.2 trillion isn’t enough — from money.cnn.com by Jeanne Sahadi
Excerpts:
That’s because under the most likely scenario, reducing deficits by $1.2 trillion won’t stop the accumulated debt from growing faster than the economy.
…
Thus, to stabilize the debt, Congress would need to pass a debt-reduction plan worth $4 trillion to $6 trillion, budget experts say.
From DSC:
How is it that corporations are sitting on trillions of dollars (estimates vary) but the unemployment rate continues to be towards the high end of historical unemployment rates? Where’s the love and compassion for one’s fellow man? (Some of Charles Dickens’ writings in The Christmas Carol come to my mind here…)
One has to ask, what’s the state of our hearts these days? Is business just about serving the almighty shareholder? Is that the ultimate goal of our businesses? Seriously…what percentage of Americans is that perspective currently benefiting? (I don’t have the answer/data, but I bet its not a majority of Americans. The lines at the soup kitchens and shelters are getting longer, not shorter.) Corporations have — today — the power to change the situation. But what’s the ultimate vision of our corporations? Who do our corporations ultimately serve?

Some relevant articles:
- Corporate profits at all-time high as recovery stumbles (March, 2011, The HuffingtonPost.com)
NEW YORK — Despite high unemployment and a largely languishing real estate market, U.S. businesses are more profitable than ever, according to federal figures released on Friday. U.S. corporate profits hit an all-time high at the end of 2010, with financial firms showing some of the biggest gains, data from the federal Bureau of Economic Analysis show. Corporations reported an annualized $1.68 trillion in profit in the fourth quarter. The previous record, without being adjusted for inflation, was $1.65 trillion in the third quarter of 2006. Many of the nation’s preeminent companies have posted massive increases in profits this year. General Electric posted worldwide profits of $14.2 billion, while profits at JPMorgan Chase were up 47 percent to $4.8 billion. - Remarks by the President to the Chamber of Commerce — President Barack Obama (February 7, 2011 from U.S. Chamber of Commerce Headquarters, Washington, D.C.)
“So if I’ve got one message, my message is now is the time to invest in America. Now is the time to invest in America. (Applause.) Today, American companies have nearly $2 trillion sitting on their balance sheets. And I know that many of you have told me that you’re waiting for demand to rise before you get off the sidelines and expand, and that with millions of Americans out of work, demand has risen more slowly than any of us would like.” - Hoarding, not hiring – Corporations stockpile mountain of cash (April, 2010, ABCNews.com)
- U.S. firms build up record cash piles (June 2010, WSJ)
- Corporate America sitting on $1 trillion in cash ($2 trillion if you count short-term investments) (Dec. 2010 from JoshuaKennon.com)
…
What does that mean? It means that when the fear subsides, and companies are convinced that the world is all sunshine and roses, the turnaround can be rapid. Putting $1 trillion of cash to work in the economy, whether in the form of new product launches, capital expenditures, or even mergers and acquisitions paying off investors for their shares of companies and forcing them to find another use for their newly freed funds, can go a long way to solving the unemployment figures.
Addendum on 10/4/11 to potentially address a part of the other side of the table here:
- Economic Conditions Snapshot, September 2011: McKinsey Global Survey results |SEPTEMBER 2011
Our latest survey shows just how gloomy executives’ economic expectations are. A majority fear the eurozone will splinter; those in emerging markets are most hopeful.
Google spending tons of money turning YouTube into a cable alternative — from dvice.com
Google TV will disrupt television, ready or not — from informitv.com
Excerpt:
Google TV is set to launch in Europe early in 2012, following a reboot in the United States that will help developers to create applications for the platform. Dr Eric Schmidt, the chairman of Google, used his keynote speech at the Edinburgh International Television Festival to call for co-operation with the television industry, between the luvvies and boffins, saying Google seeks to be a friend, not a foe, in addressing an increasingly global opportunity. Yet many in the traditionally territorial television industry may still be wary of geeks bearing gifts, suspiciously viewing Google TV as a Trojan horse at the living room door.