Virtual or in-person: The next generation of trial lawyers must be prepared for anything — from reuters.com by Stratton Horres and Karen L. Bashor
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/VC6OEOGOOFDENO7BIW6JR6RGBU.jpg)
Excerpt:
In this article, we will examine several key ways in which COVID-19 has changed trial proceedings, strategy and preparation and how mentoring programs can make a difference.
…
COVID-19 has shaken up the jury trial experience for both new and experienced attorneys. For those whose only trials have been conducted during COVID-19 restrictions and for everyone easing back into the in-person trials, these are key elements to keep in mind practicing forward. Firm mentoring programs should be considered to prepare the future generation of trial lawyers for both live and virtual trials.
From DSC:
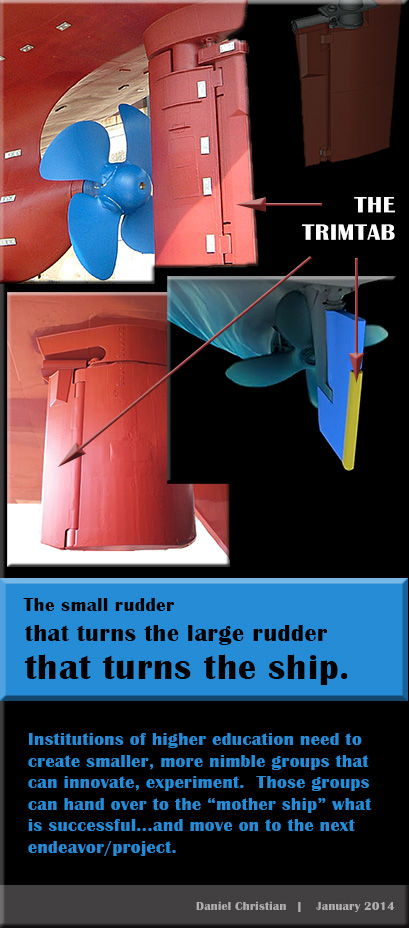
I think law firms will need to expand the number of disciplines coming to their strategic tables. That is, as more disciplines are required to successfully practice law in the 21st century, more folks with technical backgrounds and/or abilities will be needed. Web front and back end developers, User Experience Designers, Instructional Designers, Audio/Visual Specialists, and others come to my mind. Such people can help develop the necessary spaces, skills, training, and mentoring programs mentioned in this article. As within our learning ecosystems, the efficient and powerful use of teams of specialists will deliver the best products and services.