LinkedIn announced several things yesterday (9/22/16). Below are some links to these announcements:
Introducing LinkedIn Learning, a Better Way to Develop Skills and Talent — from learning.linkedin.com
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
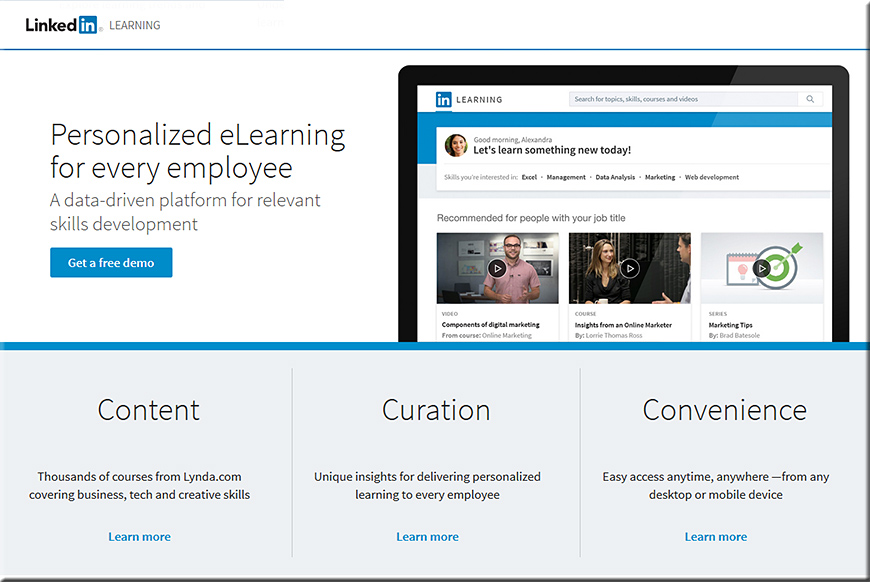
Today, we are thrilled to announce the launch of LinkedIn Learning, an online learning platform enabling individuals and organizations to achieve their objectives and aspirations. Our goal is to help people discover and develop the skills they need through a personalized, data-driven learning experience.
LinkedIn Learning combines the industry-leading content from Lynda.com with LinkedIn’s professional data and network. With more than 450 million member profiles and billions of engagements, we have a unique view of how jobs, industries, organizations and skills evolve over time. From this, we can identify the skills you need and deliver expert-led courses to help you obtain those skills. We’re taking the guesswork out of learning.
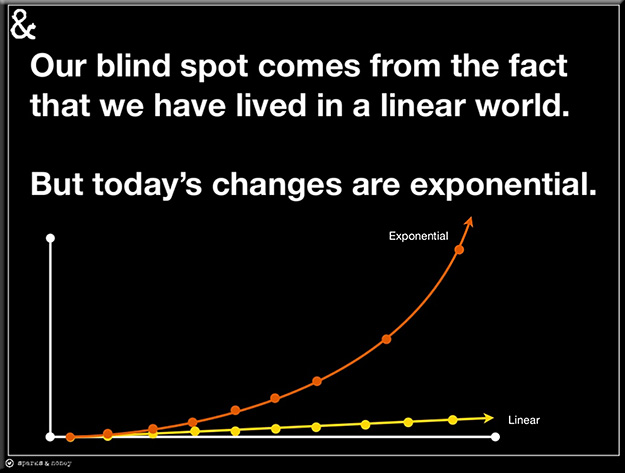
The pressure on individuals and organizations to adapt to change has never been greater. The skills that got you to where you are today are not the skills to prepare you for tomorrow. In fact, the shelf-life of skills is less than five years, and many of today’s fastest growing job categories didn’t even exist five years ago.
To tackle these challenges, LinkedIn Learning is built on three core pillars:
…
Data-driven personalization: We get the right course in front of you at the right time. Using the intelligence that comes with our network, LinkedIn Learning creates personalized recommendations, so learners can efficiently discover which courses are most relevant to their goals or job function. Organizations can use LinkedIn insights to customize multi-course Learning Paths to meet their specific needs. We also provide robust analytics and reporting to help you measure learning effectiveness.
LinkedIn’s first big move since the $26.2 billion Microsoft acquisition is basically a ‘school’ for getting a better job — from finance.yahoo.com
Excerpt:
Today, LinkedIn has launched LinkedIn Learning — its first major product launch since the news last June that Microsoft would be snapping up the social network for $26.2 billion in a deal that has yet to close.
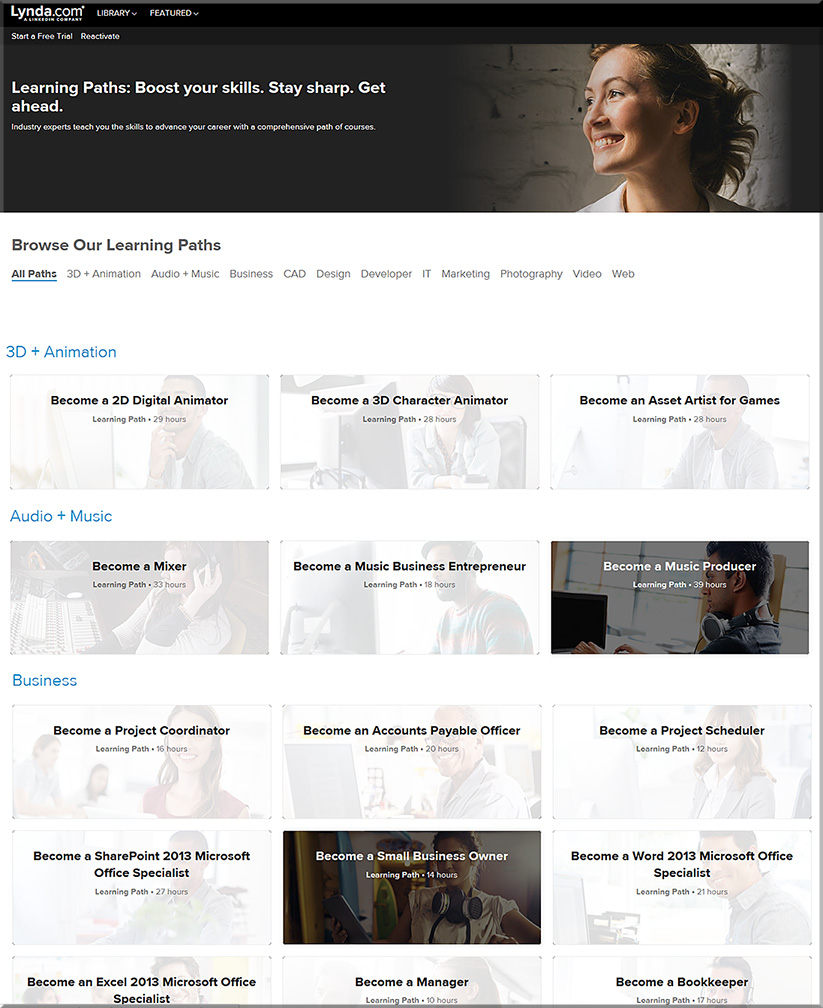
LinkedIn Learning takes the online skills training classes the company got in its 2015 acquisition of Lynda.com for $1.5 billion.
The idea, says LinkedIn CEO Jeff Weiner, is to help its 433 million-plus members get the skills they need to stay relevant in a world that’s increasingly reliant on digital skills.
LinkedIn’s New Learning Platform to Recommend Lynda Courses for Professionals — from edsurge.com by Marguerite McNeal
Excerpt:
Companies will also be able to create their own “learning paths”—bundles of courses around a particular topic—to train employees. A chief learning officer, for instance, might compile a package of courses in product management and ask 10 employees to complete the assignments over the course of a few months.
…
LinkedIn is also targeting higher-education institutions with the new offering. It is marketing the solution as a professional development tool that can help faculty learn how to use classroom tools such as Moodle, Adobe Captivate and learning management systems.
“Increasingly predictions of tech displacing workers are coming to fruition,” he added. “The idea that you can study a skill once and have a job for the rest of your life—those days are over.”
LinkedIn Learning for higher education
LinkedIn adding new training features, news feeds and ‘bots’ — from finance.yahoo.com
Excerpt:
LinkedIn is also adding more personalized features to its news feed, where members can see articles and announcements posted by their professional contacts. A new “Interest Feed” will offer a collection of articles, posts and opinion pieces on major news events or current issues.