How Long Should a Branching Scenario Be?— from christytuckerlearning.com by Christy Tucker
How long should a branching scenario be? Is 45 minutes too long? Is there an ideal length for a branching scenario?
Excerpt:
Most of the time, the branching scenarios and simulations I build are around 10 minutes long. Overall, I usually end up at 5-15 minutes for branching scenarios, with interactive video scenarios being at the longer end.
From DSC:
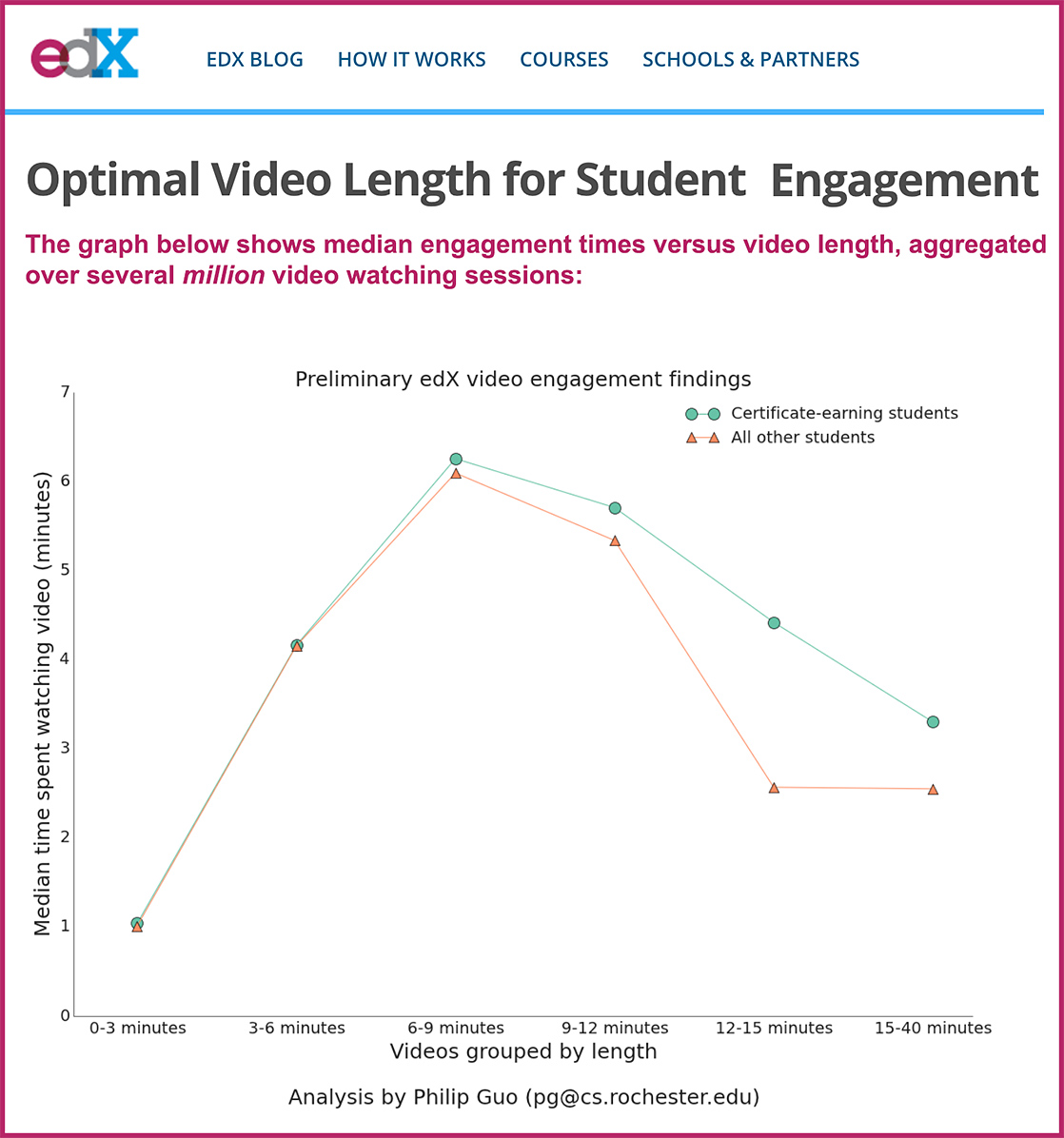
This makes sense to me, as (up to) 6 minutes turned out to be an ideal length for videos.
Excerpt from Optimal Video Length for Student Engagement — from blog.edx.org
The optimal video length is 6 minutes or shorter — students watched most of the way through these short videos. In fact, the average engagement time of any video maxes out at 6 minutes, regardless of its length. And engagement times decrease as videos lengthen: For instance, on average students spent around 3 minutes on videos that are longer than 12 minutes, which means that they engaged with less than a quarter of the content. Finally, certificate-earning students engaged more with videos, presumably because they had greater motivation to learn the material. (These findings appeared in a recent Wall Street Journal article, An Early Report Card on Massive Open Online Courses and its accompanying infographic.)
The take-home message for instructors is that, to maximize student engagement, they should work with instructional designers and video producers to break up their lectures into small, bite-sized pieces.