Students Pushback on AI Bans, India Takes a Leading Role in AI & Education & Growing Calls for Teacher Training in AI — from learningfuturesdigest.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
Key developments in the world of AI & Education at the turn of 2025
At the end of 2024 and start of 2025, we’ve witnessed some fascinating developments in the world of AI and education, from from India’s emergence as a leader in AI education and Nvidia’s plans to build an AI school in Indonesia to Stanford’s Tutor CoPilot improving outcomes for underserved students.
Other highlights include Carnegie Learning partnering with AI for Education to train K-12 teachers, early adopters of AI sharing lessons about implementation challenges, and AI super users reshaping workplace practices through enhanced productivity and creativity.
Also mentioned by Philippa:
- AI for Education and Carnegie Learning’s new partnership
- India emerges as Global Leader in AI Education: Bosch Tech Compass 2025 — from medianews4u.com
57% Indians receive employer-provided AI training, surpassing Germany, and other European nations
Bengaluru: India is emerging as a global leader in artificial intelligence (AI) education, with over 50% of its population actively self-educating in AI-related skills, according to Bosch’s fourth annual Tech Compass Survey. The report highlights India’s readiness to embrace AI in work, education, and daily life, positioning the nation as a frontrunner in the AI revolution.
ElevenLabs AI Voice Tool Review for Educators — from aiforeducation.io with Amanda Bickerstaff and Mandy DePriest
AI for Education reviewed the ElevenLabs AI Voice Tool through an educator lens, digging into the new autonomous voice agent functionality that facilitates interactive user engagement. We showcase the creation of a customized vocabulary bot, which defines words at a 9th-grade level and includes options for uploading supplementary material. The demo includes real-time testing of the bot’s capabilities in defining terms and quizzing users.
The discussion also explored the AI tool’s potential for aiding language learners and neurodivergent individuals, and Mandy presented a phone conversation coach bot to help her 13-year-old son, highlighting the tool’s ability to provide patient, repetitive practice opportunities.
While acknowledging the technology’s potential, particularly in accessibility and language learning, we also want to emphasize the importance of supervised use and privacy considerations. Right now the tool is currently free, this likely won’t always remain the case, so we encourage everyone to explore and test it out now as it continues to develop.
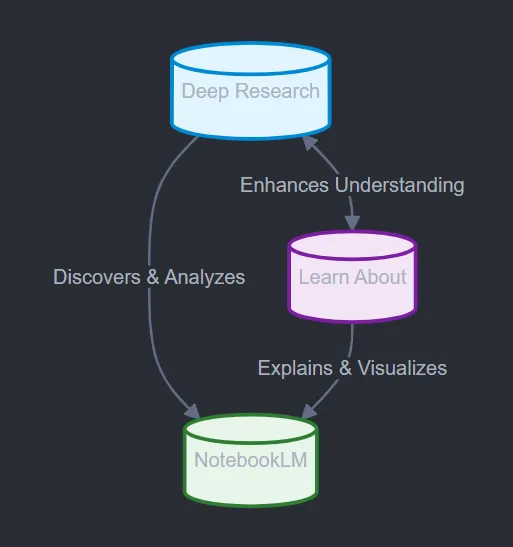
How to Use Google’s Deep Research, Learn About and NotebookLM Together — from ai-supremacy.com by Michael Spencer and Nick Potkalitsky
Supercharging your research with Google Deepmind’s new AI Tools.
Why Combine Them?
Faster Onboarding: Start broad with Deep Research, then refine and clarify concepts through Learn About. Finally, use NotebookLM to synthesize everything into a cohesive understanding.
Deeper Clarity: Unsure about a concept uncovered by Deep Research? Head to Learn About for a primer. Want to revisit key points later? Store them in NotebookLM and generate quick summaries on demand.
Adaptive Exploration: Create a feedback loop. Let new terms or angles from Learn About guide more targeted Deep Research queries. Then, compile all findings in NotebookLM for future reference.
.
Getting to an AI Policy Part 1: Challenges — from aiedusimplified.substack.com by Lance Eaton, PH.D.
Why institutional policies are slow to emerge in higher education
There are several challenges to making policy that make institutions hesitant to or delay their ability to produce it. Policy (as opposed to guidance) is much more likely to include a mixture of IT, HR, and legal services. This means each of those entities has to wrap their heads around GenAI—not just for their areas but for the other relevant areas such as teaching & learning, research, and student support. This process can definitely extend the time it takes to figure out the right policy.
That’s naturally true with every policy. It does not often come fast enough and is often more reactive than proactive.
Still, in my conversations and observations, the delay derives from three additional intersecting elements that feel like they all need to be in lockstep in order to actually take advantage of whatever possibilities GenAI has to offer.
- Which Tool(s) To Use
- Training, Support, & Guidance, Oh My!
- Strategy: Setting a Direction…
Prophecies of the Flood — from oneusefulthing.org by Ethan Mollick
What to make of the statements of the AI labs?
What concerns me most isn’t whether the labs are right about this timeline – it’s that we’re not adequately preparing for what even current levels of AI can do, let alone the chance that they might be correct. While AI researchers are focused on alignment, ensuring AI systems act ethically and responsibly, far fewer voices are trying to envision and articulate what a world awash in artificial intelligence might actually look like. This isn’t just about the technology itself; it’s about how we choose to shape and deploy it. These aren’t questions that AI developers alone can or should answer. They’re questions that demand attention from organizational leaders who will need to navigate this transition, from employees whose work lives may transform, and from stakeholders whose futures may depend on these decisions. The flood of intelligence that may be coming isn’t inherently good or bad – but how we prepare for it, how we adapt to it, and most importantly, how we choose to use it, will determine whether it becomes a force for progress or disruption. The time to start having these conversations isn’t after the water starts rising – it’s now.