This is how blockchain will change your life — from medium.com by Don Tapscott and Alex Tapscott
Excerpt:
Enter the blockchain, the first native digital medium for peer to peer value exchange. Its protocol establishes the rules — in the form of globally distributed computations and heavy duty encryption — that ensure the integrity of the data traded among billions of devices without going through a trusted third party. Trust is hard-coded into the platform. That’s why we call it the Trust Protocol. It acts as a ledger of accounts, a database, a notary, a sentry, and clearing house, all by consensus.
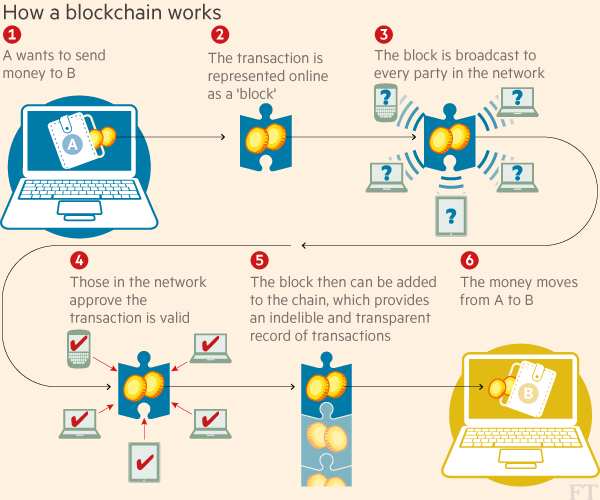
Blockchain technology: Redefining makerspaces — from worlds-of-learning.com by Laura Fleming
Excerpt:
My own personal fascination with blockchain technology lies in its potential for makerspaces and its role in the Maker Movement. The blockchain by nature is decentralized (peer-to-peer), distributed and open-source…the blueprint for makerspaces. Makerspaces both in and out of schools are about decentralizing and widening-access. This includes not only access to the spaces themselves, but also to equipment and resources. I have written before about he potential of Open Educational Resources (OER) in a makerspace. Blockchain technology could further open up access and use of resources, making our educational system that much more open and flexible.
Within schools, giving students credit for the skills they gain in a makerspace is always a challenge. The blockchain offers a real possiblity for managing and processing these types of credentials. Outside of school, no standard exists for certification or credentialing in a makerspace. You might be certified to use a tool in one makerspace, but walk into another and not be able to use that same tool there. Blockchain technology can help streamline and create a new standard for these types of certifications.
New platform aims to make it easier to develop for blockchain — from adigaskell.org
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Blockchain is undoubtedly one of the hottest technologies around at the moment. Whilst it has gained most of its notoriety for the Bitcoin financial technology, it also has a number of other possible applications.
For instance, John Holden and Greg Irving from the University of Cambridge use blockchain technology as a means of making clinical trial documents immutable. The pair wanted to tackle the thorny issue of ensuring that research data is untampered with, so that external people can have confidence in the results from the trials.
They highlighted the use of blockchain in cardiovascular diabetes and ethanol research via a report published on the F1000 website.
Bitcoin transaction initiated from fed offices, for the first time — from fee.org
Blockchain technology is maturing very quickly
Excerpt:
Some remarkable things are happening in the bitcoin/blockchain space. It’s hard to believe that just seven years ago, this technology was first revealed on an email list followed by just a handful of cypherpunks, who should be remembered by history as brilliant and dedicated innovators of a revolutionary technology. Today what they did has grabbed the attention of the world’s largest financial institutions and central banks.
And why? It’s clear this innovation is not going away. It’s simply a better method for exchanging value globally. It is a technology that will influence—if not define—the future of payments and money. It is already disrupting the status quo in more ways than even the best experts can track, especially in emerging markets.
Four of us blockchainers actually visited Janet Yellen [Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System] in her office.
Can IBM really make a business out of blockchain? — from fortune.com by Jeff Roberts
Excerpt:
One of the loudest evangelists is IBM, which has been touting the potential of blockchain—a technology that can allow companies to create quick, tamper-proof ledgers—to transform everything from finance to trading to insurance.
On Tuesday, IBM announced the formal launch of a so-called “Bluemix Garage” in New York, where developers can experiment with financial-tech software and explore new forms of blockchain innovation.
It’s a fine idea and one that could serve IBM’s long-term strategic interests. Namely, if developers flock to IBM’s platform, the company will be well-positioned to grab a big share of the “blockchain-as-a-service” market—a still nascent industry dedicated to helping firms navigate the world of ledgers, smart contracts, and all that other good stuff.

Excerpt:
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), or ‘blockchain’, has started to receive increasing media attention and investment from several sectors including governments, financial services and the creative industries. The potential application in relation to music is of particular interest, as it appears to offer solutions to problems artists have highlighted for decades – around transparency, the sharing of value and the relationships with intermediaries that sit between the artist and fan, the central and most important relationship in music.
If blockchain technology can help the commercial and contractual relationships in music keep pace with technology and the communication between artists and fans then it could be truly revolutionary.
Pink Floyd: Blockchain technology in music could be ‘truly revolutionary’ — from ibtimes.co.uk by Ian Allison
A research team at Middlesex University has released their ‘Music on the blockchain’ report.
Excerpt:
According to the report, there are four main areas where blockchain could transform the music industries:
- A single, networked database for music copyright information, rather than the many, not-quite-complete databases maintained at present;
- fast, frictionless royalty payments, whereas payments can currently take years;
- transparency through the value chain, allowing musicians and their managers to see exactly how much money they are owed, as opposed to a culture of non-disclosure agreements and “black boxes”; and
- access to alternative sources of capital, with smart contracts – contracts implemented via software – potentially transforming crowdfunding and leading to the establishment of ‘artist accelerators’ on the model of tech start-ups.
Using blockchain to re-imagine learning — from medium.com by Ben Blair, co-founder of Teachur
Excerpt:
In her recent blog, KnowledgeWorks Senior Director of Strategic Foresight Katherine Prince lists six challenges that K-12 education faces. I’m not going to go all panacea on you, but let me illustrate how blockchain technology could address at least one of those issues and gesture to how it could play an important — if not central — part in addressing all six.