Web 3.0 vs Metaverse: What’s the difference? — from homo-digitalis.net by Fabian Schmidt
Excerpt:
So what is Web 3.0?
On Twitter, a user asked if someone could explain the term in baby talk. I thought one answer was good:
-
- Web 1.0 = Read
- Web 2.0 = Read/Write
- Web 3.0 = Read/Write/Own
This is a sufficient simplification to gain an initial understanding. Yet a bit more information is still important.
Let’s get one thing straight right away. As with all things in the making, there is not yet a clear-cut definition of Web 3.0. Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the classic web, thinks of the semantic web as the next big step.
…
Since 2020/2021, there is another idea of Web3, and it is inspired by a new form of technology: Blockchains. At its core is a new wave of decentralization.
Besides decentralization, other key topics related to Web 3.0 include Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO), Non-fungible-tokens (NFT), and Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
The metaverse is a digital world that is meant to feel as real as possible and can represent all concerns of human existence. From leisure to work.
Fabian Schmidt, Homo Digitalis, 2021
Bill Gates: Most Work Meetings Will Happen In The Metaverse In 3 Years — from vrscout.com by Kyle Melnick
Excerpt:
“Within the next two or three years, I predict most virtual meetings will move from 2D camera image grids—which I call the Hollywood Squares model, although I know that probably dates me—to the metaverse, a 3D space with digital avatars,” said Gates in the post. “Both Facebook and Microsoft recently unveiled their visions for this, which gave most people their first view of what it will look like”.
Adidas to enter the metaverse with first NFT products — from dezeen.com by Rima Sabina Aouf
Excerpt:
Adidas has announced its next collection will be a mix of digital and physical items, and will be sold as NFTs produced with collaborators such as Bored Ape Yacht Club.
Titled Into the Metaverse, the collection will comprise virtual wearables that buyers can use in online platforms, but also the physical clothing to match.
It is Adidas’ first collection of NFTs, or non-fungible tokens – essentially, digital collectibles with proven authenticity. NFTs act as a blockchain-based certificate of ownership, allowing pieces to be authenticated, bought and collected.
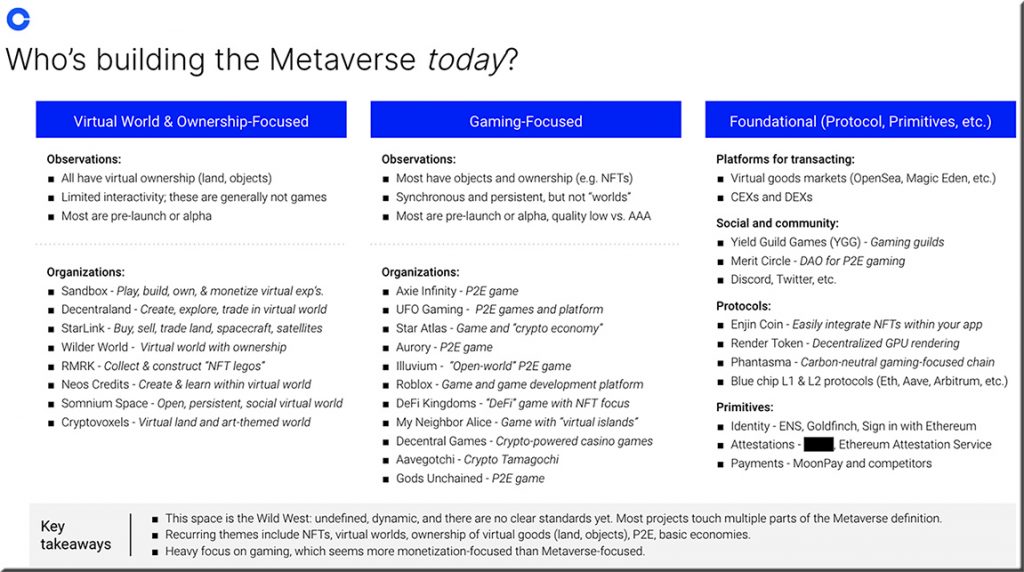
How Coinbase thinks about the Metaverse — from blog.coinbase.com by Brian Armstrong & Alex Reeve
Excerpt:
Primitive Metaverse platforms are selling virtual land for millions of dollars. Billions more are being invested in Metaverse startups. And Mark Zuckerberg recently renamed his entire company to reflect a focus on building the Metaverse.
…
Recently, our team put together an internal presentation about the Metaverse, who’s working on it, and how crypto will help make it real. I thought the presentation was well done, so I’m sharing most of the slides here.
…
Like Matt[hew Ball], we define the Metaverse as:
The future of the internet: A massively-scaled, persistent, interactive, and interoperable real-time platform comprised of interconnected virtual worlds where people can socialize, work, transact, play, and create.
…
The Metaverse is the distant evolution of Web3. In its most complete form, it will be a series of decentralized, interconnected virtual worlds with a fully functioning economy where people can do just about anything they can do in the physical world.