We can do nothing to change the past, but we have enormous power to shape the future. Once we grasp that essential insight, we recognize our responsibility and capability for building our dreams of tomorrow and avoiding our nightmares.
–Edward Cornish
From DSC:
This is the fifth posting in a series that highlights the need for us to consider the ethical implications of the technologies that are currently being developed. What kind of future do we want to have? How can we create dreams, not nightmares?
In regards to robotics, algorithms, and business, I’m hopeful that the C-suites out there will keep the state of their fellow mankind in mind when making decisions. Because if all’s we care about is profits, the C-suites out there will gladly pursue lowering costs, firing people, and throwing their fellow mankind right out the window…with massive repercussions to follow. After all, we are the shareholders…let’s not shoot ourselves in the foot. Let’s aim for something higher than profits. Businesses should have a higher calling/purpose. The futures of millions of families are at stake here. Let’s consider how we want to use robotics, algorithms, AI, etc. — for our benefit, not our downfall.
Other postings:
Part I | Part II | Part III | Part IV

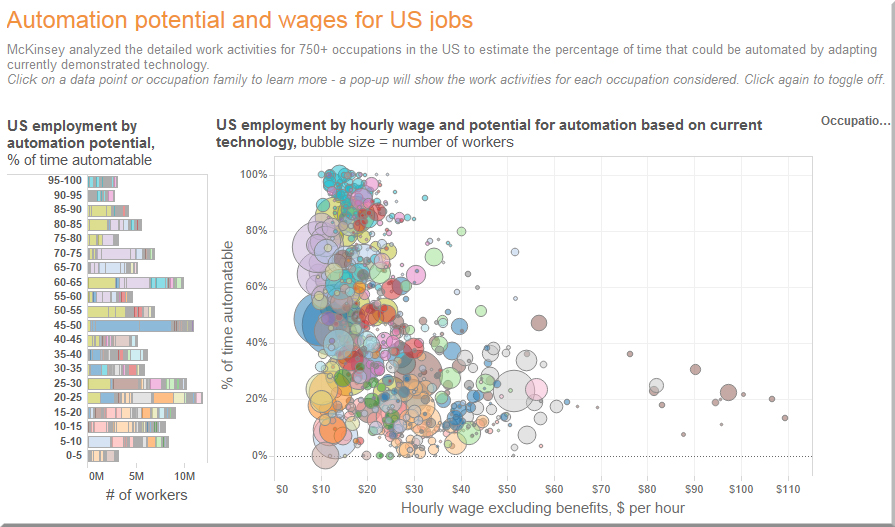
From page 212 of
Mary Meeker’s annual report re: Internet Trends 2016
The White House is prepping for an AI-powered future — from wired.com by April Glaser
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Researchers disagree on when artificial intelligence that displays something like human understanding might arrive. But the Obama administration isn’t waiting to find out. The White House says the government needs to start thinking about how to regulate and use the powerful technology while it is still dependent on humans.
“The public should have an accurate mental model of what we mean when we say artificial intelligence,” says Ryan Calo, who teaches law at University of Washington. Calo spoke last week at the first of four workshops the White House hosts this summer to examine how to address an increasingly AI-powered world.
…
“One thing we know for sure is that AI is making policy challenges already, such as how to make sure the technology remains safe, controllable, and predictable, even as it gets much more complex and smarter,” said Ed Felten, the deputy US chief of science and technology policy leading the White House’s summer of AI research. “Some of these issues will become more challenging over time as the technology progresses, so we’ll need to keep upping our game.”
Meet ‘Ross,’ the newly hired legal robot — from washingtonpost.com by Karen Turner
Excerpt:
One of the country’s biggest law firms has become the first to publicly announce that it has “hired” a robot lawyer to assist with bankruptcy cases. The robot, called ROSS, has been marketed as “the world’s first artificially intelligent attorney.”
ROSS has joined the ranks of law firm BakerHostetler, which employs about 50 human lawyers just in its bankruptcy practice. The AI machine, powered by IBM’s Watson technology, will serve as a legal researcher for the firm. It will be responsible for sifting through thousands of legal documents to bolster the firm’s cases. These legal researcher jobs are typically filled by fresh-out-of-school lawyers early on in their careers.
Confidential health care data divulged to Google’s DeepMind for new app — from futurism.com by Sarah Marquart
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Google DeepMind’s new app Streams hopes to use patient data to monitor kidney disease patients. In the process, they gained confidential data on more than 1.6 million patients, and people aren’t happy.
…
This sounds great, but the concern lies in exactly what kind of data Google has access to. There are no separate statistics available for people with kidney conditions, so the company was given access to all data including HIV test results, details about abortions, and drug overdoses.
In response to concerns about privacy, The Royal Free Trust said the data will remain encrypted so Google staff should not be able to identify anyone.
Two questions for managers of learning machines — from sloanreview.mit.edu by Theodore Kinni
Excerpt:
The first, which Dhar takes up in a new article on TechCrunch, is how to “design intelligent learning machines that minimize undesirable behavior.” Pointing to two high-profile juvenile delinquents, Microsoft’s Tay and Google’s Lexus, he reminds us that it’s very hard to control AI machines in complex settings.
The second question, which Dhar explores in an article for HBR.org, is when and when not to allow AI machines to make decisions.
All stakeholders must engage in learning analytics debate — from campustechnology.com by David Raths
Excerpt:
An Ethics Guide for Analytics?
During the Future Trends Forum session [with Bryan Alexander and George Siemens], Susan Adams, an instructional designer and faculty development specialist at Oregon Health and Science University, asked Siemens if he knew of any good ethics guides to how universities use analytics.
Siemens responded that the best guide he has seen so far was developed by the Open University in the United Kingdom. “They have a guide about how it will be used in the learning process, driven from the lens of learning rather than data availability,” he said.
“Starting with ethics is important,” he continued. “We should recognize that if openness around algorithms and learning analytics practices is important to us, we should be starting to make that a conversation with vendors. I know of some LMS vendors where you actually buy back your data. Your students generate it, and when you want to analyze it, you have to buy it back. So we should really be asking if it is open. If so, we can correct inefficiencies. If an algorithm is closed, we don’t know how the dials are being spun behind the scenes. If we have openness around pedagogical practices and algorithms used to sort and influence our students, we at least can change them.”
From DSC:
Though I’m generally a fan of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), we need to be careful how we implement it or things will turn out as depicted in this piece from The Verge. We’ll need filters or some other means of opting in and out of what we want to see.

What does ethics have to do with robots? Listen to RoboPsych Podcast discussion with roboticist/lawyer Kate Darling https://t.co/WXnKOy8UO2
— RoboPsych (@RoboPsychCom) April 25, 2016
Retail inventory robots could replace the need for store employees — from interestingengineering.com by Trevor English
Excerpt:
There are currently many industries that will likely be replaced with robots in the coming future, and with retail being one of the biggest industries across the world, it is no wonder that robots will slowly begin taking human’s jobs. A robot named Tory will perform inventory tasks throughout stores, as well as have the capability of directing customers to where what they are looking for is. Essentially, a customer will type in a product into the robot’s interactive touch screen, and it will start driving to the exact location. It will also conduct inventory using RFID scanners, and overall, it will make the retail process much more efficient. Check out the video below from the German Robotics company Metre Labs who are behind the retail robot.
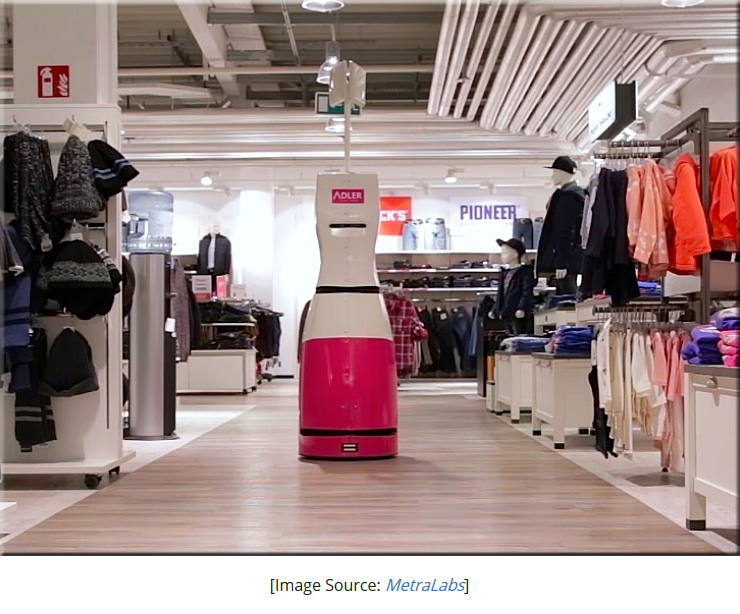

From DSC:
Do we really want to do this? Some say the future will be great when the robots, algorithms, AI, etc. are doing everything for us…while we can just relax. But I believe work serves a purpose…gives us a purpose. What are the ramifications of a society where people are no longer working? Or is that a stupid, far-fetched question and a completely unrealistic thought?
I’m just pondering what the ramifications might be of replacing the majority of human employees with robots. I can understand about using robotics to assist humans, but when we talk about replacing humans, we had better look at the big picture. If not, we may be taking the angst behind the Occupy Wall Street movement from years ago and multiplying it by the thousands…perhaps millions.
Excerpt:
We’re living in the connected age. Phones can connect wirelessly to computers, watches, televisions and anything else with access to Wi-Fi or Bluetooth and money can change hands with a few taps of a screen. Digitalization allows data to flow quicker and more freely than ever before, but it also puts the personal information we entrust it with (financial information, geographic locations and other private details) at a far greater risk of ending up in the wrong hands.
Balancing the seamless convenience customers desire with the security they need is a high-wire act of the highest order, and it’s one that automakers have to master as quickly and as thoroughly as possible.
…
Because of this, connected cars will potentially (and probably) become targets for hackers, thieves and possibly even terrorists looking to take advantage of the fledgling technology. With a wave of connected cars (220 million by 2020, according to some estimates) ready to flood U.S. roadways, it’s on both manufacturers and consumers to be vigilant in preventing the worst-case scenarios from playing out.
Also, check out the 7 techs being discussed at this year’s Gigaom Change Conference:

Scientists are just as confused about the ethics of big-data research as you — wired.com by Sarah Zhang
Excerpt:
And that shows just how untested the ethics of this new field of research is. Unlike medical research, which has been shaped by decades of clinical trials, the risks—and rewards—of analyzing big, semi-public databases are just beginning to become clear.
And the patchwork of review boards responsible for overseeing those risks are only slowly inching into the 21st century. Under the Common Rule in the US, federally funded research has to go through ethical review. Rather than one unified system though, every single university has its own institutional review board, or IRB. Most IRB members are researchers at the university, most often in the biomedical sciences. Few are professional ethicists.
Addendums on 6/3 and 6/4/16:
- Apple supplier Foxconn replaces 60,000 humans with robots in China — from marketwatch.com
Excerpt:
The first wave of robots taking over human jobs is upon us. Apple Inc. AAPL, +0.02% supplier Foxconn Technology Co. 2354, +0.95% has replaced 60,000 human workers with robots in a single factory, according to a report in the South China Morning Post, initially published over the weekend. This is part of a massive reduction in headcount across the entire Kunshan region in China’s Jiangsu province, in which many Taiwanese manufacturers base their Chinese operations.
- There are now 260,000 robots working in U.S. factories — from marketwatch.com by Jennifer Booton (back from Feb 2016)
Excerpt:
There are now more than 260,000 robots working in U.S. factories. Orders and shipments for robots in North America set new records in 2015, according to industry trade group Robotic Industries Association. A total of 31,464 robots, valued at a combined $1.8 billion, were ordered from North American companies last year, marking a 14% increase in units and an 11% increase in value year-over-year.
- Judgment Day: Google is making a ‘kill-switch’ for AI — from futurism.com
Excerpt:
Taking Safety Measures
DeepMind, Google’s artificial intelligence company, catapulted itself into fame when its AlphaGo AI beat the world champion of Go, Lee Sedol. However, DeepMind is working to do a lot more than beat humans at chess and Go and various other games. Indeed, its AI algorithms were developed for something far greater: To “solve intelligence” by creating general purpose AI that can be used for a host of applications and, in essence, learn on their own.This, of course, raises some concerns. Namely, what do we do if the AI breaks…if it gets a virus…if it goes rogue?In a paper written by researchers from DeepMind, in cooperation with Oxford University’s Future of Humanity Institute, scientists note that AI systems are “unlikely to behave optimally all the time,” and that a human operator may find it necessary to “press a big red button” to prevent such a system from causing harm. In other words, we need a “kill-switch.”
- Is the world ready for synthetic life? Scientists plan to create whole genomes — from singularityhub.com by Shelly Fan
Excerpt:
“You can’t possibly begin to do something like this if you don’t have a value system in place that allows you to map concepts of ethics, beauty, and aesthetics onto our own existence,” says Endy. “Given that human genome synthesis is a technology that can completely redefine the core of what now joins all of humanity together as a species, we argue that discussions of making such capacities real…should not take place without open and advance consideration of whether it is morally right to proceed,” he said.
- This is the robot that will shepherd and keep livestock healthy — from thenextweb.com
Excerpt:
The Australian Centre for Field Robotics (ACFR) is no stranger to developing innovative ways of modernizing agriculture. It has previously presented technologies for robots that can measure crop yields and collect data about the quality and variability of orchards, but its latest project is far more ambitious: it’s building a machine that can autonomously run livestock farms. While the ACFR has been working on this technology since 2014, the robot – previously known as ‘Shrimp’ – is set to start a two-year trial next month. Testing will take place at several farms nearby New South Wales province in Australia.