Adobe Announces the 2019 Release of Adobe Captivate, Introducing Virtual Reality for eLearning Design — from theblog.adobe.com
Excerpt:
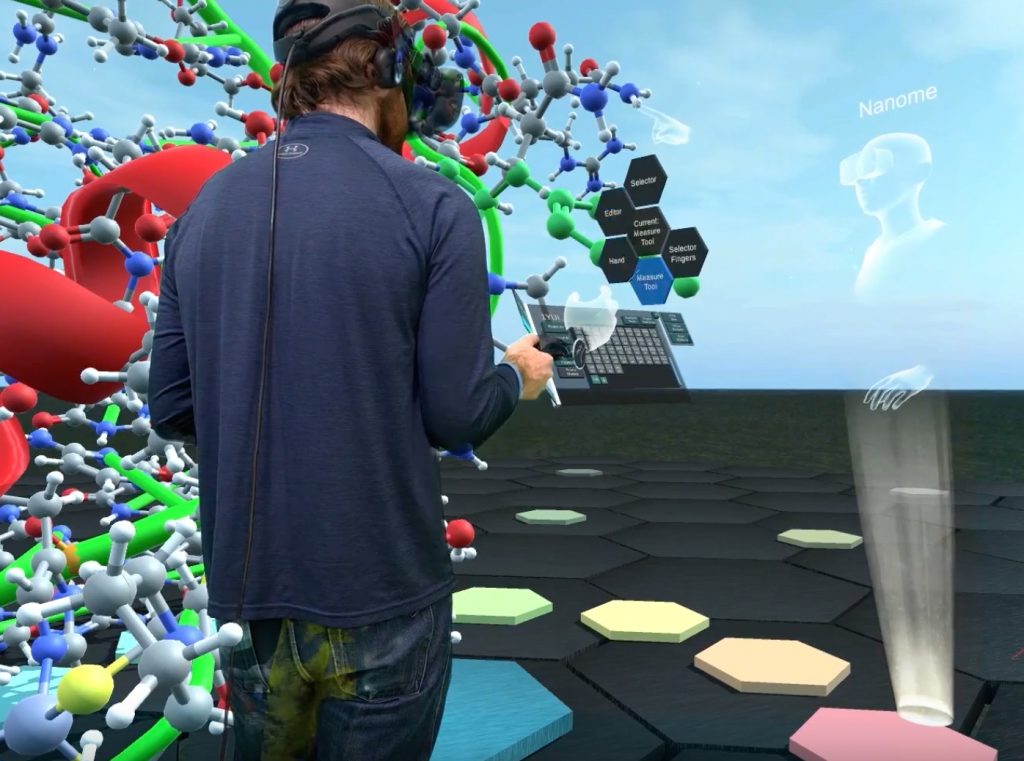
- Immersive learning with VR experiences: Design learning scenarios that your learners can experience in Virtual Reality using VR headsets. Import 360° media assets and add hotspots, quizzes and other interactive elements to engage your learners with near real-life scenarios
- Interactive videos: Liven up demos and training videos by making them interactive with the new Adobe Captivate. Create your own or bring in existing YouTube videos, add questions at specific points and conduct knowledge checks to aid learner remediation
- Fluid Boxes 2.0: Explore the building blocks of Smart eLearning design with intelligent containers that use white space optimally. Objects placed in Fluid Boxes get aligned automatically so that learners always get fully responsive experience regardless of their device or browser.
- 360° learning experiences: Augment the learning landscape with 360° images and videos and convert them into interactive eLearning material with customizable overlay items such as information blurbs, audio content & quizzes.
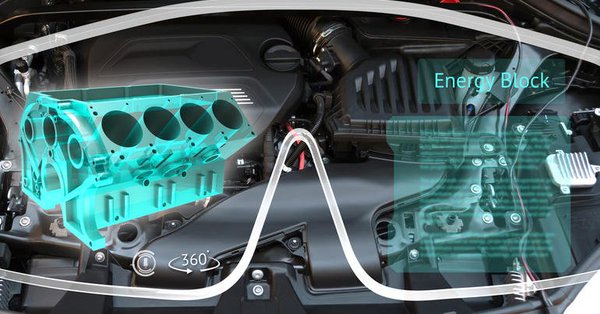
Blippar unveils indoor visual positioning system to anchor AR — from martechtoday.com by Barry Levine
Employing machine vision to recognize mapped objects, the company says it can determine which way a user is looking and can calculate positioning down to a centimeter.

The Storyteller’s Guide to the Virtual Reality Audience — from medium.com by Katy Newton
Excerpt:
To even scratch the surface of these questions, we need to better understand the audience’s experience in VR — not just their experience of the technology, but the way that they understand story and their role within it.
Hospital introducing HoloLens augmented reality into the operating room — from medgadget.com
Excerpt:
HoloLens technology is being paired with Microsoft’s Surface Hub, a kind of digital whiteboard. The idea is that the surgical team can gather together around a Surface Hub to review patient information, discuss the details of a procedure, and select what information should be readily accessible during surgery. During the procedure, a surgeon wearing a HoloLens would be able to review a CT or MRI scan, access other data in the electronic medical records, and to be able to manipulate these so as to get a clear picture of what is being worked on and what needs to be done.
Raleigh Fire Department invests in virtual reality to enrich training — from vrfocus.com by Nikholai Koolon
New system allows department personnel to learn new skills through immersive experiences.
Excerpt:
The VR solution allows emergency medical services (EMS) personnel to dive into a rich and detailed environment which allows them to pinpoint portions of the body to dissect. This then allows them then see each part of the body in great detail along with viewing it from any angle. The goal is to allow for users to gain the experience to diagnose injuries from a variety of vantage points all where working within an virtual environment capable of displaying countless scenarios.
For another emerging technology, see:
Someday this tiny spider bot could perform surgery inside your body — from fastcompany.com by Jesus Diaz
The experimental robots could also fix airplane engines and find disaster victims.
Excerpt:
A team of Harvard University researchers recently achieved a major breakthrough in robotics, engineering a tiny spider robot using tech that could one day work inside your body to repair tissues or destroy tumors. Their work could not only change medicine–by eliminating invasive surgeries–but could also have an impact on everything from how industrial machines are maintained to how disaster victims are rescued.
Until now, most advanced, small-scale robots followed a certain model: They tend to be built at the centimeter scale and have only one degree of freedom, which means they can only perform one movement. Not so with this new ‘bot, developed by scientists at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, the John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, and Boston University. It’s built at the millimeter scale, and because it’s made of flexible materials–easily moved by pneumatic and hydraulic power–the critter has an unprecedented 18 degrees of freedom.
Plus some items from a few weeks ago
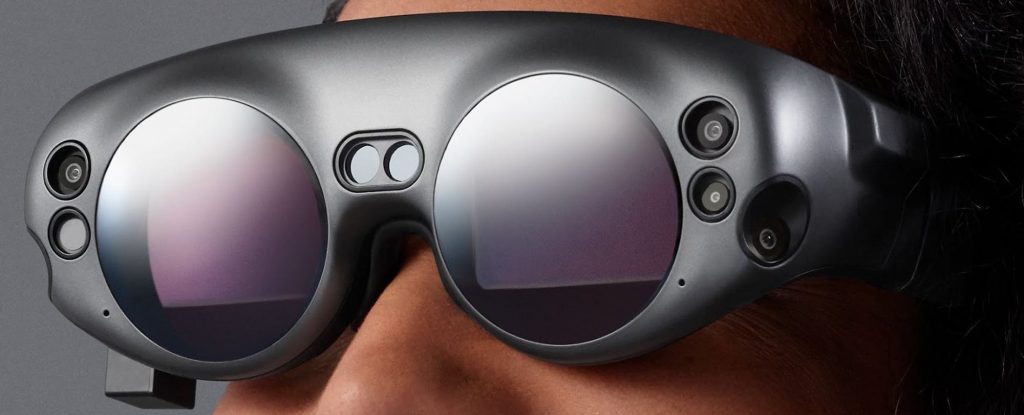
After almost a decade and billions in outside investment, Magic Leap’s first product is finally on sale for $2,295. Here’s what it’s like. — from
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
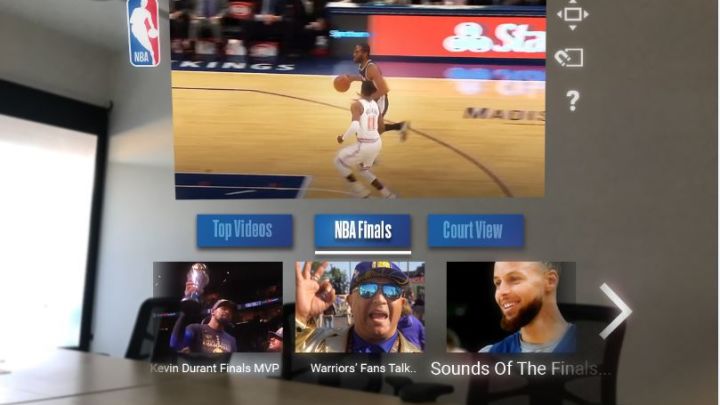
I liked that it gave a new perspective to the video clip I’d watched: It threw the actual game up on the wall alongside the kind of information a basketball fan would want, including 3-D renderings and stats. Today, you might turn to your phone for that information. With Magic Leap, you wouldn’t have to.
…
Abovitz also said that intelligent assistants will play a big role in Magic Leap’s future. I didn’t get to test one, but Abovitz says he’s working with a team in Los Angeles that’s developing high-definition people that will appear to Magic Leap users and assist with tasks. Think Siri, Alexa or Google Assistant, but instead of speaking to your phone, you’d be speaking to a realistic-looking human through Magic Leap. Or you might be speaking to an avatar of someone real.
“You might need a doctor who can come to you,” Abovitz said. “AI that appears in front of you can give you eye contact and empathy.”
And I loved the idea of being able to place a digital TV screen anywhere I wanted.
Magic Leap One Available For Purchase, Starting At $2,295 — from vrscout.com by Kyle Melnick
Excerpt:
December of last year U.S. startup Magic Leap unveiled its long-awaited mixed reality headset, a secretive device five years and $2.44B USD in the making.
This morning that same headset, now referred to as the Magic Leap One Creator Edition, became available for purchase in the U.S. On sale to creators at a hefty starting price of $2,275, the computer spatial device utilizes synthetic lightfields to capture natural lightwaves and superimpose interactive, 3D content over the real-world.
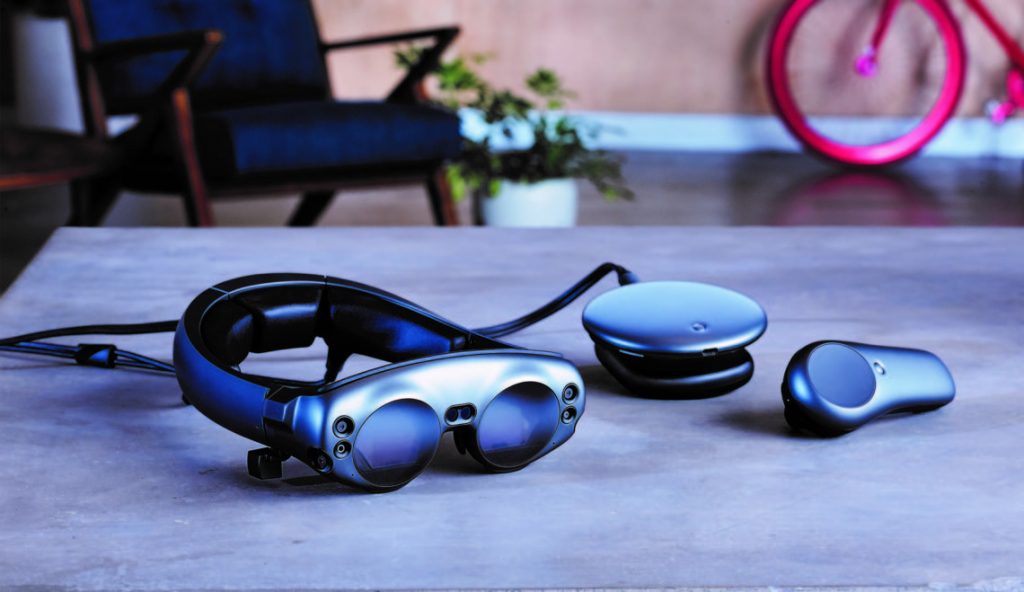

Magic Leap One First Hands-On Impressions for HoloLens Developers — from magic-leap.reality.news
Excerpt:
After spending about an hour with the headset running through set up and poking around its UI and a couple of the launch day apps, I thought it would be helpful to share a quick list of some of my first impressions as someone who’s spent a lot of time with a HoloLens over the past couple years and try to start answering many of the burning questions I’ve had about the device.
World Campus researches effectiveness of VR headsets and video in online classes — from news.psu.edu
Excerpt:
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Penn State instructional designers are researching whether using virtual reality and 360-degree video can help students in online classes learn more effectively.
Designers worked with professors in the College of Nursing to incorporate 360-degree video into Nursing 352, a class on Advanced Health Assessment. Students in the class, offered online through Penn State World Campus, were offered free VR headsets to use with their smartphones to create a more immersive experience while watching the video, which shows safety and health hazards in a patient’s home.
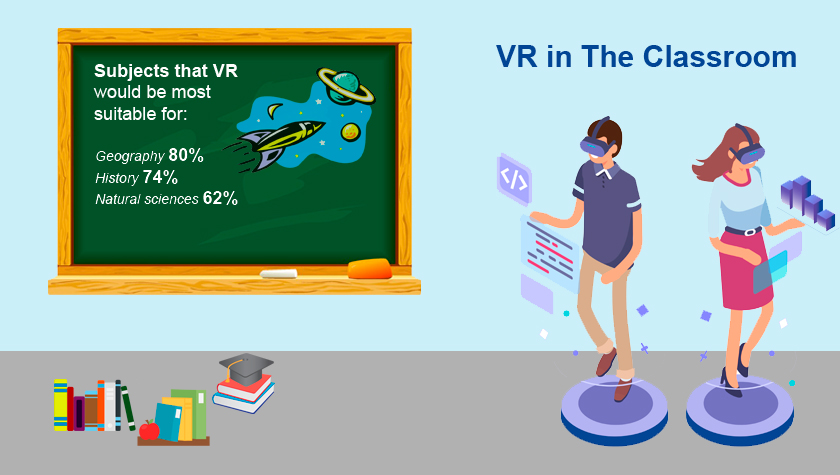
Bill Egan, the lead designer for the Penn State World Campus RN to BSN nursing program, said students in the class were surveyed as part of a study approved by the Institutional Review Board and overwhelmingly said that they enjoyed the videos and thought they provided educational value. Eighty percent of the students said they would like to see more immersive content such as 360-degree videos in their online courses, he said.
7 Practical Problems with VR for eLearning — from learnupon.com
Excerpt:
In this post, we run through some practical stumbling blocks that prevent VR training from being feasible for most.
…
There are quite a number of practical considerations which prevent VR from totally overhauling the corporate training world. Some are obvious, whilst others only become apparent after using the technology a number of times. It’s important to be made aware of these limitations so that a large investment isn’t made in tech that isn’t really practical for corporate training.
Augmented reality – the next big thing for HR? — from hrdconnect.com
Augmented reality (AR) could have a huge impact on HR, transforming long-established processes into engaging and exciting something. What will this look like? How can we shape this into our everyday working lives?
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
AR also has the potential to revolutionise our work lives, changing the way we think about office spaces and equipment forever.
Most of us still commute to an office every day, which can be a time-consuming and stressful experience. AR has the potential to turn any space into your own customisable workspace, complete with digital notes, folders and files – even a digital photo of your loved ones. This would give you access to all the information and tools that you would typically find in an office, but wherever and whenever you need them.
And instead of working on a flat, stationary, two-dimensional screen, your workspace would be a customisable three-dimensional space, where objects and information are manipulated with gestures rather than hardware. All you would need is an AR headset.
AR could also transform the way we advertise brands and share information. Imagine if your organisation had an AR stand at a conference – how engaging would that be for potential customers? How much more interesting and fun would meetings be if we used AR to present information instead of slides on a projector?
AR could transform the on-boarding experience into something fun and interactive – imagine taking an AR tour of your office, where information about key places, company history or your new colleagues pops into view as you go from place to place.
RETINA Are Bringing Augmented Reality To Air Traffic Control Towers — from vrfocus.com by Nikholai Koolonavi
Excerpt:
A new project is aiming to make it easier for staff in airport control towers to visualize information to help make their job easier by leveraging augmented reality (AR) technology. The project, dubbed RETINA, is looking to modernise Europe’s air traffic management for safer, smarter and even smoother air travel.