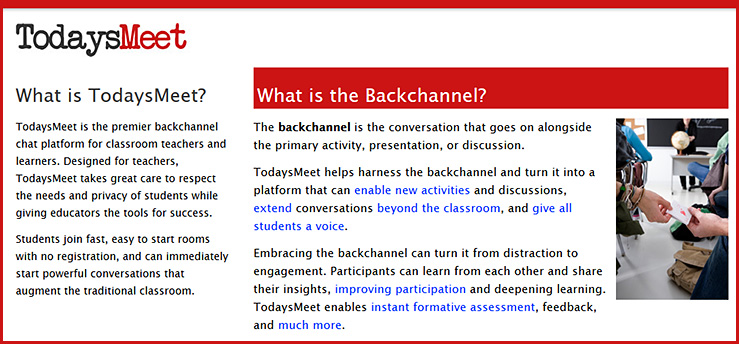
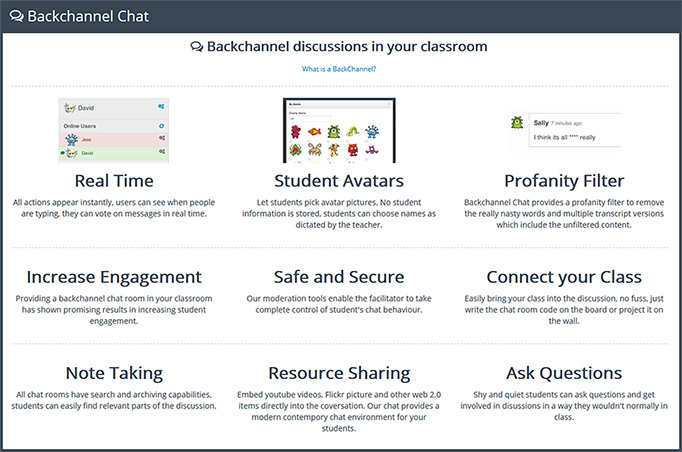
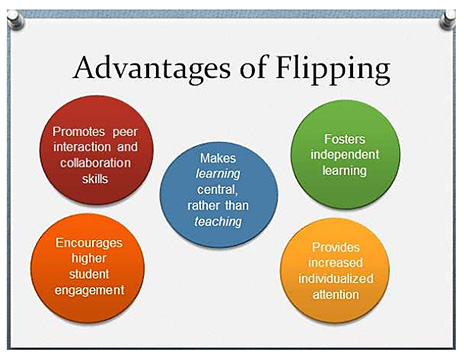
Example slides from one of the presentations at the Flipped Classroom Conference 2016
[Held at Harvey Mudd College in January; with special thanks to Mr. Jeremy VanAntwerp,
Professor of Engineering at Calvin College for this resource]



Three reasons for switching to flipped learning — from rtalbert.org by Robert Talbert, Mathematics Professor at Grand Valley State University in Michigan [USA]
Excerpt:
- The argument from pedagogy: We use flipped learning because it puts the best-known/best-available practices for teaching and learning in the spotlight, including active learning of all kinds, student-centered instruction, constructivist techniques, differentiated instruction, spaced repetition, Vygotsky’s zone of proximal development idea, self-regulated learning, and the like. Whereas these things can be featured in a traditional classroom but it feels unnatural, like the wrong tool for the job.
- The argument from logistics…
- The argument from relationships…
Peer instruction for active learning — by Harvard University Prof. Eric Mazur on difficulties of beginners, teaching each other, and making sense of information

Also see Eric’s presentation out at Auburn University from back in September 2014:

Why are we so slow to change the way we teach? — from facultyfocus.com by Maryellen Weimer, PhD
Excerpt:
However, lecture isn’t the only example of where we’re slow to change. Many aspects of teaching—course design, approaches to testing, assignments, and grading—have also changed little. Granted, some faculty do change, a lot and regularly, but not the majority. The question is, “Why?” Here are some possibilities I’ve been considering.
Crafting questions that drive projects — from learninginhand.com by Tony Vincent
Excerpt:
Not only does project based learning motivate students because it is an authentic use of technology, it facilitates active learning, critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. Projects begin with a driving question—an open-ended question that sets the stage for the project by creating interest and curiosity. Writing an effective driving question is surprisingly challenging. You want the question to be intriguing and irresistible to students, which makes it very different from the typical questions they encounter on tests.
A Driving Force
Like many educators, I call the “mission statement” of a project a driving question. It captures the heart of the project by providing purpose using clear and compelling language. With so many different flavors of project based learning (including problem based learning, challenge based learning, student centered learning, exploration, student driven inquiry, and authentic learning), it’s not surprising that we have a variety of other terms for a question or statement that is the project’s driving force. These terms include essential question, challenge, prime question, WILD HOG question, focus question, and smart question. I’ll stick with driving question, but do know that sometimes the driving question is not interrogative. It might be a statement, but I’ll still refer to is as a question.

Literacy help: Alan Peat story bags – How to develop story writing and literacy skills in younger children. — from hubpages.com
Excerpt:
There is no getting away from the fact that the more a child has been read to and the more they try to read themselves then the better their literacy skills are going to be. Parents have a massive influence on this. As a parent myself I considered reading to and teaching my daughter to read the one most important thing I could do to aid her life at school.
Sadly this is not always the case and too many students we teach read rarely at home or in rare cases don’t even own a book. Sad I know and to be honest I can’t imagine a house without books in it. I jokingly refer to my daughters collection ‘her library’ because she has so many which are updated as she reads through them.
But lets be fair, it is not only the students who struggle with reading that need help with story writing. A lot of students will benefit from this approach including your high flyers. I have taught this in year 3, although i would consider it to be more a KS1 activity, but in year 3 they do need certain aspects of a KS1 curriculum to help there development as it is a hard transitional year. Saying that I have seen other teachers use it in higher years than that and why not if it will benefit their writing.
…
On the front of each bag, so every child can read it easily should be the questions:
- Who?
- Where?
- Where next?
- Why?
- What goes wrong?
- Who helps?
- Where last?
- Feelings?

Simple tips to create a blended learning classroom — from blog.edmentum.com by Jasmine Auger
Excerpt:
We’ve compiled this list of five easy ways to start incorporating technology into your classroom and building a blended environment!
Blogging
Social Media
Virtual Presentations
Infographics
Video
Other somewhat related items:
Full STEAM ahead: Why arts are essential in a STEM education — from edutopia.org by Mary Beth Hertz
Excerpt:
The connection is also obvious for anyone who has ever worked in any traditional STEM career. Everyone from software engineers and aerospace technicians to biotechnical engineers, professional mathematicians, and laboratory scientists knows that building great things and solving real problems requires a measure of creativity. More and more, professional artists themselves are incorporating technological tools and scientific processes to their art.
Also see:
STEM to STEAM: Resources Toolkit — from edutopia.org | Originally Published: 5/21/14 | Updated: 1/20/16
Whether you are looking for resources on integrating science, technology, engineering, and math or on infusing the arts to transform STEM into STEAM, these curated compilations will help you plan different approaches to integrated studies.
…and a related item re: curriculum, but at the collegiate level:
What is the value of an education in the humanities? — from npr.org by Adam Frank
Excerpt:
In spite of being a scientist, I strongly believe an education that fails to place a heavy emphasis on the humanities is a missed opportunity. Without a base in humanities, both the students — and the democratic society these students must enter as informed citizens — are denied a full view of the heritage and critical habits of mind that make civilization worth the effort.
…
So, these are my traditional answers to the traditional questions about the value of humanities and arts education vs. science and engineering. From my standpoint as a scholar, I’ll stand by them and defend what they represent to the last breath.
But the world has changed and, I believe, these answers are no longer enough.
It’s not just the high cost of college that alters the equation. It’s also vast changes that have swept through society with the advent of a world run on information (i.e., on data). So, with that mind, here is my updated — beyond the traditional — response to the value of the humanities in education: The key is balance.
It is no longer enough for students to focus on either science/engineering or the humanities/arts.