How Your Learners *Actually* Learn with AI — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
What 37.5 million AI chats show us about how learners use AI at the end of 2025 — and what this means for how we design & deliver learning experiences in 2026
Last week, Microsoft released a similar analysis of a whopping 37.5 million Copilot conversations. These conversation took place on the platform from January to September 2025, providing us with a window into if and how AI use in general — and AI use among learners specifically – has evolved in 2025.
Microsoft’s mass behavioural data gives us a detailed, global glimpse into what learners are actually doing across devices, times of day and contexts. The picture that emerges is pretty clear and largely consistent with what OpenAI’s told us back in the summer:
AI isn’t functioning primarily as an “answers machine”: the majority of us use AI as a tool to personalise and differentiate generic learning experiences and – ultimately – to augment human learning.
Let’s dive in!
Learners don’t “decide” to use AI anymore. They assume it’s there, like search, like spellcheck, like calculators. The question has shifted from “should I use this?” to “how do I use this effectively?”
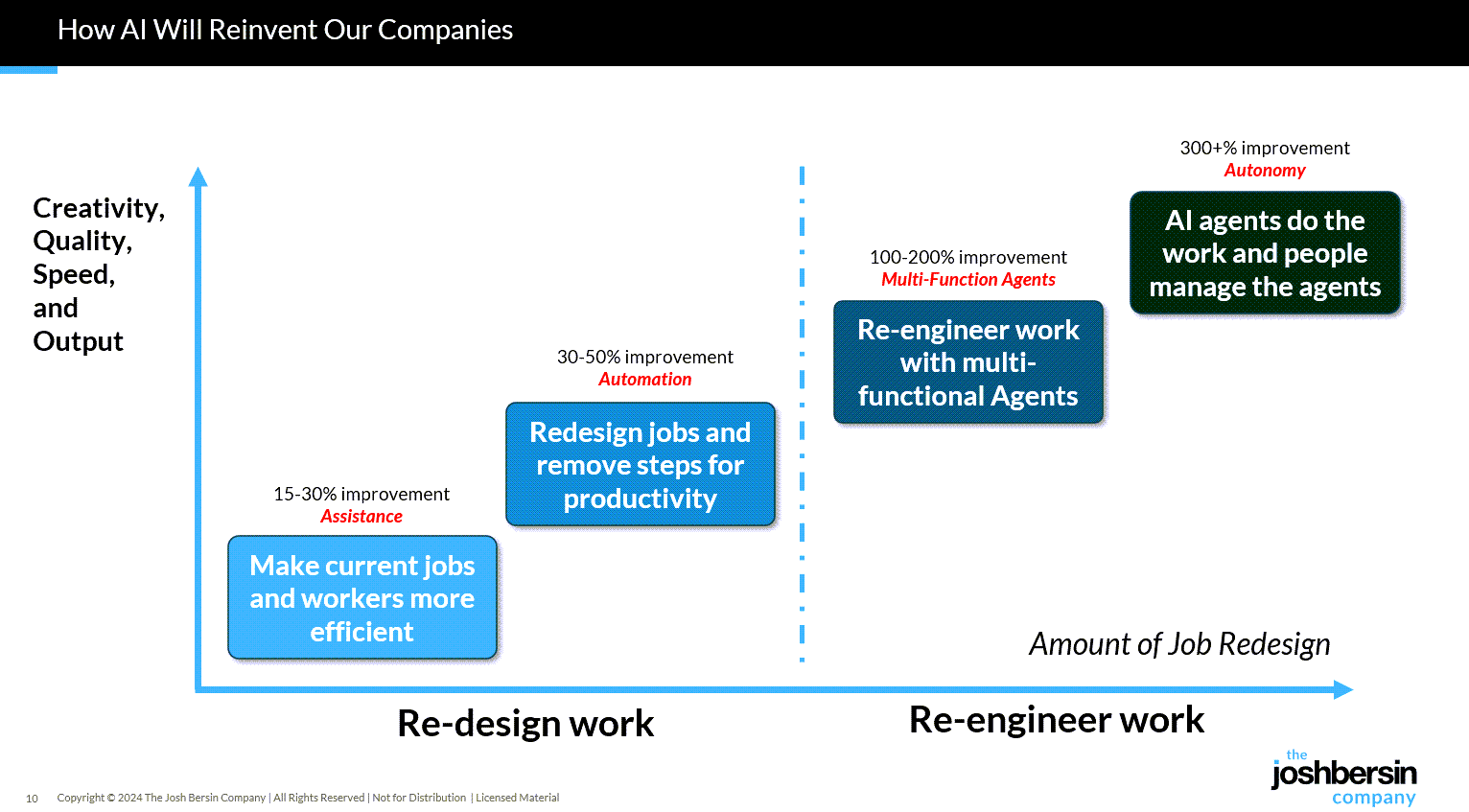
8 AI Agents Every HR Leader Needs To Know In 2026 — from forbes.com by Bernard Marr
So where do you start? There are many agentic tools and platforms for AI tasks on the market, and the most effective approach is to focus on practical, high-impact workflows. So here, I’ll look at some of the most compelling use cases, as well as provide an overview of the tools that can help you quickly deliver tangible wins.
…
Some of the strongest opportunities in HR include:
- Workforce management, administering job satisfaction surveys, monitoring and tracking performance targets, scheduling interventions, and managing staff benefits, medical leave, and holiday entitlement.
- Recruitment screening, automatically generating and posting job descriptions, filtering candidates, ranking applicants against defined criteria, identifying the strongest matches, and scheduling interviews.
- Employee onboarding, issuing new hires with contracts and paperwork, guiding them to onboarding and training resources, tracking compliance and completion rates, answering routine enquiries, and escalating complex cases to human HR specialists.
- Training and development, identifying skills gaps, providing self-service access to upskilling and reskilling opportunities, creating personalized learning pathways aligned with roles and career goals, and tracking progress toward completion.