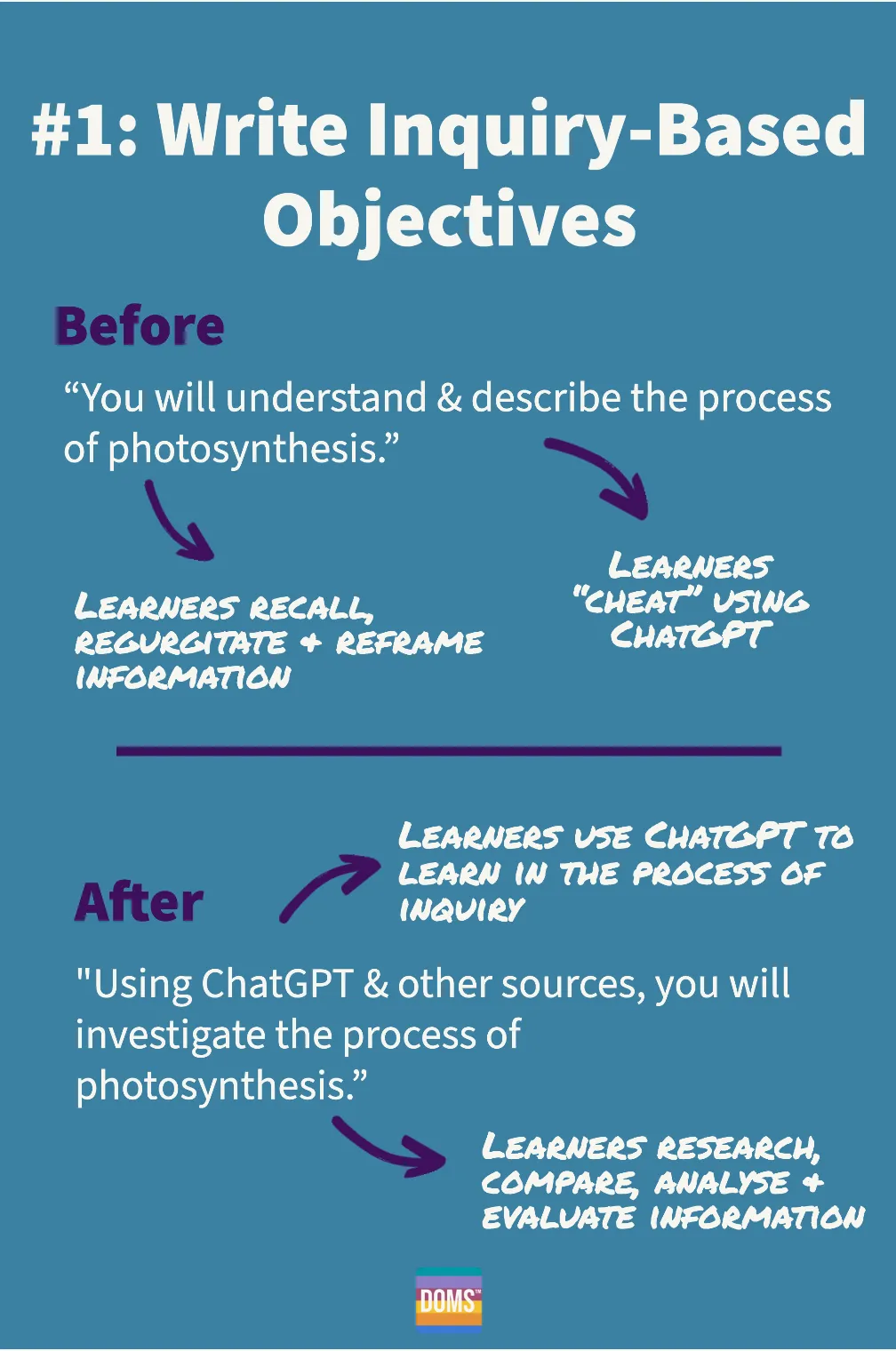
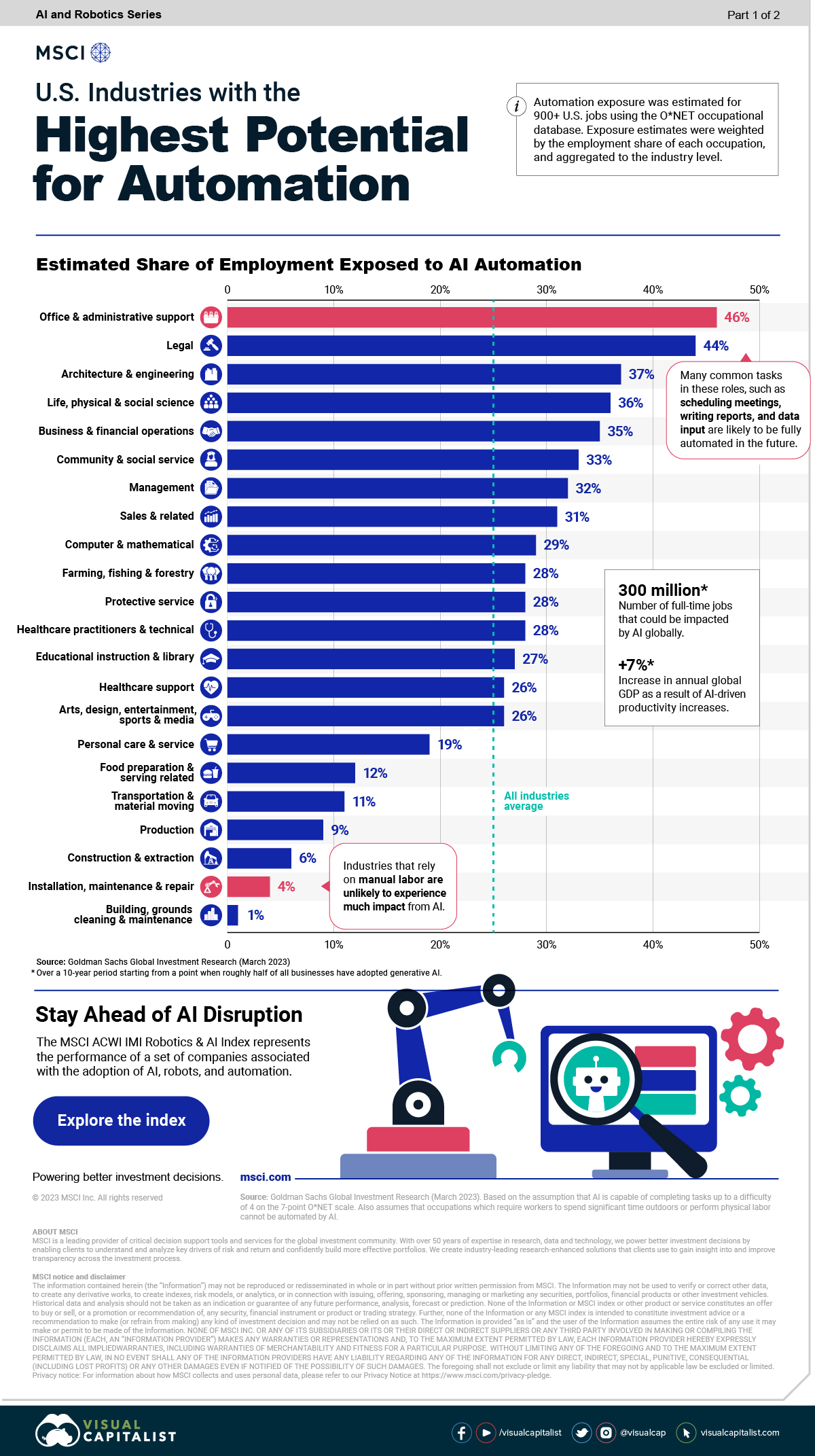
Introducing Superalignment — from openai.com
We need scientific and technical breakthroughs to steer and control AI systems much smarter than us. To solve this problem within four years, we’re starting a new team, co-led by Ilya Sutskever and Jan Leike, and dedicating 20% of the compute we’ve secured to date to this effort. We’re looking for excellent ML researchers and engineers to join us.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
How do we ensure AI systems much smarter than humans follow human intent?
…
Currently, we don’t have a solution for steering or controlling a potentially superintelligent AI, and preventing it from going rogue. Our current techniques for aligning AI, such as reinforcement learning from human feedback, rely on humans’ ability to supervise AI. But humans won’t be able to reliably supervise AI systems much smarter than us, and so our current alignment techniques will not scale to superintelligence. We need new scientific and technical breakthroughs.
…
Our goal is to build a roughly human-level automated alignment researcher. We can then use vast amounts of compute to scale our efforts, and iteratively align superintelligence.
From DSC:
Hold up. We’ve been told for years that AI is at the toddler stage. But now assertions are being made that AI systems are smarter than humans — much smarter even. That said, then why is the goal of OpenAI to build a roughly human-level automated alignment researcher if humans aren’t that smart after all…? Which is it? I must be missing or misunderstanding something here…
OpenAI are jumping back on the alignment bandwagon with the brilliantly-named Superalignment Team. And you guessed it – they’re researching alignment of future superintelligent AIs. They reckon that AI can align other AI faster than humans can, and the plan is to build an AI that does just that. Head-spinning stuff…
Ben’s Bites
Plus…
Who else should be on this team? We certainly don’t want a team comprised of just technical people. How about including rabbis, pastors, priests, parents, teachers, professors, social workers, judges, legislators, and many others who can help represent other specialties, disciplines, and perspectives to protect society?
Authors file a lawsuit against OpenAI for unlawfully ‘ingesting’ their books — from theguardian.com by Ella Creamer; via Ben’s Bytes
Mona Awad and Paul Tremblay allege that their books, which are copyrighted, were ‘used to train’ ChatGPT because the chatbot generated ‘very accurate summaries’ of the works
.
How AI is Transforming Workplace Architecture and Design — from workdesign.com by Christian Lehmkuhl

London Futurists | Generative AI drug discovery breakthrough, with Alex Zhavoronkov — from londonfuturists.buzzsprout.com
Alex Zhavoronkov is our first guest to make a repeat appearance, having first joined us in episode 12, last November. We are delighted to welcome him back, because he is doing some of the most important work on the planet, and he has some important news.
In 2014, Alex founded Insilico Medicine, a drug discovery company which uses artificial intelligence to identify novel targets and novel molecules for pharmaceutical companies. Insilico now has drugs designed with AI in human clinical trials, and it is one of a number of companies that are demonstrating that developing drugs with AI can cut the time and money involved in the process by as much as 90%.
Watch This Space: New Field of Spatial Finance Uses AI to Estimate Risk, Monitor Assets, Analyze Claims — from blogs.nvidia.com
When making financial decisions, it’s important to look at the big picture — say, one taken from a drone, satellite or AI-powered sensor.
The emerging field of spatial finance harnesses AI insights from remote sensors and aerial imagery to help banks, insurers, investment firms and businesses analyze risks and opportunities, enable new services and products, measure the environmental impact of their holdings, and assess damage after a crisis.
Secretive hardware startup Humane’s first product is the Ai Pin — from techcrunch.com by Kyle Wiggers; via The Rundown AI
Excerpt:
Humane, the startup launched by ex-Apple design and engineering duo Imran Chaudhri and Bethany Bongiorno, today revealed details about its first product: The Humane Ai Pin.
…
Humane’s product, as it turns out, is a wearable gadget with a projected display and AI-powered features. Chaudhri gave a live demo of the device onstage during a TED Talk in April, but a press release issued today provides a few additional details.

He Spent $140 Billion on AI With Little to Show. Now He Is Trying Again. — from wsj.com by Eliot Brown; via Superhuman
Billionaire Masayoshi Son said he would make SoftBank ‘the investment company for the AI revolution,’ but he missed out on the most recent frenzy
“Stunning”—Midjourney update wows AI artists with camera-like feature — from arstechnica.com by Benj Edwards; via Sam DeBrule from Machine Learnings
Midjourney v5.2 features camera-like zoom control over framing, more realism.

What is AIaaS? Guide to Artificial Intelligence as a Service — from eweek.com by Shelby Hiter
Artificial intelligence as a service, AIaaS, is an outsourced AI service provided by cloud-based AI providers.
AIaaS Definition
When a company is interested in working with artificial intelligence but doesn’t have the in-house resources, budget, and/or expertise to build and manage its own AI technology, it’s time to invest in AIaaS.
Artificial intelligence as a service, or AIaaS, is an outsourced service model AI that cloud-based companies provide to other businesses, giving them access to different AI models, algorithms, and other resources directly through a cloud computing platform; this access is usually managed through an API or SDK connection.
The Rise of the AI Engineer — from latent.space
Boost ChatGPT with new plugins — from wondertools.substack.com by Jeremy Caplan
Wonder Tools | Six new ways to use AI
.
A series re: AI from Jeff Foster out at ProvideoCoalition.com
The AI upskilling imperative to build a future-ready workforce — from businessinsider.com
Excerpts:
Skill development has always been crucial, but recent technological advancements have raised the stakes. We are currently in the midst of the fourth industrial revolution, where automation and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionising the workplace. In this era of quick change and short half-life of skills, upskilling shouldn’t be an afterthought. Instead, reskilling and upskilling have to evolve into requirements for effective professional development.
To understand the significance of upskilling for your career trajectory, it is important to recognise the ever-evolving nature of technology and the rapid pace of digital transformation. Business Insider India has been exploring how businesses and thought leaders are driving innovation by educating their staff on the technologies and skills that will shape the future.