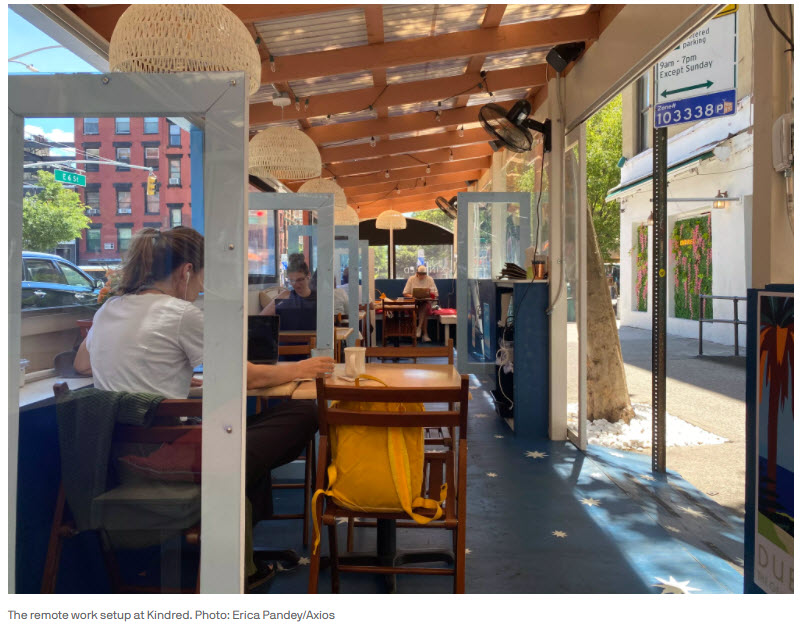
If You Thought Working From Home Was Messy, Here Comes Hybrid Work — from wsj.com by Chip Cutter
Mandatory Mondays and Fridays. Unused desks and crowded conference rooms. Employers and workers navigate a return to offices.
Excerpts:
Some companies that are hiring say they can’t find knowledge workers willing to come into an office five days a week, according to chief executives, human-resource chiefs and recruiters.
…
It’s become really sort of a requirement if you’re looking for top talent,” Mr. Herrington says. “Those folks are pretty much saying, ‘Hey, if I can’t have a bit of a hybrid work environment, then I’m probably not going to be interested.’”
From DSC:
I’ve often noticed that the problems that we work on in higher ed are occurring in K12 and also in the corporate world. How to move forward from this Covid19 situation is another similar problem being worked on. Perhaps with some different/additional questions for HE and K12:
- Where do the students prefer to be? In face-to-face (F2F)-based situations? 100% online? Hyflex? Hybrid? Other?
But really, I wonder if things don’t boil down to what the market will dictate…?