What Students Are Saying About Teachers Using A.I. to Grade — from nytimes.com by The Learning Network; via Claire Zau
Teenagers and educators weigh in on a recent question from The Ethicist.
Is it unethical for teachers to use artificial intelligence to grade papers if they have forbidden their students from using it for their assignments?
That was the question a teacher asked Kwame Anthony Appiah in a recent edition of The Ethicist. We posed it to students to get their take on the debate, and asked them their thoughts on teachers using A.I. in general.
While our Student Opinion questions are usually reserved for teenagers, we also heard from a few educators about how they are — or aren’t — using A.I. in the classroom. We’ve included some of their answers, as well.
OpenAI wants to pair online courses with chatbots — from techcrunch.com by Kyle Wiggers; via James DeVaney on LinkedIn
If OpenAI has its way, the next online course you take might have a chatbot component.
Speaking at a fireside on Monday hosted by Coeus Collective, Siya Raj Purohit, a member of OpenAI’s go-to-market team for education, said that OpenAI might explore ways to let e-learning instructors create custom “GPTs” that tie into online curriculums.
“What I’m hoping is going to happen is that professors are going to create custom GPTs for the public and let people engage with content in a lifelong manner,” Purohit said. “It’s not part of the current work that we’re doing, but it’s definitely on the roadmap.”
15 Times to use AI, and 5 Not to — from oneusefulthing.org by Ethan Mollick
Notes on the Practical Wisdom of AI Use
There are several types of work where AI can be particularly useful, given the current capabilities and limitations of LLMs. Though this list is based in science, it draws even more from experience. Like any form of wisdom, using AI well requires holding opposing ideas in mind: it can be transformative yet must be approached with skepticism, powerful yet prone to subtle failures, essential for some tasks yet actively harmful for others. I also want to caveat that you shouldn’t take this list too seriously except as inspiration – you know your own situation best, and local knowledge matters more than any general principles. With all that out of the way, below are several types of tasks where AI can be especially useful, given current capabilities—and some scenarios where you should remain wary.
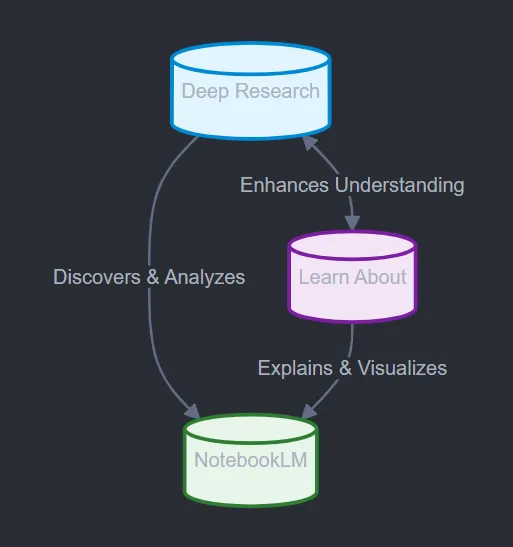
Learning About Google Learn About: What Educators Need To Know — from techlearning.com by Ray Bendici
Google’s experimental Learn About platform is designed to create an AI-guided learning experience
Google Learn About is a new experimental AI-driven platform available that provides digestible and in-depth knowledge about various topics, but showcases it all in an educational context. Described by Google as a “conversational learning companion,” it is essentially a Wikipedia-style chatbot/search engine, and then some.
In addition to having a variety of already-created topics and leading questions (in areas such as history, arts, culture, biology, and physics) the tool allows you to enter prompts using either text or an image. It then provides a general overview/answer, and then suggests additional questions, topics, and more to explore in regard to the initial subject.
The idea is for student use is that the AI can help guide a deeper learning process rather than just provide static answers.
What OpenAI’s PD for Teachers Does—and Doesn’t—Do — from edweek.org by Olina Banerji
What’s the first thing that teachers dipping their toes into generative artificial intelligence should do?
They should start with the basics, according to OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT and one of the world’s most prominent artificial intelligence research companies. Last month, the company launched an hour-long, self-paced online course for K-12 teachers about the definition, use, and harms of generative AI in the classroom. It was launched in collaboration with Common Sense Media, a national nonprofit that rates and reviews a wide range of digital content for its age appropriateness.
…the above article links to:
ChatGPT Foundations for K–12 Educators — from commonsense.org
This course introduces you to the basics of artificial intelligence, generative AI, ChatGPT, and how to use ChatGPT safely and effectively. From decoding the jargon to responsible use, this course will help you level up your understanding of AI and ChatGPT so that you can use tools like this safely and with a clear purpose.
Learning outcomes:
- Understand what ChatGPT is and how it works.
- Demonstrate ways to use ChatGPT to support your teaching practices.
- Implement best practices for applying responsible AI principles in a school setting.
Takeaways From Google’s Learning in the AI Era Event — from edtechinsiders.substack.com by Sarah Morin, Alex Sarlin, and Ben Kornell
Highlights from Our Day at Google + Behind-the-Scenes Interviews Coming Soon!
- NotebookLM: The Start of an AI Operating System
- Google is Serious About AI and Learning
- Google’s LearnLM Now Available in AI Studio
- Collaboration is King
- If You Give a Teacher a Ferrari
Rapid Responses to AI — from the-job.beehiiv.com by Paul Fain
Top experts call for better data and more short-term training as tech transforms jobs.
AI could displace middle-skill workers and widen the wealth gap, says landmark study, which calls for better data and more investment in continuing education to help workers make career pivots.
…
Ensuring That AI Helps Workers
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a general purpose technology with sweeping implications for the workforce and education. While it’s impossible to precisely predict the scope and timing of looming changes to the labor market, the U.S. should build its capacity to rapidly detect and respond to AI developments.
That’s the big-ticket framing of a broad new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Congress requested the study, tapping an all-star committee of experts to assess the current and future impact of AI on the workforce.
“In contemplating what the future holds, one must approach predictions with humility,” the study says…
“AI could accelerate occupational polarization,” the committee said, “by automating more nonroutine tasks and increasing the demand for elite expertise while displacing middle-skill workers.”
…
The Kicker: “The education and workforce ecosystem has a responsibility to be intentional with how we value humans in an AI-powered world and design jobs and systems around that,” says Hsieh.
AI Predators: What Schools Should Know and Do — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
AI is increasingly be used by predators to connect with underage students online. Yasmin London, global online safety expert at Qoria and a former member of the New South Wales Police Force in Australia, shares steps educators can take to protect students.
The threat from AI for students goes well beyond cheating, says Yasmin London, global online safety expert at Qoria and a former member of the New South Wales Police Force in Australia.
Increasingly at U.S. schools and beyond, AI is being used by predators to manipulate children. Students are also using AI generate inappropriate images of other classmates or staff members. For a recent report, Qoria, a company that specializes in child digital safety and wellbeing products, surveyed 600 schools across North America, UK, Australia, and New Zealand.
Why We Undervalue Ideas and Overvalue Writing — from aiczar.blogspot.com by Alexander “Sasha” Sidorkin
A student submits a paper that fails to impress stylistically yet approaches a worn topic from an angle no one has tried before. The grade lands at B minus, and the student learns to be less original next time. This pattern reveals a deep bias in higher education: ideas lose to writing every time.
This bias carries serious equity implications. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds, including first-generation college students, English language learners, and those from under-resourced schools, often arrive with rich intellectual perspectives but struggle with academic writing conventions. Their ideas – shaped by unique life experiences and cultural viewpoints – get buried under red ink marking grammatical errors and awkward transitions. We systematically undervalue their intellectual contributions simply because they do not arrive in standard academic packaging.
Google Scholar’s New AI Outline Tool Explained By Its Founder — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
Google Scholar PDF reader uses Gemini AI to read research papers. The AI model creates direct links to the paper’s citations and a digital outline that summarizes the different sections of the paper.
Google Scholar has entered the AI revolution. Google Scholar PDF reader now utilizes generative AI powered by Google’s Gemini AI tool to create interactive outlines of research papers and provide direct links to sources within the paper. This is designed to make reading the relevant parts of the research paper more efficient, says Anurag Acharya, who co-founded Google Scholar on November 18, 2004, twenty years ago last month.
The Four Most Powerful AI Use Cases in Instructional Design Right Now — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
Insights from ~300 instructional designers who have taken my AI & Learning Design bootcamp this year
- AI-Powered Analysis: Creating Detailed Learner Personas…
- AI-Powered Design: Optimising Instructional Strategies…
- AI-Powered Development & Implementation: Quality Assurance…
- AI-Powered Evaluation: Predictive Impact Assessment…
How Are New AI Tools Changing ‘Learning Analytics’? — from edsurge.com by Jeffrey R. Young
For a field that has been working to learn from the data trails students leave in online systems, generative AI brings new promises — and new challenges.
In other words, with just a few simple instructions to ChatGPT, the chatbot can classify vast amounts of student work and turn it into numbers that educators can quickly analyze.
Findings from learning analytics research is also being used to help train new generative AI-powered tutoring systems.
…
Another big application is in assessment, says Pardos, the Berkeley professor. Specifically, new AI tools can be used to improve how educators measure and grade a student’s progress through course materials. The hope is that new AI tools will allow for replacing many multiple-choice exercises in online textbooks with fill-in-the-blank or essay questions.
Increasing AI Fluency Among Enterprise Employees, Senior Management & Executives — from learningguild.com by Bill Brandon
This article attempts, in these early days, to provide some specific guidelines for AI curriculum planning in enterprise organizations.
The two reports identified in the first paragraph help to answer an important question. What can enterprise L&D teams do to improve AI fluency in their organizations?
You could be surprised how many software products have added AI features. Examples (to name a few) are productivity software (Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace); customer relationship management (Salesforce and Hubspot); human resources (Workday and Talentsoft); marketing and advertising (Adobe Marketing Cloud and Hootsuite); and communication and collaboration (Slack and Zoom). Look for more under those categories in software review sites.