Updating Education for the Evolving Job Market: Learning at the Pace of Life and Work — from huffingtonpost.com by Sophie Wade
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
A technology-stimulated, connected, and accelerated marketplace is generating different roles and additional skills requirements for us as workers. The traditional model of completing our lifelong education needs before we enter the workforce is now obsolete. On-the-job experience must now be supplemented as business and technological requirements evolve significantly and rapidly. Compelling new multilevel learning options are emerging to cater to the new necessity of updating important knowledge and capabilities at work. Many new offerings are online and modular in order to be accessible and flexible, giving labor force participants greater opportunity to remain relevant and competitive.
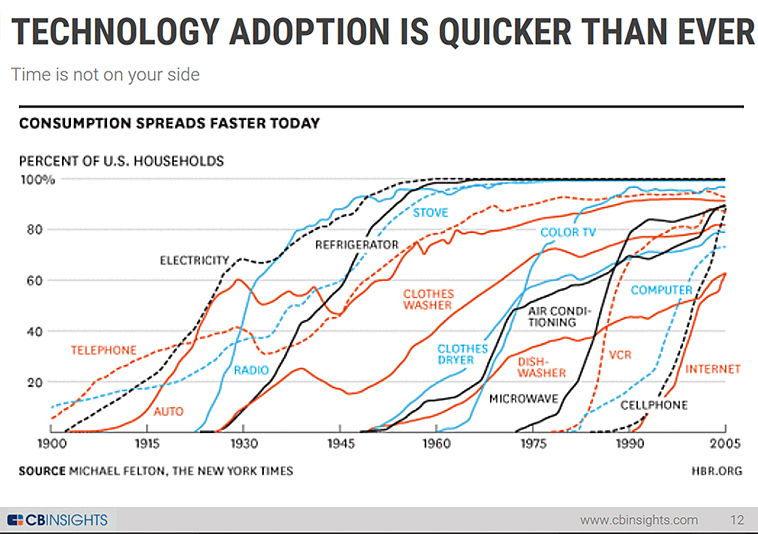
Since the beginning of the Industrial Era, evolution typically occurred from generation to generation. New developments were adopted by incoming cohorts, adding to and then replacing well-established workers’ existing practices of which could be phased out gradually. However, the exponential pace that is characteristic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is requiring modifications to be absorbed and adapted within a generation accompanied by frequent incremental updates and revisions. Innovative learning models and modules that target incoming and existing working populations are being built out to respond to business-related requirements as new fields, disciplines, and roles appear and are established.
I talked to Anant Agarwal, CEO and Founder of edX, and Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT about the situation for new workforce entrants and the future education of workers. He spoke of what he called “MOOC 2.0” as the next phase of evolution of this high-profile MOOC (Massively Open Online Course) platform and the strategic rationale and content of edX’s new MicroMasters program offerings.
As a member of the International Education Committee, at edX we are extremely aware of the changing nature of work and jobs. It is predicted that 50 percent of current jobs will disappear by 2030.
Anant Agarwal, CEO and Founder of edX, and
Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT
From DSC:
We are moving towards providing up-to-date, relevant “streams of content” (which will in many cases represent unbundled content/courses). Mark my words, that’s the future that we’re heading for — and the future that we’ll need to successfully adapt to the new, exponential pace of change. Organizations offering such streams will be providing a valuable service in terms identifying, presenting, curating the most relevant, up-to-date content.












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9477517/hpheadset.jpg)