We Built an ‘Unbelievable’ (but Legal) Facial Recognition Machine — from nytimes.com by Sahil Chinoy
“The future of human flourishing depends upon facial recognition technology being banned,” wrote Woodrow Hartzog, a professor of law and computer science at Northeastern, and Evan Selinger, a professor of philosophy at the Rochester Institute of Technology, last year. ‘Otherwise, people won’t know what it’s like to be in public without being automatically identified, profiled, and potentially exploited.’ Facial recognition is categorically different from other forms of surveillance, Mr. Hartzog said, and uniquely dangerous. Faces are hard to hide and can be observed from far away, unlike a fingerprint. Name and face databases of law-abiding citizens, like driver’s license records, already exist. And for the most part, facial recognition surveillance can be set up using cameras already on the streets.” — Sahil Chinoy; per a weekly e-newsletter from Sam DeBrule at Machine Learnings in Berkeley, CA
Excerpt:
Most people pass through some type of public space in their daily routine — sidewalks, roads, train stations. Thousands walk through Bryant Park every day. But we generally think that a detailed log of our location, and a list of the people we’re with, is private. Facial recognition, applied to the web of cameras that already exists in most cities, is a threat to that privacy.
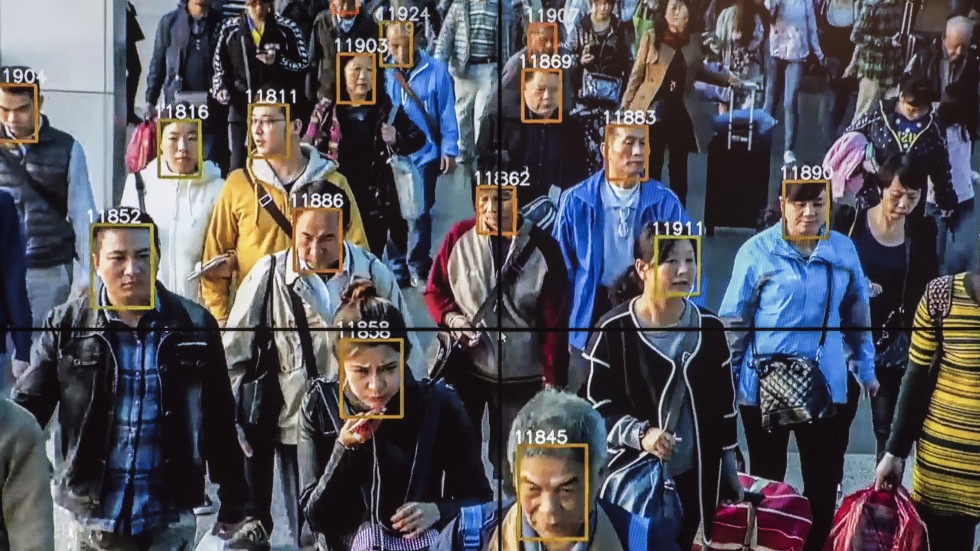
To demonstrate how easy it is to track people without their knowledge, we collected public images of people who worked near Bryant Park (available on their employers’ websites, for the most part) and ran one day of footage through Amazon’s commercial facial recognition service. Our system detected 2,750 faces from a nine-hour period (not necessarily unique people, since a person could be captured in multiple frames). It returned several possible identifications, including one frame matched to a head shot of Richard Madonna, a professor at the SUNY College of Optometry, with an 89 percent similarity score. The total cost: about $60.

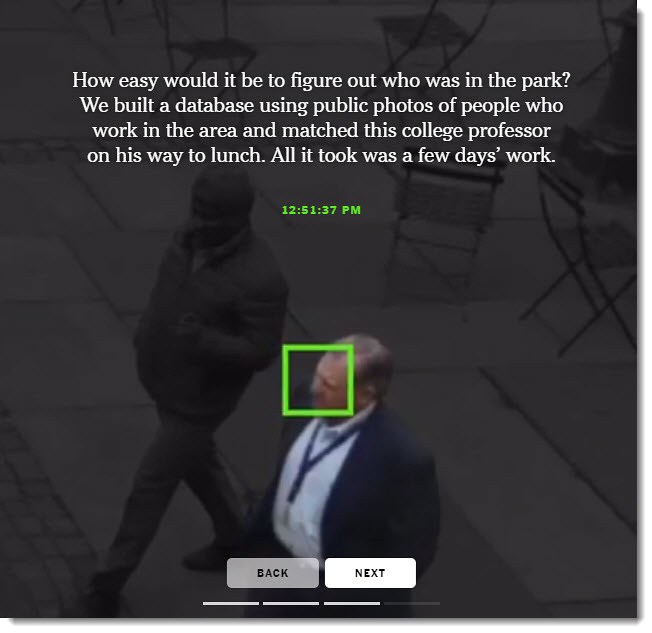

From DSC:
What do you think about this emerging technology and its potential impact on our society — and on other societies like China? Again I ask…what kind of future do we want?
As for me, my face is against the use of facial recognition technology in the United States — as I don’t trust where this could lead.
This wild, wild, west situation continues to develop. For example, note how AI and facial recognition get their foot in the door via techs installed years ago:
The cameras in Bryant Park were installed more than a decade ago so that people could see whether the lawn was open for sunbathing, for example, or check how busy the ice skating rink was in the winter. They are not intended to be a security device, according to the corporation that runs the park.
So Amazon’s use of facial recognition is but another foot in the door.
This needs to be stopped. Now.
Facial recognition technology is a menace disguised as a gift. It’s an irresistible tool for oppression that’s perfectly suited for governments to display unprecedented authoritarian control and an all-out privacy-eviscerating machine.
We should keep this Trojan horse outside of the city. (source)















