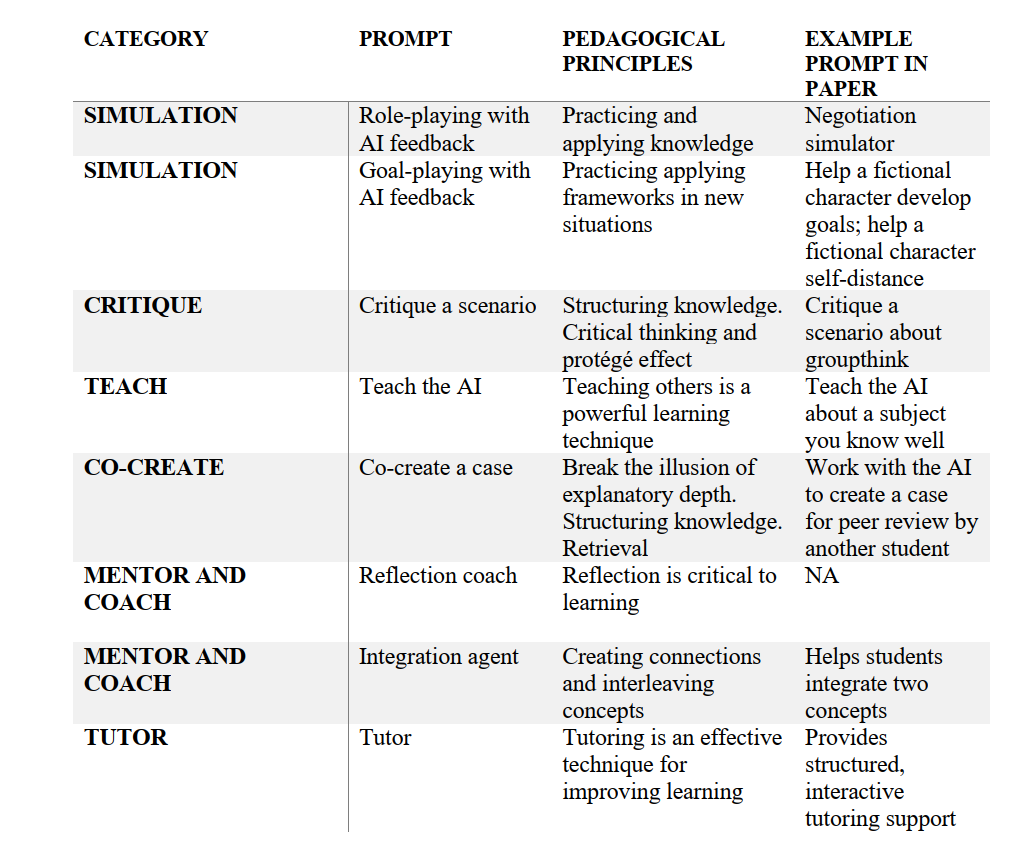
AI Policy 101: a Beginners’ Framework — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
How to make a case for AI experimentation & testing in learning & development
6 AI Tools Recommended By Teachers That Aren’t ChatGPT — from forbes.com by Dan Fitzpatrick
Here are six AI tools making waves in classrooms worldwide:
- Brisk Teaching
- SchoolAI
- Diffit
- Curipod
- Skybox by Blockade Labs in ThingLink
- Ideogram
With insights from educators who are leveraging their potential, let’s explore them in more detail.
AI Is Speeding Up L&D But Are We Losing the Learning? — from learningguild.com by Danielle Wallace
The role of learning & development
Given these risks, what can L&D professionals do to ensure generative AI contributes to effective learning? The solution lies in embracing the role of trusted learning advisors, guiding the use of AI tools in a way that prioritizes achieving learning outcomes over only speed. Here are three key steps to achieve this:
1. Playtest and Learn About AI…
2. Set the Direction for AI to Be Learner-Centered…
3. Become Trusted Learning Advisors…
Some other tools to explore:
Descript: If you can edit text, you can edit videos. — per Bloomberg’s Vlad Savov
Descript is the AI-powered, fully featured, end-to-end video editor that you already know how to use.
Audeze | Filter — per Bloomberg’s Vlad Savov
AI Chatbots in Schools Findings from a Poll of K-12 Teachers, Students, Parents, and College Undergraduates — from Impact Research; via Michael Spencer and Lily Lee
Key Findings
- In the last year, AI has become even more intertwined with our education system. More teachers, parents, and students are aware of it and have used it themselves on a regular basis. It is all over our education system today.
- While negative views of AI have crept up over the last year, students, teachers, and parents feel very positive about it in general. On balance they see positive uses for the technology in school, especially if they have used it themselves.
- Most K-12 teachers, parents, and students don’t think their school is doing much about AI, despite its widespread use. Most say their school has no policy on it, is doing nothing to offer desired teacher training, and isn’t meeting the demand of students who’d like a career in a job that will need AI.
- The AI vacuum in school policy means it is currently used “unauthorized,” while instead people want policies that encourage AI. Kids, parents, and teachers are figuring it out on their own/without express permission, whereas all stakeholders would rather have a policy that explicitly encourages AI from a thoughtful foundation.
The Value of AI in Today’s Classrooms — from waltonfamilyfoundation.org
There is much discourse about the rise and prevalence of AI in education and beyond. These debates often lack the perspectives of key stakeholders – parents, students and teachers.
In 2023, the Walton Family Foundation commissioned the first national survey of teacher and student attitudes toward ChatGPT. The findings showed that educators and students embrace innovation and are optimistic that AI can meaningfully support traditional instruction.
A new survey conducted May 7-15, 2024, showed that knowledge of and support for AI in education is growing among parents, students and teachers. More than 80% of each group says it has had a positive impact on education.